February 13, 2025
American Rare Earths (ASX:ARR,OTCQX:ARRNF,ADR:AMRRY) unlocks the USA’s rare earths potential through its strategic, high-value asset in Wyoming. The flagship project, Halleck Creek, is one of North America’s largest REE deposits. With a 2.63-billion-ton JORC resource at 3,292 ppm TREO, American Rare Earths is ramping up its development to bolster the North American critical minerals supply chain.
Halleck Creek offers significant exploration upside, presenting a multi-generational opportunity to establish a sustainable rare earths supply chain in the US. The support from EXIM Bank further highlights the strategic importance of Halleck Creek in reducing U.S. dependency on foreign suppliers.
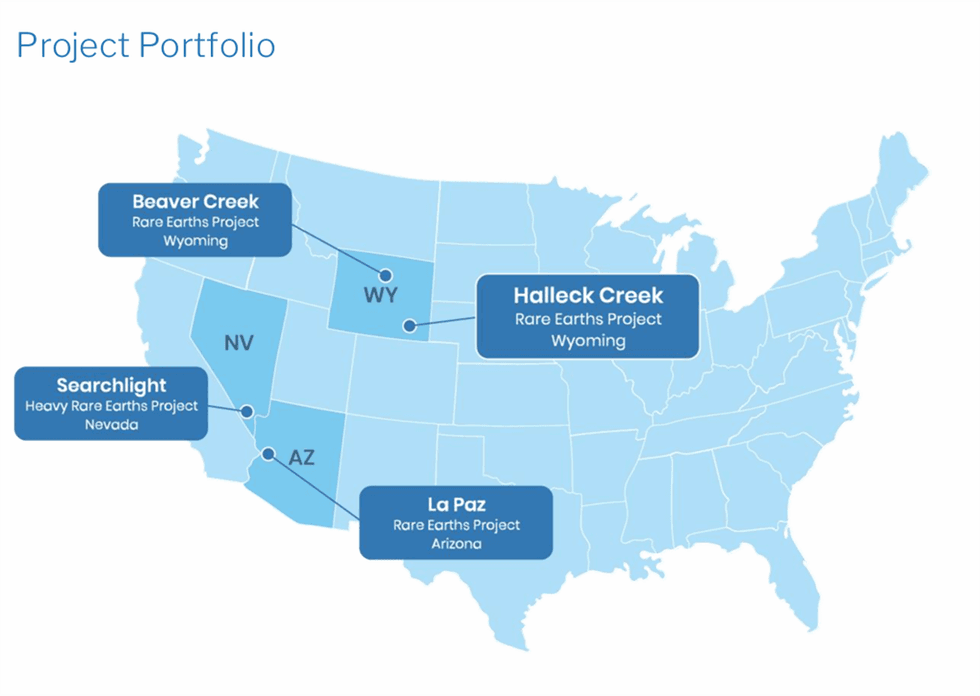 Key Projects
Key ProjectsThe Halleck Creek project in Albany County, Wyoming, is the cornerstone of ARR’s growth strategy. Recognized as one of the largest, rare-earth deposits in North America, it boasts a JORC-compliant resource of 2.63 billion tons at 3,292 ppm TREO. The deposit is hosted in Precambrian granites and metamorphic rocks, which contain REE-enriched minerals like monazite and bastnaesite. The coarse-grained nature of the mineralization ensures cost-effective extraction and processing.
Company Highlights
- American Rare Earth’s flagship project, Halleck Creek, is one of North America’s largest REE deposits. With a 2.63-billion-ton JORC resource at 3,292 ppm TREO, it holds the potential to meet US rare earths demand for approximately 100 years.
- The company is completely focused on developing a US-based critical minerals supply chain, aligning with US policies to reduce reliance on China for rare earth supply.
- The Halleck Creek project’s planned development consists of two phases. Phase 1 entails development of the Cowboy State mine, which is located entirely on Wyoming state land, enabling faster permitting and streamlined regulatory processes. Subsequently, cash flow generated from CSM will support development of the federal portions of Halleck Creek in Phase 2.
- This phased approach allows ARR to accelerate its pathway to production, enhance shareholder value, and strengthen its position as a key domestic supplier of rare earth elements in the United States.
