Great Bear Completes 14 Drill Fences Along 3.2 Kilometres of the LP Fault
Great Bear Resources Ltd. today provided a progress update from its ongoing 90,000 metre drill program at its 100% owned Dixie project.
Great Bear Resources Ltd. (the “Company” or “Great Bear”, TSXV:GBR) today provided a progress update from its ongoing 90,000 metre drill program at its 100% owned Dixie project in the Red Lake district of Ontario, including new drill results.
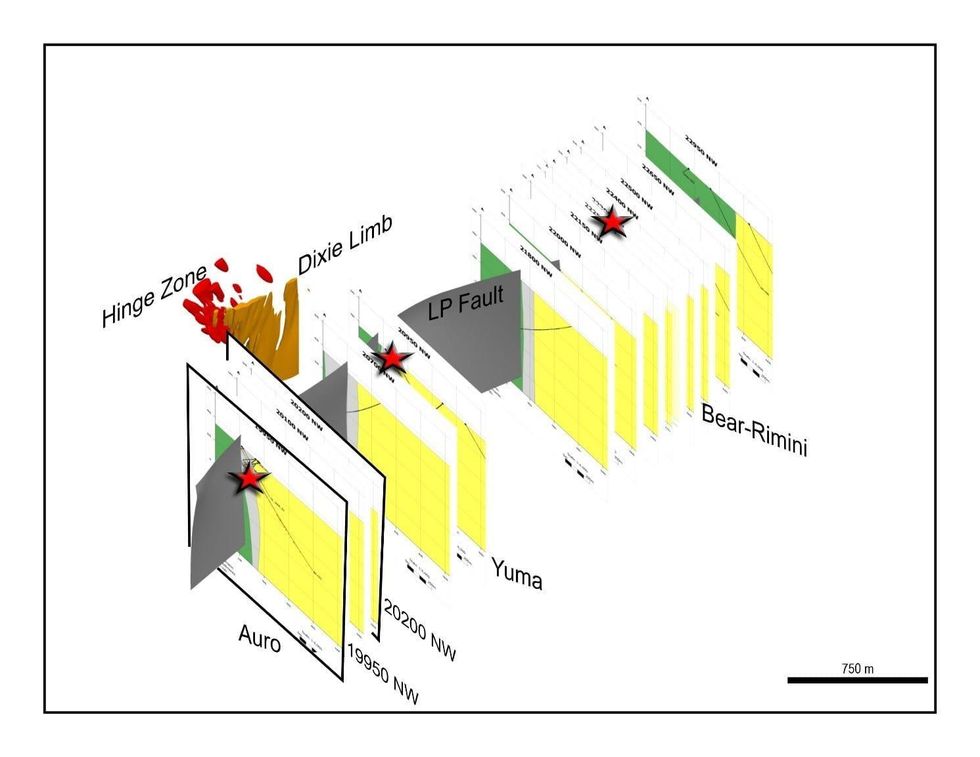
Figure 1: Completed drill sections along 3.2 kilometres of the LP Fault deformation zone to-date. Sub-zones along the LP Fault are labeled. Examples of drill core segments from various drill fences are shown as insets. Drill holes with disclosed results are shown in black, drill holes with pending results are shown in blue. The adjacent Dixie Limb and Hinge Zones are also shown. (CNW Group/Great Bear Resources Ltd.)
