Global Energy Metals Provides Project Details on High-Grade Past Producing Cobalt Asset Acquisition in the Superior Mining Jurisdiction of Nevada
Global Energy Metals Corporation (TSXV:GEMC) (“Global Energy Metals”, the “Company” and/or “GEMC”) is pleased to provide details on the Lovelock Cobalt Mine and Treasure Box projects.
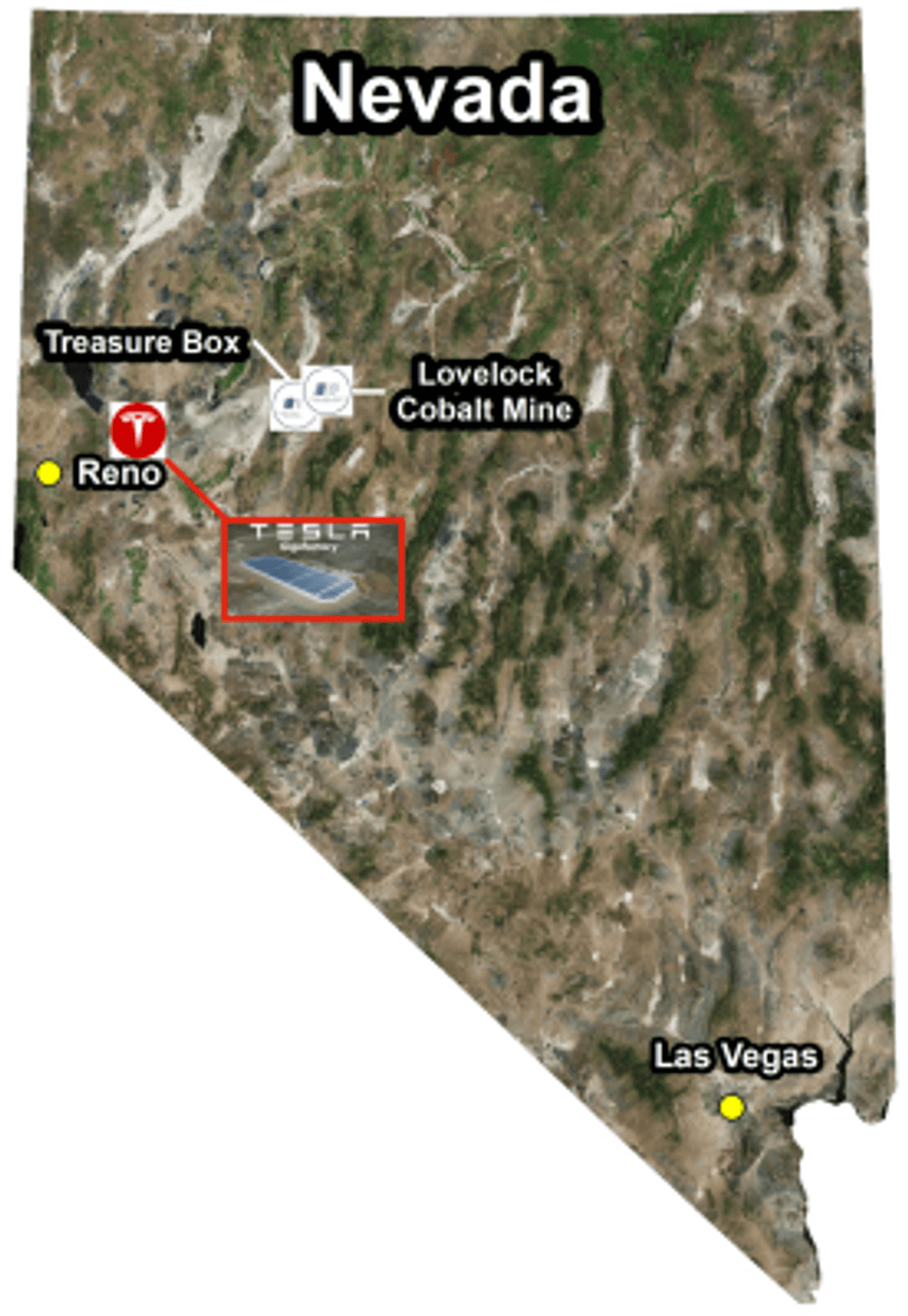
Global Energy Metals Corporation (TSXV:GEMC) (“Global Energy Metals”, the “Company” and/or “GEMC”) is pleased to provide details on the Lovelock Cobalt Mine and Treasure Box projects. GEMC announced yesterday that it has entered into a letter of intent to acquire an 80% interest in the Lovelock Mine and Treasure Box projects located in Churchill County, approximately 150 kilometres east of Sparks, Nevada. Sparks is home to the Tesla Gigafactory that is scaling up to be the largest lithium-ion battery factory in the world.
