October 30, 2024
Elixir Energy Limited (“Elixir” or the “Company”) is pleased to present its Quarterly Activities and Cash Flow Report.
HIGHLIGHTS
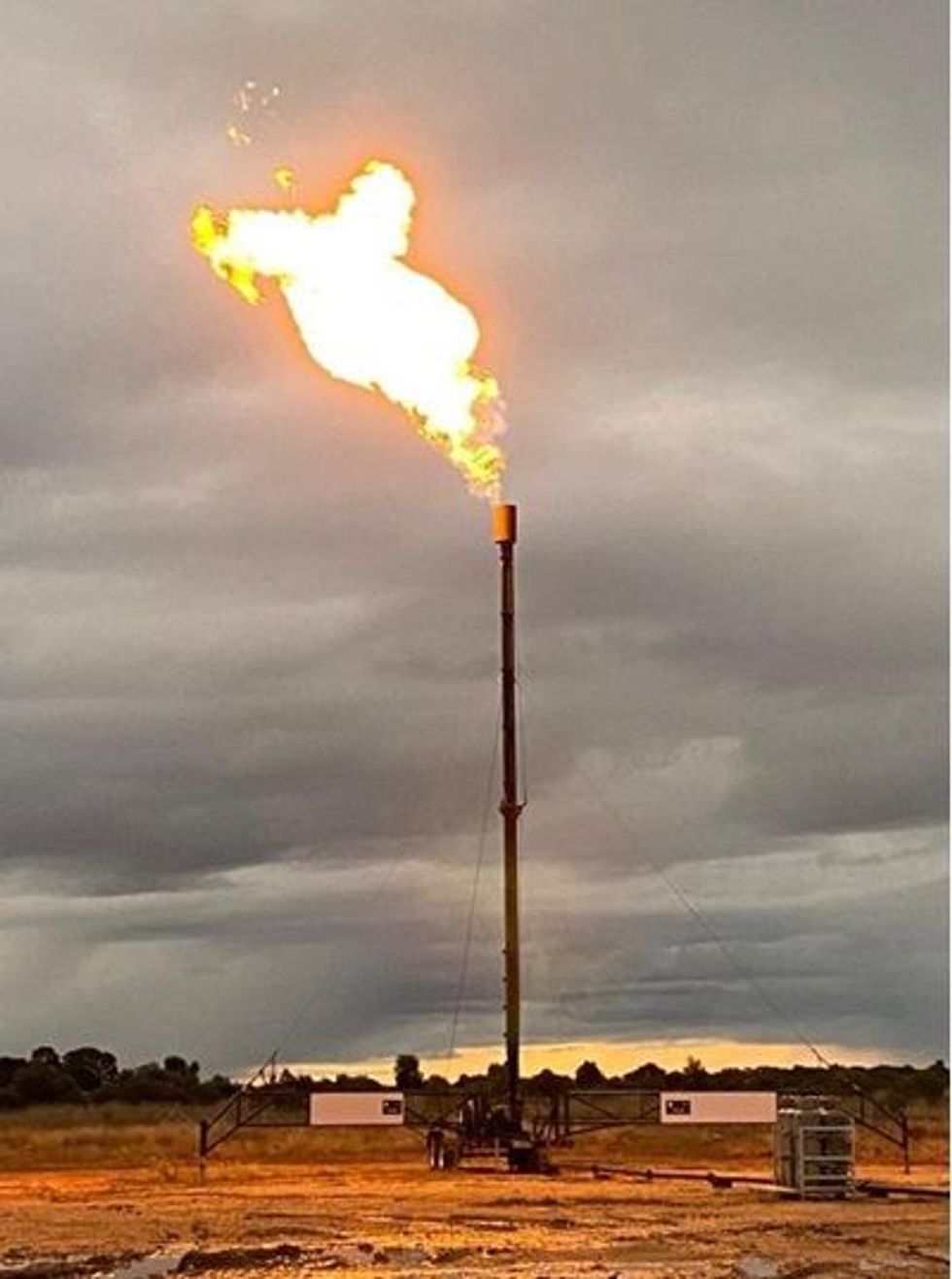
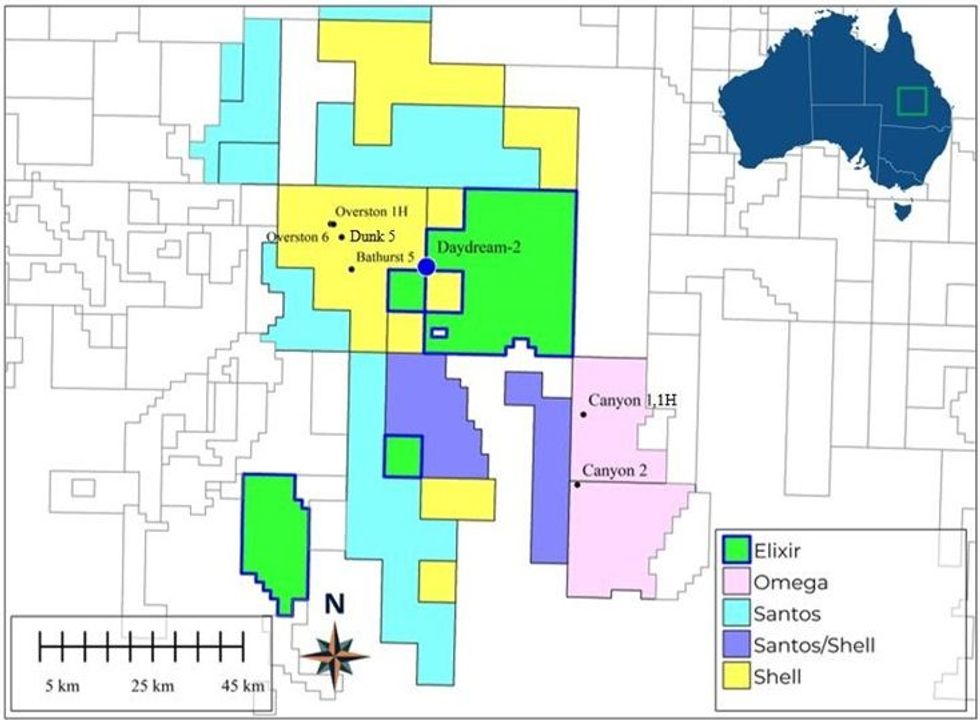
- Daydream-2 well successfully stimulated and flow tested
- Gas flowed from multiple stimulated zones, including deep coals for the first time
- ATP 2077 formally awarded and 173 Bcf additional contingent resources booked
- Elixir’s fiscal position remains strong - $10M at quarter end
MANGAGING DIRECTOR’S REPORT TO SHAREHOLDERS FOR THE QUARTER
The Daydream-2 appraisal well was again the key focus for Elixir during the quarter. The considerable successes of this program (albeit with some ebbs and flows typical of an early stage appraisal program) has provided the Company with a very strong platform to continue to de-risk the Grandis Project.
North America’s considerable experience in large unconventional plays over the last two decades indicates that having multiple operators try different approaches to “cracking the code” to most effectively liberate gas presents by far the optimal approach to really open up such plays.
In this context Elixir is very pleased to be currently accompanied by other active explorers in Queensland’s Taroom Trough. Collectively, considerable sums are being invested, contingent resources booked, knowledge transferred and service sector capabilities continuously improved.
During the last quarter Elixir’s contributions to these collective efforts were material and multiple. These included flowing gas from five out of six stimulated zones, including from deep coals for the first time in this region.
Elixir expects the various current – and likely new – Taroom Operators to expand their efforts in the years to come - to ultimately deliver a lot of gas into the nearby infrastructure that can readily take it to desperately short domestic and international markets.