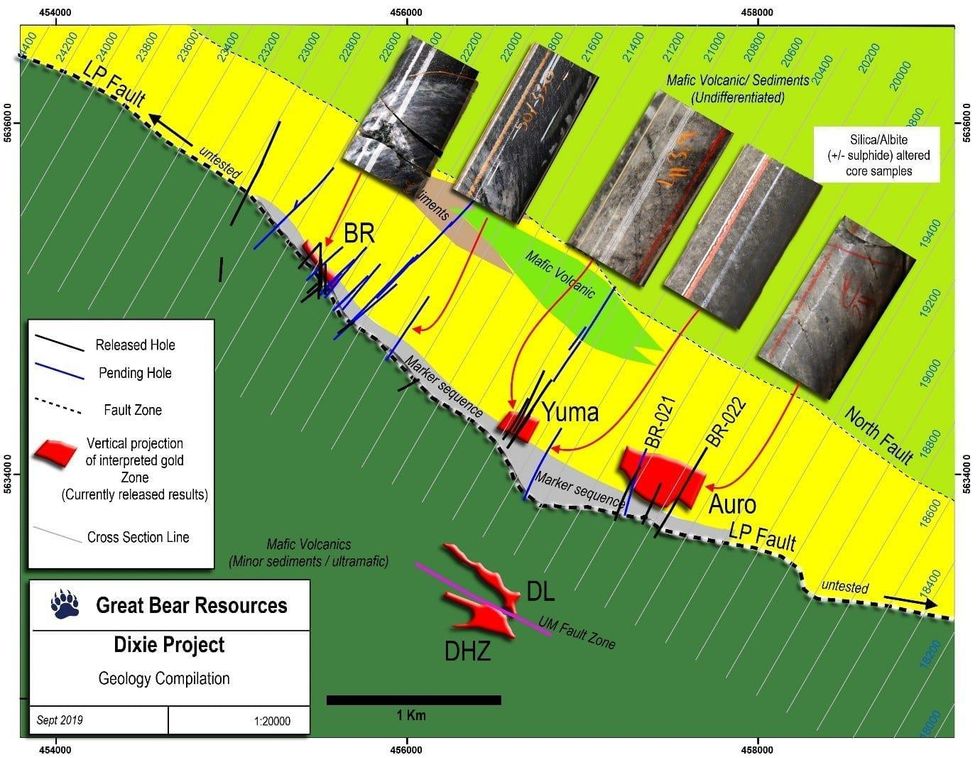
Figure 3: 3D view to west of approximately 3.5 kilometres of the LP Fault deformation zone, to approximately 750 metres depth. The locations of all drill fences completed to-date are shown in true scale and spatial orientation. The adjacent Dixie Limb and Hinge Zones are also shown. (CNW Group/Great Bear Resources Ltd.)
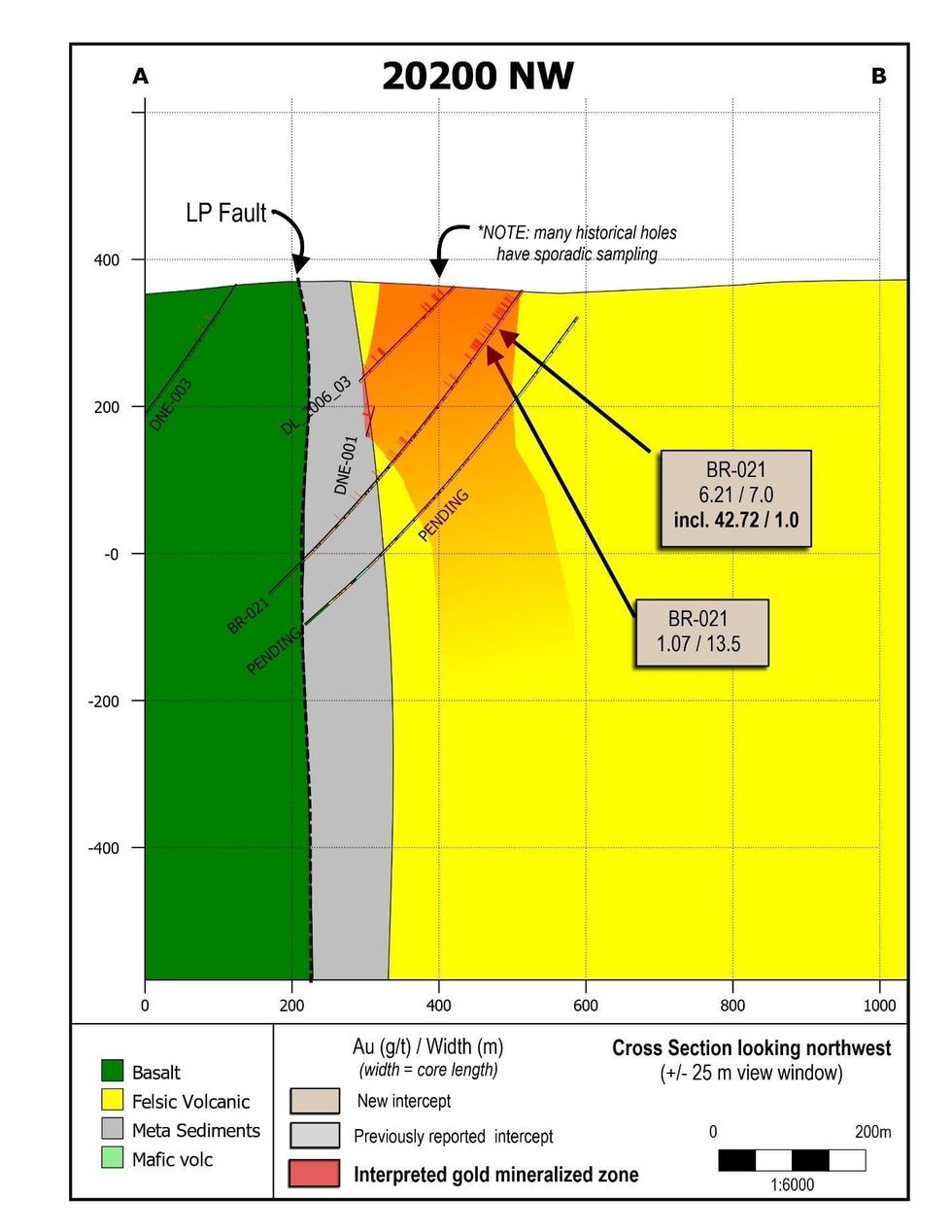
Figure 4: Cross section showing drill hole BR-021, and nearby historical drilling. (CNW Group/Great Bear Resources Ltd.)
Chris Taylor, President and CEO of Great Bear said, “With aggressive drilling we have now completed 14 drill fences spaced from 50 to 800 metres apart along 3.2 kilometres (or just 18%) of the LP Fault and have a large number of drill results pending. New observations have transformed our understanding of the LP Fault mineralization system. We have observed similar and correlatable geology and/or mineralization styles within all drill holes intersecting the structure to-date. We will continue to utilize sub-zone names such as Bear-Rimini, Yuma and Auro for geographic reference, however it now appears these are portions of a continuous mineralized system spanning kilometres of strike length which remains open along strike and at depth.”
Highlights of the LP Fault drill program’s progress to-date include:
- 14 drill fences have been completed along 3.2 kilometres of strike length, with one to three drill holes per drill fence. Completed drill hole locations are shown on Figure 1. The locations of recent drill sections within the broader LP Fault target are shown on Figure 2. A 3D view of all current drill sections is shown on Figure 3.
