May 21, 2024
Charger Metals NL (ASX: CHR, “Charger” or the “Company”) is pleased to announce that results have been received for the infill soil sampling programme completed across the Mt Gordon Prospect at its Lake Johnston Lithium Project (“Lake Johnston”), in Western Australia. This work is being funded by Rio Tinto Exploration Pty Limited (“RTX”) pursuant to RTX’s farm-in agreement with Charger in relation to the project.2
- Infill soil-sampling programme has further delineated surface lithium anomalies at the Mt Gordon Prospect at Lake Johnston, including anomalies not previously identified.
- New lithium anomalies have been defined near historic drill-holes that logged pegmatite intersections with elevated lithium values.1
- The soils programme has also defined a large niobium anomaly 1.8 km by 1.7 km in the south of the tenement.
- Field mapping and potential air core (AC) drilling is required to determine the source of the elevated niobium at surface.
- Approvals for reverse circulation (RC) drill programmes at Mt Gordon and Medcalf are expected to be received later this quarter.
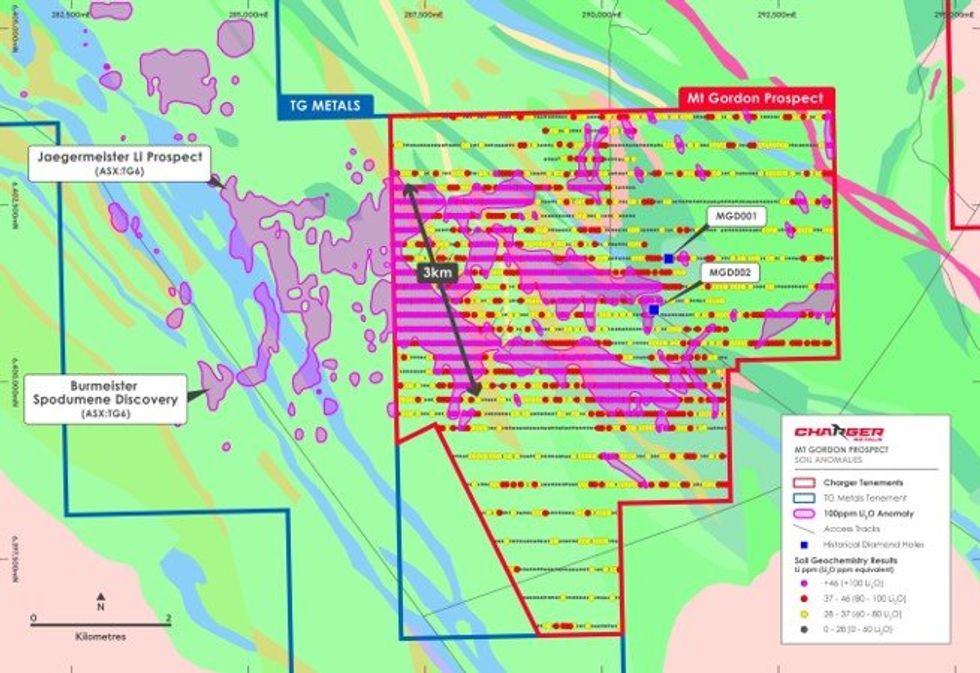
An infill soil sampling programme was completed last month across the Mt Gordon Prospect, which comprises large soil anomalies (>100ppm Li2O) extending for over 3km,3 and which lies adjacent to the Jaegermeister Lithium Prospect delineated by TG Metals Ltd (ASX:TG6).4
864 samples were taken at 50m spacing on infill lines which reduced sample line spacing to 200m (see Figure 1).
The results from the closer-spaced samples have better defined the large lithium soil anomalies at Mt Gordon, as shown in Figure 1. Furthermore, new more discreet lithium anomalies have been defined. In particular, a new lithium surface anomaly has been delineated in close proximity to a historic diamond drill-hole MGD002, in which thin pegmatite intervals with elevated lithium values were logged at depth.1
Charger’s Managing Director, Aidan Platel, commented:
“The results from the recent phase of soil sampling at Mt Gordon have successfully increased the resolution of the large lithium surface anomalies defined by the first phase of sampling, thus providing more accurate targets for the upcoming RC drill programme.
The new, more subtle lithium anomalies defined by the recent soils exhibit good prospectivity, particularly the anomaly in proximity to known lithium-bearing pegmatites intersected in historical drilling.
We continue to work with the Department of Mines Department of Energy, Mines, Industry Regulation and Safety (DMIRS) with regards to our drilling approvals, with the next phase of RC drilling scheduled for next month.”
In addition to the lithium anomalies, the results from the recent phase of soil sampling at Mt Gordon have defined a large niobium (Nb) anomaly in the south of the tenement (Figure 2). The anomaly (>10ppm Nb) covers an area of approximately 1.8km by 1.7km with results up to 21.4ppm Nb and is coincident with an underlying magnetic high (Figure 2). Further work such as field mapping and sampling, and potentially shallow AC drilling, is required to determine the potential source of this large anomaly (this is yet to be considered by RTX under the current funding arrangements).
Click here for the full ASX Release
This article includes content from Charger Metals, licensed for the purpose of publishing on Investing News Australia. This article does not constitute financial product advice. It is your responsibility to perform proper due diligence before acting upon any information provided here. Please refer to our full disclaimer here.
CHR:AU
The Conversation (0)
12 February
Albemarle Lifts Lithium Demand Forecast as Energy Storage Surges
Albemarle (NYSE:ALB) is raising its long-term lithium demand outlook after a breakout year for stationary energy storage, underscoring a shift in the battery materials market that is no longer driven solely by electric vehicles.The US-based lithium major reported fourth quarter 2025 net sales of... Keep Reading...
21 January
Official signing of the Portuguese State Grant
Savannah joins other grant recipient companies at official signing ceremony
Savannah Resources Plc, the developer of the Barroso Lithium Project in Portugal, a 'Strategic Project' under the European Critical Raw Materials Act and Europe's largest spodumene lithium deposit (the 'Project'), was delighted to join with other recipients of State grants yesterday at the... Keep Reading...
21 January
Excellent Results from 2025 Core Drilling Program at McDermitt
Jindalee Lithium Limited (Jindalee, or the Company; ASX: JLL, OTCQX: JNDAF) is pleased to report assay results from the drilling program at the McDermitt Lithium Project completed late 2025. All holes returned strong lithium and magnesium intercepts from shallow depths, including:R92: 36.5m @... Keep Reading...
08 January
Top 5 US Lithium Stocks (Updated January 2026)
The global lithium market enters 2026 after a punishing 2025 marked by oversupply, weaker-than-expected EV demand and sustained price pressure, although things began turning around for lithium stocks in Q4. Lithium carbonate prices in North Asia fell to four-year lows early in the year,... Keep Reading...
07 January
5 Best-performing ASX Lithium Stocks (Updated January 2026)
Global demand for lithium presents a significant opportunity for Australia and Australian lithium companies.Australia remains the world’s largest lithium miner, supplying nearly 30 percent of global output in 2024, though its dominance is easing as other lithium-producing countries such as... Keep Reading...
05 January
CEOL Application for Laguna Verde Submitted
CleanTech Lithium PLC ("CleanTech Lithium" or "CleanTech" or the "Company") (AIM: CTL, Frankfurt:T2N), an exploration and development company advancing sustainable lithium projects in Chile, is pleased to announce it has submitted its application (the "Application") for a Special Lithium... Keep Reading...
Latest News
Interactive Chart
Latest Press Releases
Related News
TOP STOCKS
American Battery4.030.24
Aion Therapeutic0.10-0.01
Cybin Corp2.140.00