April 29, 2024
Oceana Lithium Limited (ASX: OCN, “Oceana” or “the Company”) is pleased to announce that the results of recent soil sampling have defined a uranium anomaly in excess of 4.5km in length and up to 700m in width at its 100% owned Napperby Project in the Northern Territory, Australia.
Highlights
Napperby Project, Northern Territory, Australia
- Soil sampling results have delineated a large uranium anomaly in excess of 4.5km in length and up to 700m in width
- Re-examination of hyperspectral data by HyVista supports ‘roll-front’ style uranium mineralisation interpretation for the anomaly
- Follow-up mapping of the identified uranium and sulphide targets to commence, with results to refine / generate drill targets
- Field exploration activities will assess lithium-caesium-tantalum (LCT) pegmatites potential along with uranium and Rare Earth Elements
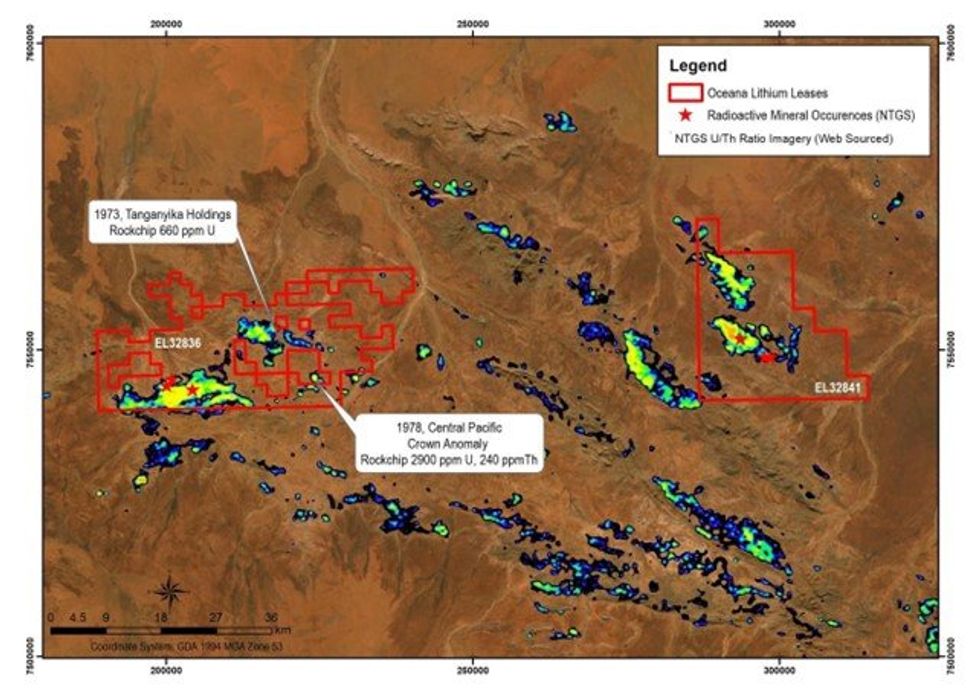
The Napperby Project is located within the highly prospective Arunta Province, which is endowed with some of the most prospective rocks for lithium (Li), Rare Earth Elements (REEs) and uranium (U) mineralisation in the Northern Territory.
As announced on 21 February 2024, the Paleoproterozoic Wangala and Ennugan Mountains granites have long been recognised as “Hot Granites” and known to be anomalously enriched in a range of elements including U, thorium and REEs. Both granite plutons show outstanding uranium/thorium ratios and are almost fully encapsulated within Oceana’s Napperby Project leases EL32836 and ELA32841 (under application), as shown in Figure 1.
A soil geochemistry infill sampling program was completed during the December quarter in the southeast corner of EL32836 to better define and understand the lithium anomalies highlighted by the 2022 soil sampling program (refer to ASX Announcement dated 28 November 2022).
A total of 107 samples were collected in the last campaign at 200m spacings for approximately 30 line-km, infilling the previous 2km line spacing to 500m. Although initially targeting lithium, the results from the soil sampling have defined a large arcuate uranium anomaly, as shown in Figure 2.
