Phosphate Outlook 2019: Supply Constraints to Bolster Prices
In 2018, phosphate prices trended higher throughout the year, but what’s the phosphate outlook for next year?
Although analysts expected a price decrease in the phosphate sector over 2018 the opposite actually occurred, and prices trended higher throughout the year.
In fact, 2018 ended up being an eventful year for the phosphate market — most notable was the implementation of strict regulations around the raw materials used to make phosphate in China.
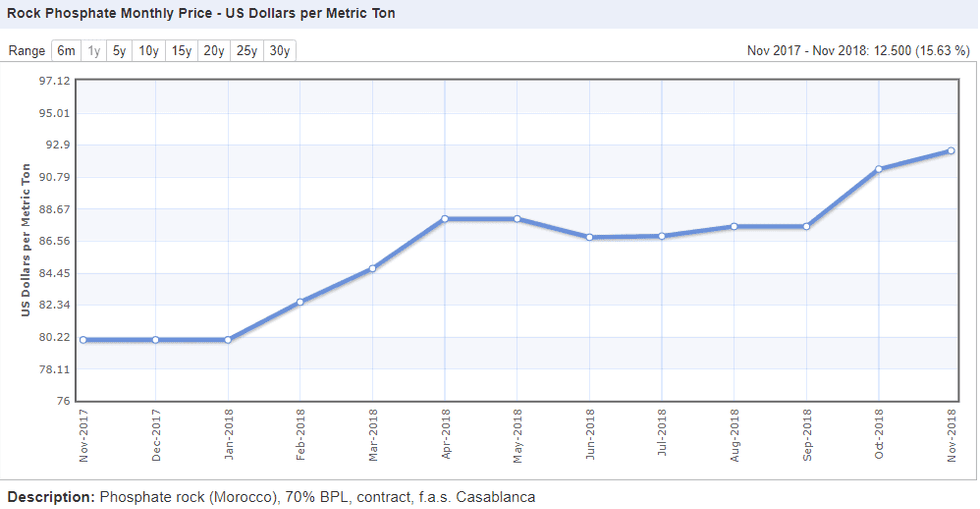
In December 2017, the price for 1 metric tonne of phosphate was US$80.22, while in November 2018 that price had grown to US$92.50. Prices were flat from December 2017 to February 2018, but from there rose incrementally every month with only a brief period of decrease mid-year.
Here the Investing News Network examines what catalysts occurred in the phosphate sector during 2018, and explores the phosphate outlook for the year ahead.
Phosphate trends 2018: A global appetite for fertilizer
As an essential ingredient for healthy crop life, it is only natural to expect phosphate demand to grow as more food is harvested to feed the rapidly growing global population. Increased demand worldwide is expected to impact pricing throughout 2019, especially if output cannot keep pace.
In January 2018, Canadian fertilizer producers Potash Corporation of Saskatchewan and Agrium merged to form Nutrien (TSX:NTR,NYSE:NTR), the largest fertilizer company in Canada and a global powerhouse in agriculture. The move signaled the need for enhanced focus on global food sustainability.
The new company’s latest quarterly update shows it has been able to reap the benefits of higher phosphate prices.
“The average combined net [phosphate] selling price in the third quarter was up 17 percent compared to the same period last year primarily due to a 25 percent increase in phosphate fertilizer net selling prices. Global phosphate prices were supported by strong demand and higher input costs for ammonia and sulfur,” states Nutrien’s Q3 update.
The creation of the global fertilizer major was one of the most newsworthy stories out of the sector in early 2018, but by the end of the year Chinese regulations had overshadowed Nutrien’s thunder.
As a major end user of phosphate products and a relatively new major producer of the agricultural ingredient, the country has an influence on price volatility in the sector.
In order to fight various forms of pollution, the Asian nation has enacted a number of environmental regulations, some of which impact the phosphate sector. These guidelines are expected to impact the global price of phosphate.
“The new tax targets solid waste, gaseous emissions, water pollution and noise pollution. Regional governments have retained the power to set the new tax rates, meaning different cost implications across the provinces,” states a report by Alexander Derricot, fertilizer costs senior analyst at CRU Group.
“CRU estimates that, on average, costs will rise by around 1-3% for both phosphate and nitrogen producers,” it continues.
By April, the cost of phosphate had climbed to sit at US$88. At that point prices plateaued briefly before experiencing a slight decline over the summer months.
In June, prices dipped to US$86 before making a steady climb back into positive territory. From August on, prices grew slightly to reach US$92.50, where they sat in November.
Chart via Index Mundi.
Phosphate outlook 2019: Tighter supply, new output
Despite China reining in on mining sector pollutants, other countries are ready and willing to ramp up phosphate production, particularly in the Middle East and North Africa, where it is cheaper to produce phosphate.
“[W]ith sentiment improving, demand remaining strong and lingering environmental issues in China, investment opportunities are now being considered more seriously,” states a CRU report authored by Chris Lawson, head of phosphates.
Lawson points to a number of divestments as an indication that supply may fall while demand grows.
“Vinachem recently announced it would be selling its stake in its fertilizer production assets in Vietnam, while PEMEX is looking to divest from the fertilizer industry in Mexico,” he notes.
However, with major mergers like the one seen between PotashCorp and Agrium, and Mosaic (NYSE:MOS) acquiring Vale’s (NYSE:VALE) phosphate fertilizer assets, there are still plenty of opportunities for investors to get in and see value for their investment dollars.
“This has opened the door for relative new comers to the industry like ITAFOS (TSXV:IFOS), a company that has recently purchased a string of assets across the region,” explains Lawson in the report.
Another Canada-listed phosphate company with big plans for the new year is Arianne Phosphate (TSXV:DAN), which recently got approval from the federal government to construct a maritime terminal facility on the north shore of the Saguenay River in Quebec.
The company’s end goal is to use the port to fulfill international shipment orders.
“This is a very decisive event for our company and, the region as a whole,” CEO Brian Ostroff said at the time. “I believe that this greatly increases the chances of our project coming to fruition and something that many of the potential customers and financiers we are in discussions with wanted to see happen.”
In addition to the Canadian companies looking to expand their presence in the phosphate sector, there are also Australia-focused firms wanting to increase their stake in the growing market.
In mid-October, Verdant Minerals (ASX:VRM) received approval from the Northern Territory Environment Protection Authority to move ahead with its Ammaroo phosphate project.
Meanwhile, in November, Australian phosphate developer Fertoz (ASX:FTZ) entered an agreement with international fertilizer company Humic Growth Solutions to supply phosphates that will be blended with Humic products.
“Developments in China will be key to how the industry evolves over the medium term. While new capacity will continue to be built elsewhere, potential closures and issues in China could present opportunities in this ever-changing market,” noted CRU’s Lawson.
“Producers will need to be wary of any drastic price increases, with favourable fertilizer affordability levels a major factor behind recent demand growth. Nevertheless, sentiment is seemingly turning more positive in the downstream phosphate market.”
Don’t forget to follow us @INN_Resource for real-time news updates!
Securities Disclosure: I, Georgia Williams, hold no direct investment interest in any company mentioned in this article.
The Investing News Network does not guarantee the accuracy or thoroughness of the information reported in the interviews it conducts. The opinions expressed in these interviews do not reflect the opinions of the Investing News Network and do not constitute investment advice. All readers are encouraged to perform their own due diligence.