In the current early stage of such a large play, the teething issues that typically arise include rationing of the required equipment, service sector companies requiring different approaches, etc. Elixir has experienced some of these – but we are convinced that we can see these already being ironed out. For instance, the collective efforts in the region are already leading to interest from the likes of new service sector and infrastructure companies, with highly relevant international expertise and equipment.
During the quarter Elixir was formally granted ATP 2077 – which immediately added 175 Bcf of new contingent resources. The timeline from being notified as preferred tenderer to formal award was very rapid – reflecting the strong Queensland regulatory environment generally and the well established oil and gas presence in the immediate region specifically.
Post the end of the quarter, Elixir was pleased to execute a Memorandum of Understanding with Australian Gas Infrastructure Group (AGIG) to provide a framework under which to better investigate the development of the required infrastructure to take Taroom sourced gas to the nearby market interfaces. Elixir sees this is also an area of potential fruitful cooperation.
Click here for the full ASX Release
This article includes content from Elixir Energy, licensed for the purpose of publishing on Investing News Australia. This article does not constitute financial product advice. It is your responsibility to perform proper due diligence before acting upon any information provided here. Please refer to our full disclaimer here.
EXR:AU
The Conversation (0)
02 May 2024
Elixir Energy
Early-mover in natural gas exploration and appraisal in Australia and Mongolia.
Early-mover in natural gas exploration and appraisal in Australia and Mongolia. Keep Reading...
12h
Oil Tops US$100 as Iran Conflict Threatens Strait of Hormuz Supply Route
Global oil and gas prices rallied sharply over the weekend as escalating geopolitical tensions in the Middle East rattled energy markets and triggered fears of a major supply disruption. Benchmark crude prices surged to their highest levels in years, with traders pricing in the possibility of... Keep Reading...
12h
Force Majeure Spreads Across Global Commodities as Iran War Disrupts Supply Chains
Force majeure declarations are beginning to ripple across the global commodities sector as the escalating conflict in the Middle East threatens to spread shocks beyond oil and gas.Energy companies, producers and traders are already grappling with interruptions to shipments through the Strait of... Keep Reading...
06 March
Syntholene Energy Corp. Announces Completion of Conceptual Design Report and Technoeconomic Analysis
Report Validates Pathway to Industrial Scale Synthetic Fuel Production Targeting Cost Competitiveness with Fossil FuelsSyntholene Energy Corp. (TSXV: ESAF,OTC:SYNTF) (OTCQB: SYNTF) ("Syntholene" or the "Company") announces the completion of its Conceptual Design Report ("CDR") and integrated... Keep Reading...
06 March
Angkor Resources Announces Closing of Evesham Oil and Gas Sale
(TheNewswire) GRANDE PRAIRIE, ALBERTA TheNewswire - March 6, 2026 - Angkor Resources Corp. (TSXV: ANK,OTC:ANKOF) ("ANGKOR" OR "THE COMPANY") announces the completion of all final payments and closing of the sale of its 40% participating interest (the "Assets") in the Evesham Macklin oil and gas... Keep Reading...
05 March
Oil Prices Surge as Iran Conflict Halts Tanker Traffic Through Hormuz
Oil and gas prices extended their sharp climb this week as the escalating conflict between the US, Israel and Iran disrupts shipping through one of the world’s most critical energy chokepoints.Crude oil futures surged again on Thursday (March 5), with the US benchmark climbing roughly 3.5... Keep Reading...
03 March
Syntholene Energy Corp. Closes Oversubscribed $3.75 Million Non-Brokered Private Placement
Proceeds to be used to Accelerate Procurement and Component Assembly for Demonstration Facility Deployment in IcelandSyntholene Energy CORP. (TSXV: ESAF,OTC:SYNTF) (FSE: 3DD0) (OTCQB: SYNTF) (the "Company" or "Syntholene") is pleased to announce that it has closed its previously announced... Keep Reading...
Latest News
Interactive Chart
Latest Press Releases
Related News
TOP STOCKS
American Battery4.030.24
Aion Therapeutic0.10-0.01
Cybin Corp2.140.00