- The Company has noted very strong geological continuity including similar geology, alteration, structural characteristics, geochemistry, geophysical signature and gold mineralization along all drill holes intersecting the LP Fault deformation zone to-date. Results suggest a continuous, multi-kilometre zone that remains open to extension along strike and at depth, with mineralization projecting to the near-surface in all locations. Examples of drill core from various drill sections are included in Figure 1.
- Gold zones in all results reported to-date for the LP Fault are associated with silica and albite alteration with minor sulphides including pyrite and sphalerite, with lesser amounts of arsenopyrite and chalcopyrite. Visible gold is also noted in several of the reported intervals. Quartz sericite alteration associated with gold mineralization extends for up to 500 metres of core length.
- There are two primary styles of gold mineralization along the LP Fault, both of which extend to the near-surface and are being actively drilled by Great Bear: 1) Near-vertical high-grade gold zones, and 2) disseminated zones of low to moderate gold grades which surround and flank the high-grade intervals.
Fully funded with $18m in cash, Great Bear plans to drill along approximately 18 kilometres of the strike length of the LP Fault target between now and summer 2020. Drilling will continue along strike of the LP Fault in generally 100 metre to 1 kilometre step-outs.
The LP fault represents a major break/deformation zone between felsic and mafic volcanic rocks and is associated with significant gold-bearing alteration. It is similar in character to other large gold-hosting deformation zones in Archean greenstone belts. Well-known Canadian examples include the Larder Lake Cadillac Break that extends through Kirkland Lake and Val D’Or, the Porcupine Destor Fault Zone of the Timmins Camp, the Detour Lake Fault Zone, the Pike Fault in the Meliadine camp of Nunavut, and the Cochenour-Gullrock deformation zone of the Red Lake Mine complex.
