April 27, 2025
Eclipse Metals Ltd (ASX: EPM) is pleased to report highly encouraging analytical results from 23 selected core samples from six historic diamond drill holes that were completed at the Company’s flagship Ivigtût multi-commodity project in southwest Greenland.
The results confirm the presence of high-grade rare earth element (REE) mineralisation at the Grønnedal Prospect, which is located within the Ivigtût Project Area.
The analyses, conducted by SGS Laboratories in Canada, demonstrate the occurrence of significant Total Rare Earth Oxide (TREO) values. A sample from drillhole R between 25.5 and
25.8m returned 20,092ppm (2.01%) TREO thus reinforcing the project's potential as a strategically located and globally significant source of magnetic and critical REEs essential for decarbonisation and advanced technologies.
Significant Analytical Results include:
- Drillhole R (25.5–25.8m) returned 20,092ppm (2.01%)TREO with 4,677ppm Nd₂O₃, 1,143ppm Pr₂O₃, 246ppm Dy₂O₃, 855ppm Y₂O₃ and 58ppm Tb₂O₃;
- Drillhole S (14.7–15.2m) returned 17,595ppm TREO including 4,269ppm Nd₂O₃, 484ppm Y₂O₃ and 371ppm Gd₂O₃
Director of Eclipse Metals, Mr Carl Poppal, stated:
“These latest analytical results are outstanding. They exceed our expectations and confirm the scale and quality of REE mineralisation present at depth in the Grønnedal prospect. With TREO grades over 2%, including significant Nd, Pr, Dy and Tb concentrations, the magnetic rare earth potential is truly world-class. Importantly, these findings allow us to calibrate the HyperXRF system, enabling rapid assessment across the broader project area and helping fast-track our pathway to an expanded MRE and feasibility development.”
Introduction
The Grønnedal carbonatite-hosted mineral resource is located within the Grønnedal Igneous Complex (Figure 1). The initial mineral resource estimate (MRE) (Table 1) is based on limited shallow drill testing of a small portion of the larger carbonatite complex.
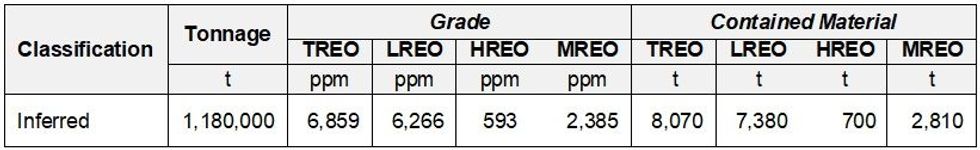
The MRE is underpinned by analytical data derived from both exploration trenching and shallow drilling programs (refer to ASX announcement 25 July and 8th August 2023). Thus, the vertical extents of the MRE are limited to an average depth of only 12m.
In 1950, Kryolitselskabet Øresund A/S, Cryolite Company drilled six diamond holes in the vicinity of the Grønnedal resource to test for a potential iron ore deposit (Figure 1). This drilling extends to depths of up to 200m.
During 2024, the Greenland Government granted Eclipse permission to conduct non-destructive analyses of the government-archived core from these drillholes using the Minalyze XRF TruScan technology developed by Veracio in Gothenburg, Sweden. These data, which are summarised in Table 2, suggest that anomalous rare earth mineralisation, as defined by six key indicator elements, extends to depths of approximately 200m (refer to ASX announcement January 2025).
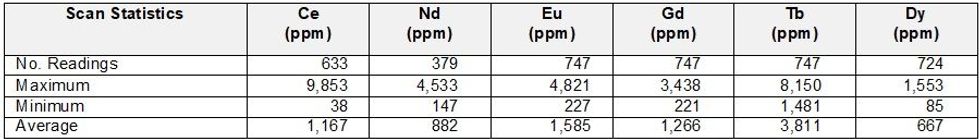
To verify the TruScan data, conventional laboratory analyses were required. In late 2024 Eclipse were allowed to extract small specimens from selected core intervals, using sampling protocols approved by the Greenland Government, from 23 intervals representing key lithologies for analytical test work. Sample treatment was carried out by SGS Lakefield, Canada using a sodium peroxide (Na₂O₂) digestion followed by ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry).
Click here for the full ASX Release
This article includes content from Eclipse Metals, licensed for the purpose of publishing on Investing News Australia. This article does not constitute financial product advice. It is your responsibility to perform proper due diligence before acting upon any information provided here. Please refer to our full disclaimer here.
EPM:AU
The Conversation (0)
25 March 2024
Eclipse Metals
Pursuing Multi-commodity Assets to Support Decarbonization
Pursuing Multi-commodity Assets to Support Decarbonization Keep Reading...
2h
Final Assay Results Highlight Potential for New Discoveries
Vital Metals Limited (ASX: VML) (“Vital Metals” or “the Company”) is pleased to report final overlimit assay results from grab samples collected at Nechalacho, confirming exceptional rare earth grades of up to 292,145ppm TREO. Highlights:F009416 (target 1029A) returned the highest TREO value... Keep Reading...
05 March
Top Australian Mining Stocks This Week: OD6 Metals Shines on US Fluorspar Acquisition
Welcome to the Investing News Network's weekly round-up of the top-performing mining stocks listed on the ASX, starting with news in Australia's resource sector.Critical minerals companies dominate this week’s list, with OD6 Metals emerging as the top gainer.The Northern Territory government... Keep Reading...
26 February
Top Australian Mining Stocks This Week: European Resources Soars on Rare Earth Results
Welcome to the Investing News Network's weekly round-up of the top-performing mining stocks listed on the ASX, starting with news in Australia's resource sector.Gold, lithium and copper companies continue to dominate our top ASX stocks of the week. This week, the Northern Territory's Minister... Keep Reading...
25 February
China's Rare Earths Export Ban Hits Japanese Defense Sector
China has moved to freeze exports of rare earth magnets and other critical materials to dozens of major Japanese companies, with the measures to take effect immediately.China’s commerce ministry said Tuesday (February 24) that it will suspend shipments of so-called “dual-use” goods — referring... Keep Reading...
24 February
Application to Trade on OTCQB Market
Altona Rare Earths plc (LSE: REE), the critical raw materials exploration and development company focused on Africa, is pleased to announce that it has applied for its ordinary shares to be admitted to trading on the OTCQB Venture Market in the United States ( "OTCQB").The Company has submitted... Keep Reading...
24 February
Brazil, India Ink Rare Earths Pact to Expand Supply Chain Cooperation
Brazil and India have signed a new agreement to deepen cooperation on rare earths and critical minerals as both countries seek to strengthen supply chains and reduce reliance on trading partners.The non-binding memorandum of understanding, sealed on February 21 during Brazilian President Luiz... Keep Reading...
Latest News
Interactive Chart
Latest Press Releases
Related News
TOP STOCKS
American Battery4.030.24
Aion Therapeutic0.10-0.01
Cybin Corp2.140.00