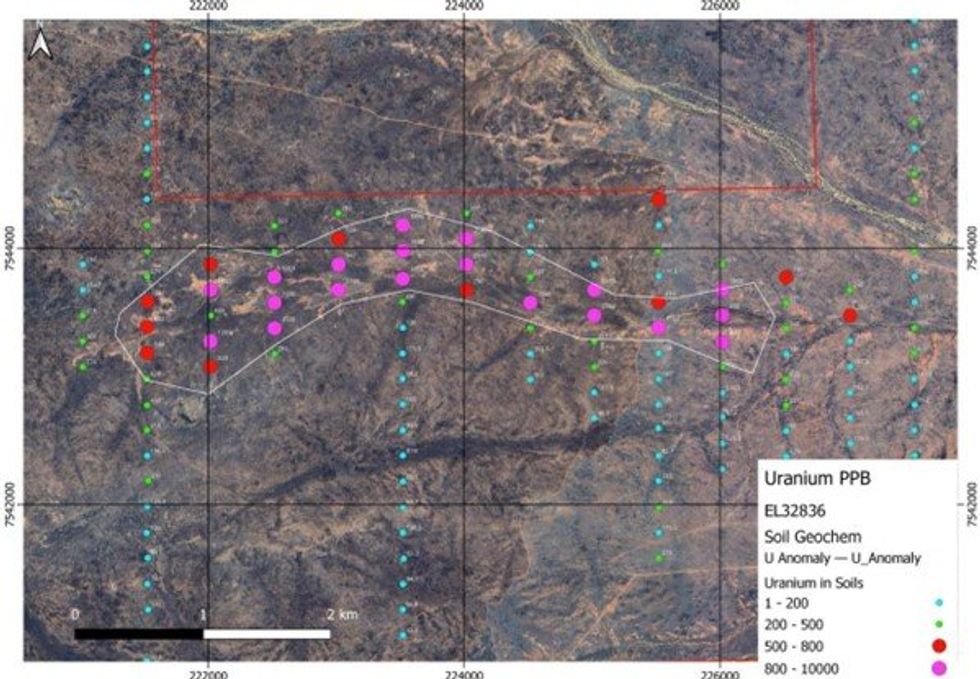
The uranium anomaly is mostly covered by Quaternary sediments and residual soils. The relatively low absolute values for the anomaly (500 – 3,680ppb U) are the result of using mobile metal ion sampling techniques which enables field teams to sample large areas without the need to carry large heavy samples around in the field. Because the samples are not crushed and pulverized, it is only unbound or weakly attached metal ions that are removed from soils and as such it is not the absolute values of elements that are of interest but the relative differences of values within a given data set.
Modelling and interpretation of the available hyperspectral data at Napperby was completed by HyVista Pty Ltd (HyVista). Modelling of the geochemical alteration zones interpreted from the hyperspectral data relative to the uranium surface anomaly confirmed that the anomaly has the potential to host significant “roll-front” type uranium mineralisation.
Click here for the full ASX Release
This article includes content from Oceana Lithium, licensed for the purpose of publishing on Investing News Australia. This article does not constitute financial product advice. It is your responsibility to perform proper due diligence before acting upon any information provided here. Please refer to our full disclaimer here.
OCN:AU
The Conversation (0)
12 March 2024
Oceana Lithium
Large-scale, highly prospective, pre-discovery projects in Brazil and Australia
Large-scale, highly prospective, pre-discovery projects in Brazil and Australia Keep Reading...
27 February
UK Enters Commercial Lithium Production with Geothermal Plant Launch
The UK has entered commercial lithium production for the first time as Geothermal Engineering Ltd (GEL) began operations in its plant at Cornwall, anchoring the government's hopes of a domestic battery metals supply chain.The Redruth-based facility marks the country’s first commercial-scale... Keep Reading...
26 February
Zimbabwe Imposes Immediate Ban on Raw Mineral and Lithium Exports
Zimbabwe has imposed an immediate ban on exports of all raw minerals and lithium concentrates, halting shipments already in transit as the government tightens control over the country’s mining sector.Mines and Mining Development Minister Polite Kambamura announced Wednesday that the suspension... Keep Reading...
19 February
Top Australian Mining Stocks This Week: Lithium Valley Results Boost Gold Mountain
Welcome to the Investing News Network's weekly round-up of the top-performing mining stocks listed on the ASX, starting with news in Australia's resource sector.Mining giant BHP (ASX:BHP,NYSE:BHP,LSE:BHP) reported strong half-year copper results, saying that its copper operations accounted for... Keep Reading...
17 February
Howard Klein Doubles Down on Strategic Lithium Reserve as Project Vault Takes Shape
Before the Trump administration revealed plans for Project Vault, Howard Klein, co-founder and partner at RK Equity, proposed the idea of a strategic lithium reserve. “The goal of a strategic lithium reserve is to stabilize prices and allow the industry to develop,” he told the Investing News... Keep Reading...
17 February
Sigma Lithium Makes New Lithium Fines Sale, Unlocks US$96 Million Credit Facility
Sigma Lithium (TSXV:SGML,NASDAQ:SGML) has secured another large-scale sale of high-purity lithium fines and activated a production-backed revolving credit facility as it ramps up operations in Brazil.The lithium producer announced it has agreed to sell 150,000 metric tons (MT) of high-purity... Keep Reading...
12 February
Albemarle Lifts Lithium Demand Forecast as Energy Storage Surges
Albemarle (NYSE:ALB) is raising its long-term lithium demand outlook after a breakout year for stationary energy storage, underscoring a shift in the battery materials market that is no longer driven solely by electric vehicles.The US-based lithium major reported fourth quarter 2025 net sales of... Keep Reading...
Latest News
Interactive Chart
Latest Press Releases
Related News
TOP STOCKS
American Battery4.030.24
Aion Therapeutic0.10-0.01
Cybin Corp2.140.00