- Well-positioned to address critical supply chain vulnerabilities, Halleck Creek benefits from strong federal and state support, including a non-binding EXIM Bank letter of interest for funding up to $456 million.
This American Rare Earths profile is part of a paid investor education campaign.*
Click here to connect with American Rare Earths (ASX:ARR) to receive an Investor Presentation
ARR:AU

Sign up to get your FREE
American Rare Earths Limited Investor Kit
and hear about exciting investment opportunities.
- Corporate info
- Insights
- Growth strategies
- Upcoming projects
GET YOUR FREE INVESTOR KIT
The Conversation (0)
12 February 2025
American Rare Earths Limited
Advancing one of the largest REE deposits in North America
Advancing one of the largest REE deposits in North America Keep Reading...
27 January
Quarterly Activities/Appendix 5B Cash Flow Report
American Rare Earths Limited (ARR:AU) has announced Quarterly Activities/Appendix 5B Cash Flow ReportDownload the PDF here. Keep Reading...
09 November 2025
Optimisation Update
American Rare Earths Limited (ARR:AU) has announced Optimisation UpdateDownload the PDF here. Keep Reading...
16 October 2025
Quarterly Activities/Appendix 5B Cash Flow Report
American Rare Earths Limited (ARR:AU) has announced Quarterly Activities/Appendix 5B Cash Flow ReportDownload the PDF here. Keep Reading...
12 October 2025
Successful Completion-Impurity Removal Neutralization Tests
American Rare Earths Limited (ARR:AU) has announced Successful Completion-Impurity Removal Neutralization TestsDownload the PDF here. Keep Reading...
02 October 2025
COB: Repayment of Promissory Note
American Rare Earths Limited (ARR:AU) has announced COB: Repayment of Promissory NoteDownload the PDF here. Keep Reading...
26 February
Top Australian Mining Stocks This Week: European Resources Soars on Rare Earth Results
Welcome to the Investing News Network's weekly round-up of the top-performing mining stocks listed on the ASX, starting with news in Australia's resource sector.Gold, lithium and copper companies continue to dominate our top ASX stocks of the week. This week, the Northern Territory's Minister... Keep Reading...
25 February
China's Rare Earths Export Ban Hits Japanese Defense Sector
China has moved to freeze exports of rare earth magnets and other critical materials to dozens of major Japanese companies, with the measures to take effect immediately.China’s commerce ministry said Tuesday (February 24) that it will suspend shipments of so-called “dual-use” goods — referring... Keep Reading...
24 February
Application to Trade on OTCQB Market
Altona Rare Earths plc (LSE: REE), the critical raw materials exploration and development company focused on Africa, is pleased to announce that it has applied for its ordinary shares to be admitted to trading on the OTCQB Venture Market in the United States ( "OTCQB").The Company has submitted... Keep Reading...
24 February
Brazil, India Ink Rare Earths Pact to Expand Supply Chain Cooperation
Brazil and India have signed a new agreement to deepen cooperation on rare earths and critical minerals as both countries seek to strengthen supply chains and reduce reliance on trading partners.The non-binding memorandum of understanding, sealed on February 21 during Brazilian President Luiz... Keep Reading...
22 February
LKY Commences Diamond Drilling at Desert Antimony Mine
Locksley Resources (LKY:AU) has announced LKY Commences Diamond Drilling at Desert Antimony MineDownload the PDF here. Keep Reading...
20 February
Cellulose Breakthrough Could Simplify Rare Earths Separation
A team of researchers at Penn State have developed a plant-based nanomaterial capable of selectively extracting dysprosium from rare earth mixtures, according to a recent report.The findings published in the study detail how the team engineered a modified form of cellulose capable of isolating... Keep Reading...
Latest News

Sign up to get your FREE
American Rare Earths Limited Investor Kit
and hear about exciting investment opportunities.
- Corporate info
- Insights
- Growth strategies
- Upcoming projects
GET YOUR FREE INVESTOR KIT
Interactive Chart
Latest Press Releases
Related News
TOP STOCKS
American Battery4.030.24
Aion Therapeutic0.10-0.01
Cybin Corp2.140.00







