April 29, 2024
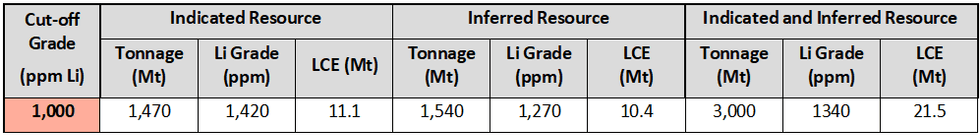
On 30 January 2024, Jindalee Lithium Limited (Jindalee, the Company) lodged its December 2023 Quarterly Activities Report, which summarised activities undertaken at the Company’s 100% owned McDermitt Lithium Project located in Oregon, USA (Project)1. McDermitt is currently the largest lithium deposit in the USA by contained lithium in Mineral Resource and is a globally significant resource with the potential to supply lithium carbonate equivalent (LCE) to US supply chains for decades2 (Table 1).
- Grant applications lodged with two US Government agencies (Defense and Energy) with strong support from state politicians, agencies and potential industry partners.
- Substantial Government funding for US critical mineral projects continues.
Jindalee is pleased to provide an update on US government funding opportunities for McDermitt.
Grant applications lodged with two US Government agencies (Defense and Energy)
Jindalee advises that the Company has lodged applications for non-dilutive grant funding with both the Department of Defense (DoD) and the Department of Energy (DoE) (Battery Manufacturing and Recycling Grant).
If successful, the DoD grant application is expected to co-fund an accelerated Feasibility Study and associated drilling and testwork, whilst the DoE grant application is designed to potentially co-fund the engineering, procurement, construction and development of a lithium processing facility at McDermitt.
Both grant applications have passed initial reviews by the agencies. The DoE grant application was accompanied by letters of support from Oregon and Nevada politicians and agencies, as well as potential Project partners.
The Company expects to provide updates regarding the status of applications and any potential award decision in the second half of 2024.
Substantial Government funding for US critical mineral projects continues
The US Government is committed to securing a domestic supply for critical minerals to reduce reliance on foreign sourced materials, including lithium, and is providing significant support and funding via the Inflation Reduction Act, the Defense Production Act and other initiatives as recent developments indicate.
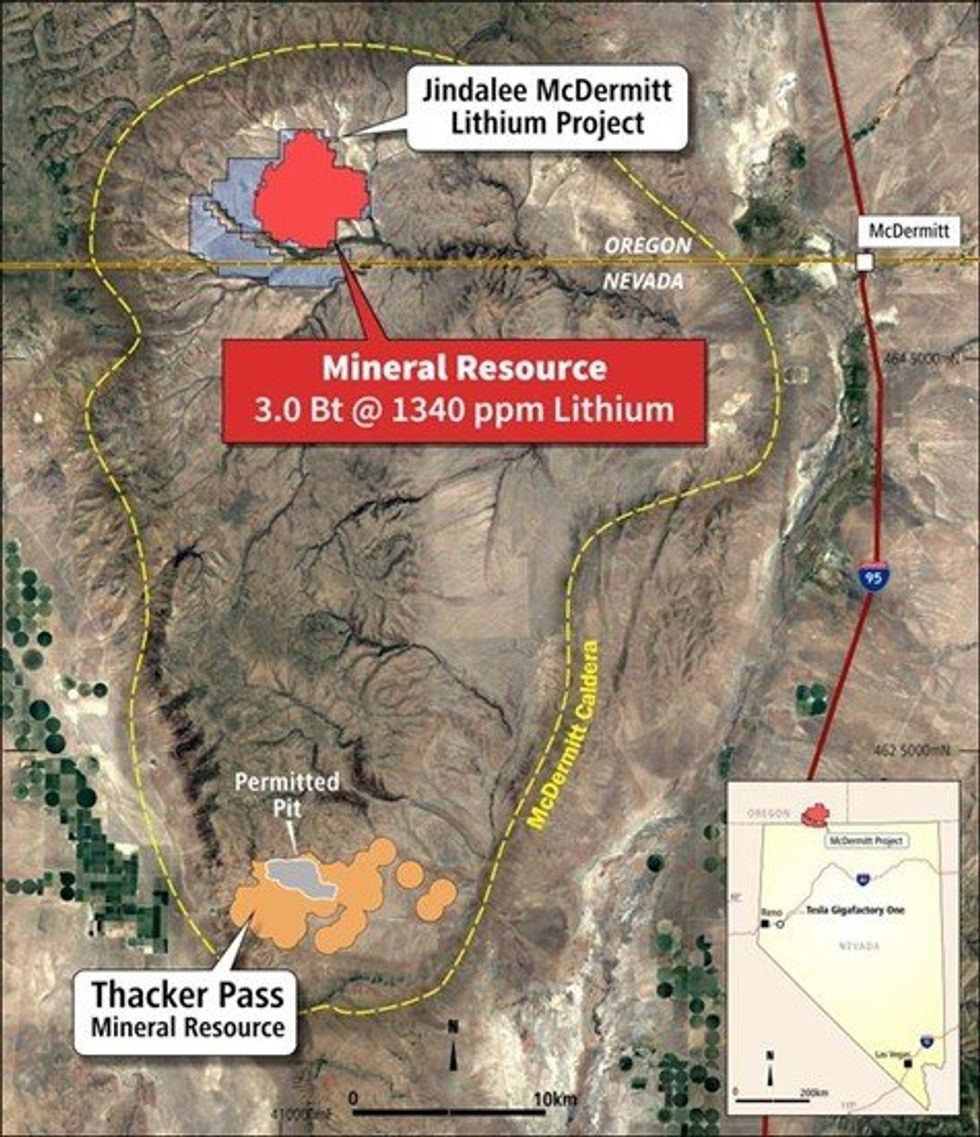
On 14 March 2024 Lithium Americas Corp (TSX: LAC, Market Cap: C$1.5bn6) announced that it had received a conditional commitment from the DoE for a US$2.26 billion loan for financing the Phase 1 construction of processing facilities at the Thacker Pass Lithium Project3, located approximately 30km south of McDermitt (Figure 1). The loan, anticipated to cover approximately 75% of Thacker Pass’s initial capital cost, offers favourable terms with an interest rate equivalent to the US Treasury rates (0% spread) and a tenor of 24 years.