Figure 1. Lovelock and Treasure Box Location Map
Click Image To View Full Size
About the Lovelock Cobalt Mine
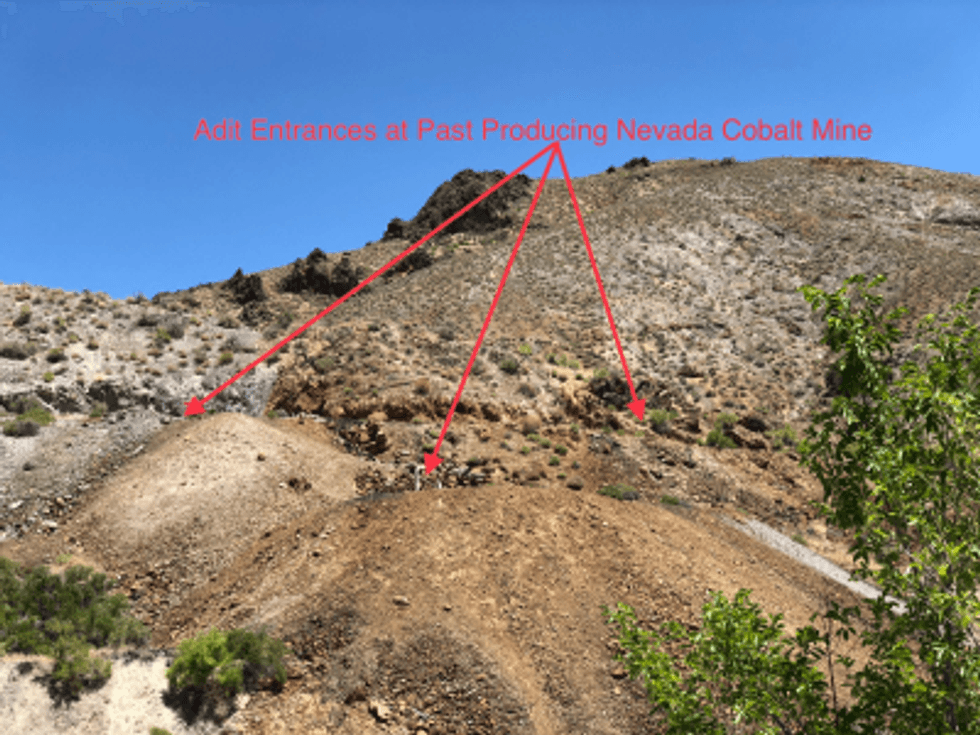
The Property currently consists of 70 unpatented lode claims in the Cottonwood Canyon area of the Stillwater Range totaling approximately 1,400 acres (567 hectares). It was discovered by George Lovelock and Charles Bell about 1880. According to U.S. Government annual reports, the Lovelock Mine saw limited production of nickel, copper and cobalt beginning in 1883. The primary cobalt mineral was identified as “cobaltite”. The general average of the 200 tons shipped in 1886 averaged 14 percent cobalt and 12 percent nickel. The mine operated from 1883 to 1890 to the 100 foot level, reporting 500 tons of cobalt and nickel mineralized material shipped to England for processing. After intermittent production, an English company attempted smelting on site in 1898 but little or no production was made (Source: “Mineral Resources of the United States for 1886). No further production from the Lovelock Mine is known for well over a century providing GEMC an excellent opportunity to unlock the potential value of the deposit through new exploration work.