While most additional drill results remain pending at this time, completed assays from two additional Auro Zone drill holes have been returned to-date and are summarized in Table 1:
- Drilling has expanded the Auro Zone’s tested strike length to over 300 metres, including northwest towards the adjacent Yuma Zone, and southeast towards areas previously undrilled by Great Bear.
- Drilling intersected gold mineralization from surface to over 420 metres vertical depth. This shows a similar drill-established depth extent to gold mineralization as observed at the Yuma Zone (480 vertical metres), located 1 kilometre to the northwest of Auro. Gold mineralization remains open in all directions.
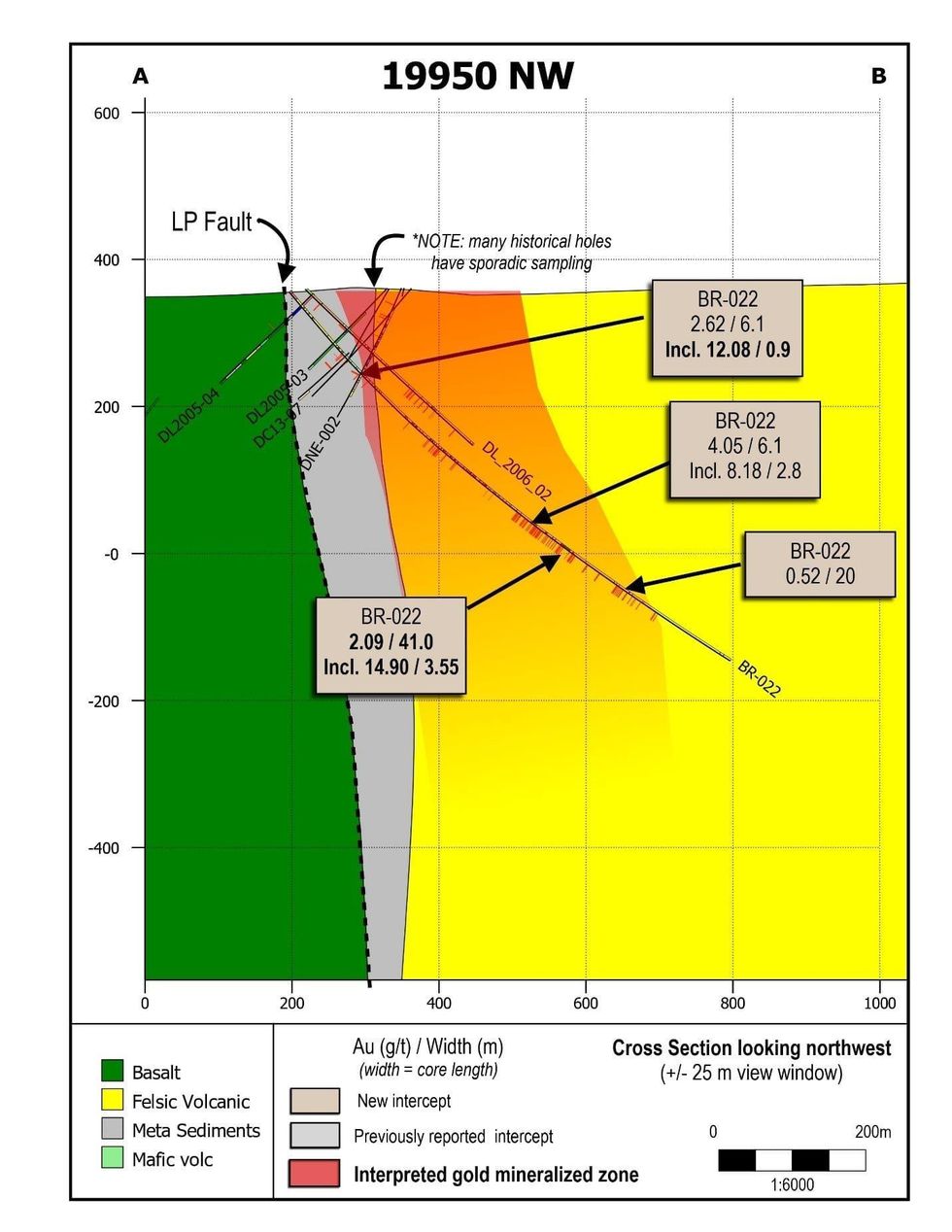
- Multiple gold mineralized intervals were observed along 510 metres of core length from 110 metres to 620 metres depth in drill hole BR-022. This is the most southeasterly drill hole completed along the LP Fault to-date,and has the widest observed interval of gold mineralization as defined by core length.