On 8 April 2024 Perpetua Resources Corp (TSX: PPTA, Market Cap: C$538m6) announced that it had received a Letter of Interest from the US Export-Import Bank for potential debt of up to US$1.8 billion for capital funding of the Stibnite Gold and Antimony Project in Idaho, USA4. This follows earlier grants of up to US$59.4 million received by Perpetua Resources from the DoD to assist with construction readiness and permitting of the Stibnite Project5.
Jindalee’s CEO Ian Rodger commented “We are very pleased with the progress of our grant applications for the McDermitt Lithium Project, particularly with the strong backing we’ve received from key stakeholders, including US politicians and potential Project Partners. The support for our applications highlights the strategic importance of our Project and its alignment with US national interests. These non-dilutive grants, if successful, promise to significantly enhance equity returns, reinforcing our strategy and amplifying the value we deliver to our shareholders.
Click here for the full ASX Release
This article includes content from Jindalee Lithium Limited, licensed for the purpose of publishing on Investing News Australia. This article does not constitute financial product advice. It is your responsibility to perform proper due diligence before acting upon any information provided here. Please refer to our full disclaimer here.
JLL:AU

Sign up to get your FREE
Jindalee Lithium Investor Kit
and hear about exciting investment opportunities.
- Corporate info
- Insights
- Growth strategies
- Upcoming projects
GET YOUR FREE INVESTOR KIT
The Conversation (0)
16 April 2025
Jindalee Lithium
Game-changing, economically significant lithium resource for North American battery supply chain
Game-changing, economically significant lithium resource for North American battery supply chain Keep Reading...
23 January
Quarterly Cashflow Report - December 2025
Jindalee Lithium (JLL:AU) has announced Quarterly Cashflow Report - December 2025Download the PDF here. Keep Reading...
23 January
Quarterly Activities Report - December 2025
Jindalee Lithium (JLL:AU) has announced Quarterly Activities Report - December 2025Download the PDF here. Keep Reading...
11 December 2025
US Government Approves Major Drilling Program at McDermitt
Jindalee Lithium (JLL:AU) has announced US Government Approves Major Drilling Program at McDermittDownload the PDF here. Keep Reading...
08 December 2025
Trading Halt
Jindalee Lithium (JLL:AU) has announced Trading HaltDownload the PDF here. Keep Reading...
04 November 2025
Drilling Underway at McDermitt Lithium Project
Jindalee Lithium (JLL:AU) has announced Drilling Underway at McDermitt Lithium ProjectDownload the PDF here. Keep Reading...
27 February
UK Enters Commercial Lithium Production with Geothermal Plant Launch
The UK has entered commercial lithium production for the first time as Geothermal Engineering Ltd (GEL) began operations in its plant at Cornwall, anchoring the government's hopes of a domestic battery metals supply chain.The Redruth-based facility marks the country’s first commercial-scale... Keep Reading...
26 February
Zimbabwe Imposes Immediate Ban on Raw Mineral and Lithium Exports
Zimbabwe has imposed an immediate ban on exports of all raw minerals and lithium concentrates, halting shipments already in transit as the government tightens control over the country’s mining sector.Mines and Mining Development Minister Polite Kambamura announced Wednesday that the suspension... Keep Reading...
19 February
Top Australian Mining Stocks This Week: Lithium Valley Results Boost Gold Mountain
Welcome to the Investing News Network's weekly round-up of the top-performing mining stocks listed on the ASX, starting with news in Australia's resource sector.Mining giant BHP (ASX:BHP,NYSE:BHP,LSE:BHP) reported strong half-year copper results, saying that its copper operations accounted for... Keep Reading...
17 February
Howard Klein Doubles Down on Strategic Lithium Reserve as Project Vault Takes Shape
Before the Trump administration revealed plans for Project Vault, Howard Klein, co-founder and partner at RK Equity, proposed the idea of a strategic lithium reserve. “The goal of a strategic lithium reserve is to stabilize prices and allow the industry to develop,” he told the Investing News... Keep Reading...
17 February
Sigma Lithium Makes New Lithium Fines Sale, Unlocks US$96 Million Credit Facility
Sigma Lithium (TSXV:SGML,NASDAQ:SGML) has secured another large-scale sale of high-purity lithium fines and activated a production-backed revolving credit facility as it ramps up operations in Brazil.The lithium producer announced it has agreed to sell 150,000 metric tons (MT) of high-purity... Keep Reading...
12 February
Albemarle Lifts Lithium Demand Forecast as Energy Storage Surges
Albemarle (NYSE:ALB) is raising its long-term lithium demand outlook after a breakout year for stationary energy storage, underscoring a shift in the battery materials market that is no longer driven solely by electric vehicles.The US-based lithium major reported fourth quarter 2025 net sales of... Keep Reading...
Latest News

Sign up to get your FREE
Jindalee Lithium Investor Kit
and hear about exciting investment opportunities.
- Corporate info
- Insights
- Growth strategies
- Upcoming projects
GET YOUR FREE INVESTOR KIT
Interactive Chart
Latest Press Releases
Related News
TOP STOCKS
American Battery4.030.24
Aion Therapeutic0.10-0.01
Cybin Corp2.140.00