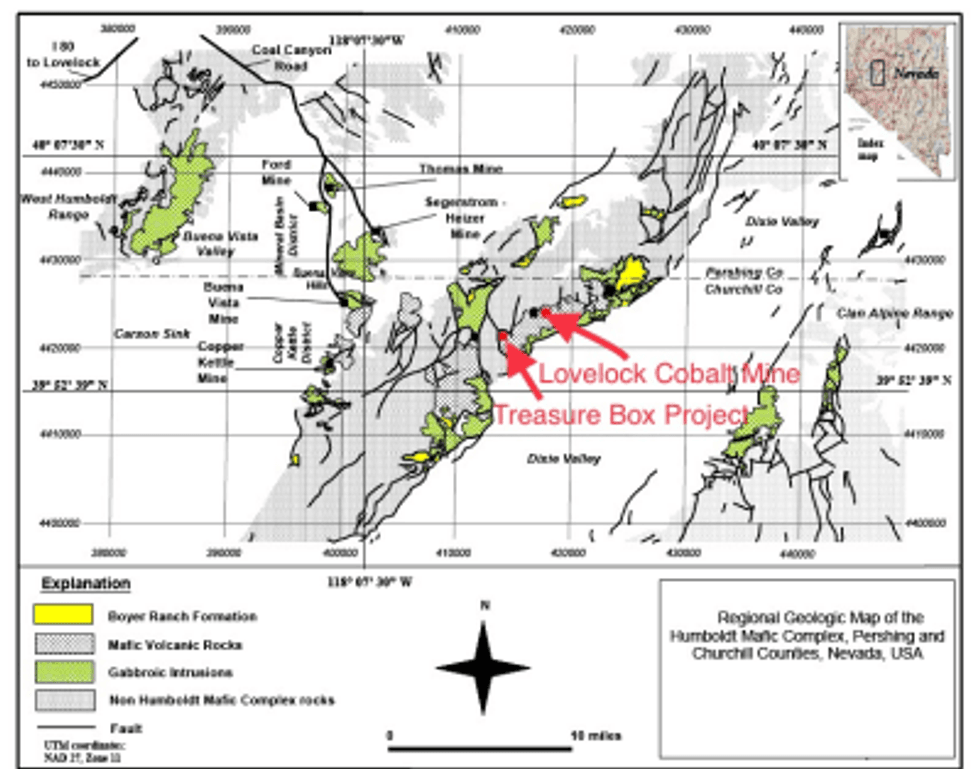
Figure 2. Regional Geologic Map with Location of the Lovelock and Treasure Box Projects
Click Image To View Full Size
Figure 3. Adit Entrances at Lovelock, a past producing Cobalt Mine in Nevada
Click Image To View Full Size
Geochemical Sampling
The vendor carried out two site visits to the Lovelock Mine in November and December 2017 and collected representative grab rock samples of historical mine waste, and various bedrock samples at the Lovelock Mine and in the areas of other nearby historical adits. The analytical results of several of the rock samples show strong enrichment in cobalt, nickel and copper.
Geophysical Survey
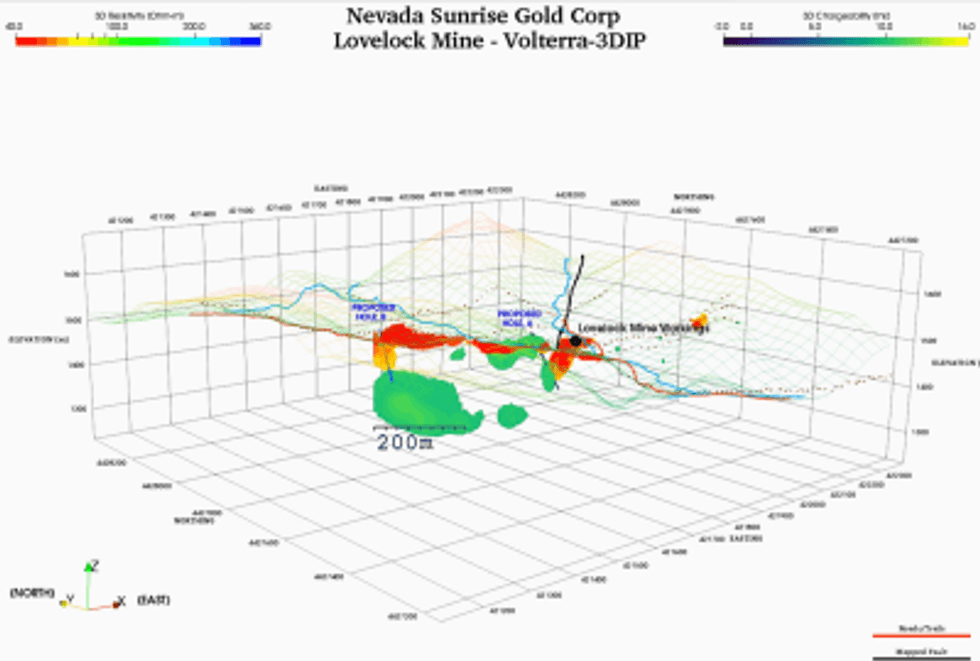
In December 2017, an initial 4.2 kilometre (2.6 miles) reconnaissance DC resistivity/induced polarization (“DC-IP”) survey by SJ Geophysics of Delta, BC, consisting of stations spaced 25 to 50 metres (80-160 feet) apart on five lines was completed across the Lovelock Mine area. This DC-IP survey is projected to have a depth of investigation deeper than the mining to the 100-foot level reported in the 1880s.