- Drill hole BR-022 was completed approximately 150 metres southeast of Auro Zone discovery hole BR-020, as shown on Figure 5.
- Significant intercepts include 100.48 g/t gold over 0.5 metres, within 14.90 g/t gold over 3.55 metres, which is hosted within a broader interval of 41.00 metres of 2.09 g/t gold.
- Drill hole BR-021 was completed approximately 200 metres to the northwest of discovery hole BR-020. Gold-bearing intervals were noted along 112 metres of core length from 10 metres to 100 metres vertical depth, as shown on Figure 4.
- Significant intercepts include 42.72 g/t gold over 1.0 metre at 50 metres vertical depth, and 13.50 metres of 1.07 g/t gold at 80 metres vertical depth.
Great Bear will continue to provide regular drill program updates throughout the remainder of 2019 and through 2020. Assay results will continue to be released in batches as received and processed. Approximately 28,000 metres of drilling remain to be completed as part of the Company’s ongoing 90,000 metre drill program.
Table 1: Assay intervals from the newest LP Fault drilling in Auro Zone area. Vertical depths reported from the centre of each interval.
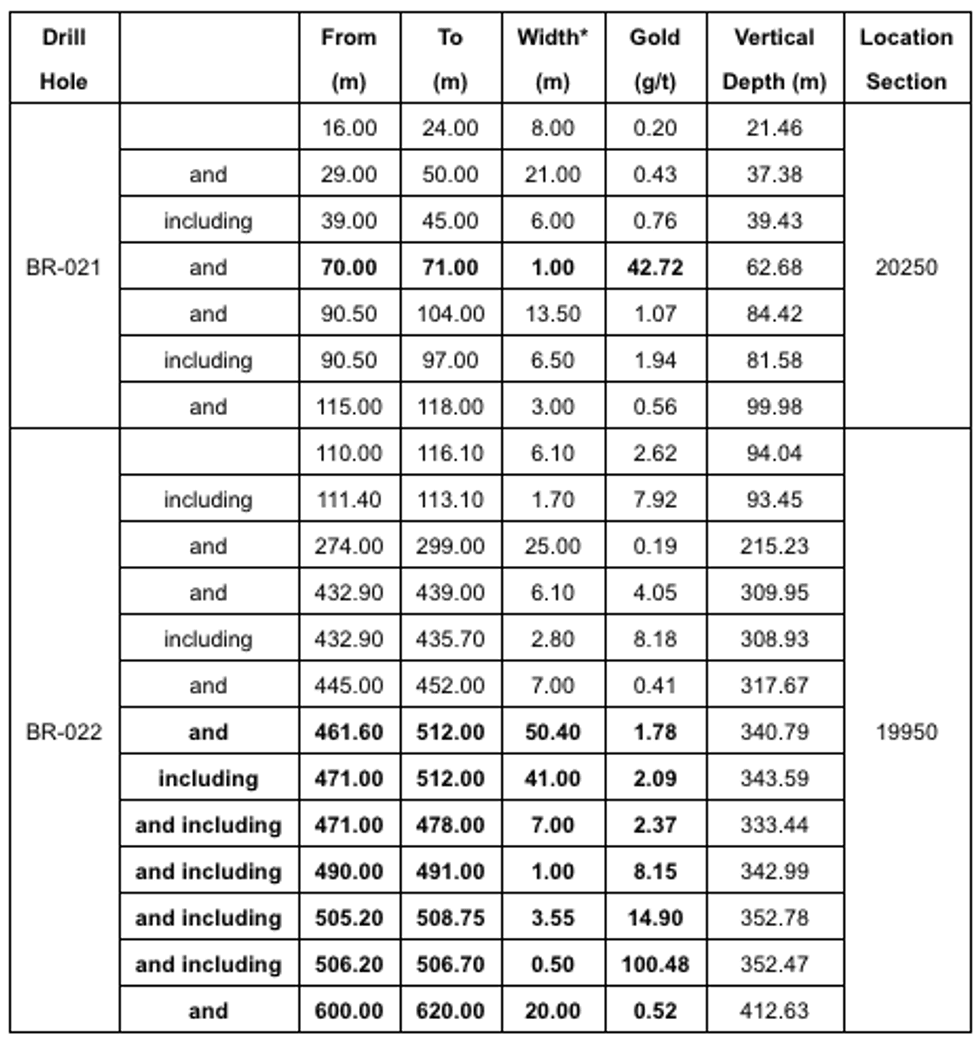
| *Widths are drill indicated core length, as insufficient drilling has been undertaken to determine true widths at this time. Average grades are calculated with un-capped gold assays, as insufficient drilling has been completed in the Auro Zone to determine capping levels for higher grade gold intercepts. Average widths are calculated using a 0.10 g/t gold cut-off grade with < 3 m of internal dilution of zero grade. |
About Great Bear
Great Bear Resources Ltd. (TSX-V: GBR) is a well-financed company based in Vancouver, Canada, managed by a team with a track record of success in the mineral exploration sector. Great Bear holds a 100% interest, royalty free, in its flagship Dixie property, which is road accessible year-round via Highway 105, a 15 minute drive from downtown Red Lake, Ontario. The Red Lake mining district is one of the premier mining districts in Canada, benefitting from major active mining operations including the Red Lake Gold Mine of Newmont Goldcorp Corp., plus modern infrastructure and a skilled workforce. Production from the Red Lake district does not necessarily reflect the mineralization that may, or may not be hosted on the Company’s Dixie property.