The results of the survey not only detected the historic, near-surface mine workings and interpreted alteration (red areas on figure), but also show chargeability features (green areas on figure) related to structure and possible mineralization to a depth from surface of approximately 200 metres (656 feet).
Figure 4. 3-D Figure of the Survey Results with Proposed Drill Holes
Click Image To View Full Size
About the Treasure Box Project
Treasure Box hosts mine workings from limited copper production, which occurred until early into the 20th century. A historical diamond drill hole (circa 1910) drilled at the Treasure Box by the Boyer-Nevada Copper Company reportedly intersected 1.52% copper over 85 feet (25.9 metres) with mineralization beginning at surface. A reverse circulation hole drilled on the Treasure Box by Utah International in 1976 returned 1.55% copper over 40 feet (12.2 metres) from a depth of 85 to 125 feet (25.9 to 38.1 metres), and the hole was stopped in chalcopyrite mineralization. The core Treasure Box claims were held continuously for over 20 years by a private company but were relinquished in September 2017, leading to their acquisition by Nevada Sunrise.
Geology and Mineralization of the Region
The rocks of the Lovelock Mine and Treasure Box area include highly altered sedimentary and volcanic rocks cut by a larger mass of diorite and by aplitic dikes, all of which are now highly altered. The altered volcanic rocks lie in a syncline bordered on the west, north and east by the altered sedimentary rocks. Probable faults, inferred from the nature of the contacts, form the boundaries between the sedimentary and volcanic rocks to the northwest.
The cobalt and nickel minerals of the Lovelock Mine and the nearby Nickel Mine occur in stringers that cut the rock immediately surrounding the diorite. In the case of the Lovelock Mine, the stringers cut a highly-altered greenstone. The minerals recognized are tetrahedrite, erythrite (cobalt bloom), azurite, and green crusts that contain copper and nickel arsenates and sulphates. Other sources reported the principal mineral present is cobaltite. It was postulated by historical observers that there has been post-mineral faulting with downthrow on the west, and that the extension of the productive zone is west of the Lovelock Mine shaft and at greater depth than the historical workings could reach (Source: “Nickel Deposits in Cottonwood Canyon, Churchill County, Nevada”, H.G. Ferguson, 1939).
Qualified Person
Mr. Paul Sarjeant, P. Geo., the Company’s VP Projects and Director, is the qualified person for this release as defined by National Instrument 43-101 – Standards of Disclosure for Mineral Projects and has reviewed and verified the technical information contained herein.
Global Energy Metals Corporation
(TSXV:GEMC | OTCQB:GBLEF | FSE:5GE1)
Global Energy Metals is focused on offering security of supply of cobalt, a critical material to the growing rechargeable battery market, by building a diversified global portfolio of cobalt assets including project stakes, projects and other supply sources. GEMC anticipates growing its business by acquiring project stakes in battery metals related projects with key strategic partners. Global Energy Metals currently owns and is advancing the Werner Lake Cobalt Mine in Ontario, Canada and has entered into an agreement to earn-in to the Millennium Cobalt Project in Mt. Isa, Australia.
For Further Information:
Global Energy Metals Corporation
#1501-128 West Pender Street
Vancouver, BC, V6B 1R8
Email: info@globalenergymetals.com
t. + 1 (604) 688-4219 extensions 236/237
Cautionary Statement on Forward-Looking Information:
Certain information in this release may constitute forward-looking statements under applicable securities laws and necessarily involve risks associated with regulatory approvals and timelines. Although Global Energy Metals believes the expectations expressed in such forward-looking statements are based on reasonable assumptions, such statements are not guarantees of future performance and actual results or developments may differ materially from those in the forward-looking statements. Except as required by law, the Company undertakes no obligation to update these forward-looking statements in the event that management’s beliefs, estimates or opinions, or other factors, should change. For more information on Global Energy and the risks and challenges of their businesses, investors should review the filings that are available at www.sedar.com.
Neither TSX Venture Exchange nor its Regulation Services Provider (as that term is defined in the policies of the TSX Venture Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy or accuracy of this release.
We seek safe harbour.
Source: www.thenewswire.com