The Dixie property hosts different styles of gold mineralization. High-grade gold-bearing quartz veins and silica-sulphide replacement zones hosted by mafic volcanic rocks, and localized near regional-scale D2 folds occur at the Dixie Limb and Hinge Zones. These mineralization styles are also typical of the significant mined deposits of the Red Lakedistrict.
The LP Fault is large a trans-crustal deformation zone that is interpreted to traverse the Dixie property for approximately 20 kilometres of strike length and has been drilled along 3.2 kilometres of strike length to-date. It hosts high-grade gold mineralization that is controlled by structural and geological contacts, and low to moderate grade disseminated gold that surrounds and flanks the high-grade intervals. The dominant gold-hosting stratigraphy consists of felsic sediments and volcanic units.
In addition, Great Bear is also earning a 100% royalty-free interest in the Pakwash, Dedee and Sobel properties, which cover regionally significant gold-controlling structures and prospective geology. All of Great Bear’s Red Lake projects are accessible year-round through existing roads.
Drill core is logged and sampled in a secure core storage facility located in Red Lake Ontario. Core samples from the program are cut in half, using a diamond cutting saw, and are sent to SGS Canada Inc. in Red Lake, Ontario, and Activation Laboratories in Ontario, both of which are accredited mineral analysis laboratories, for analysis. All samples are analysed for gold using standard Fire Assay-AA techniques. Samples returning over 10.0 g/t gold are analysed utilizing standard Fire Assay-Gravimetric methods. Pulps from approximately 5% of the gold mineralized samples are submitted for check analysis to a second lab. Selected samples are also chosen for duplicate assay from the coarse reject of the original sample. Selected samples with visible gold are also analyzed with a standard 1 kg metallic screen fire assay. Certified gold reference standards, blanks and field duplicates are routinely inserted into the sample stream, as part of Great Bear’s quality control/quality assurance program (QAQC). No QAQC issues were noted with the results reported herein.
Mr. R. Bob Singh, P.Geo, Director and VP Exploration, and Ms. Andrea Diakow P.Geo, Exploration Manager for Great Bear are the Qualified Persons as defined by National Instrument 43-101 responsible for the accuracy of technical information contained in this news release.
Click here to connect with Great Bear Resources (TSXV:GBR, OTC:GTBDF) for an Investor Presentation.