- NORTH AMERICA EDITIONAustraliaNorth AmericaWorld
September 18, 2023
Lithium exploration and project development company Critical Resources Limited ASX:CRR (“Critical Resources” or “the Company”) is pleased to report exceptional new thick, high-grade results from ongoing following drilling around the recent breakthrough drill-hole MF23-207, with assays continuing to validate and expand the recently discovered “Swell Zone” at the Mavis Lake Lithium Project in Ontario, Canada.
Highlights
- Exceptional new results from drilling following up the recently reported results from drill-hole MF23-207 (74.4m @ 1.18% Li2O including 32.95m @ 1.81% Li2O).
- Drill holes testing the Swell Zone both East and West of MF23-207 have continued to intersect large, high-grade intervals of mineralisation, providing a greater level of confidence that the thick, high-grade mineralisation extends over a 200m strike.
- Assays confirm:
- Drill-hole MF23-213 with 50.2m @ 1.28% Li2O from 203.6m down-hole, including multiple meter-wide segments of extremely high-grade spodumene mineralisation, from 2.11% Li2O to 4.18% Li2O.
- Drill-hole MF23-214 with 65.45m @ 0.84% Li2O from 186.25m down-hole, including 55m @ 0.95% Li2O from 194m down-hole, including 25.85m @ 1.30% Li2O from 214m down-hole.
- Permit approval for further drill pads to continue testing the Swell Zone are expected imminently, allowing follow-up drilling to commence in the coming weeks.
- All drilling results are rapidly adding tonnage to the existing Resource, putting the Company on track for a major Resource upgrade in H1 2024.
Critical Resources Managing Director, Alex Cheeseman said:
“These outstanding results in terms of both thickness and grade provide further evidence that the Mavis Lake Swell Zone is a game-changing discovery for the Company.
“Continued wide, high-grade results make it clear that Mavis Lake is a project with significant potential. Its location, within 10km of the City of Dryden, immediate access to world-class infrastructure and the surrounding automotive industries in Southern Ontario and Michigan State, make this a project of strategic importance.”
Exploration Overview
Drilling has been designed to continue to test the Swell Zone both east and west of Drill Hole MF23- 207, within the limits of current approved drill pads. Assay results have confirmed that the Swell Zone has a current strike of 200m, showing consistency of mineralisation thickness (from 50m to 74m) and also consistency of grade (from 0.84% Li2O to 1.28% Li2O), including localised peaks of extremely high grade up to 4.18% Li2O.
Current drilling forms part of the 2023 resource extension drilling program, seeking to establish Mavis Lake as the largest single-site, JORC Code 2012 Compliant Lithium Resource in Ontario.
Full exploration results are provided in Appendix 1.
Demonstrating Consistency in the Swell Zone
The outstanding high-grade assays and broad zones of mineralisation in MF23-213 and MF23-214 extend the Swell Zone laterally while continuing to solidify the significance of the Swell Zone. Figure 1 shows the Plan view of the key intercepts in the Swell Zone, with Figures 2 and 3, a long section and cross section respectively, showing Swell consistency. Significant assay data can be seen in Table 1.
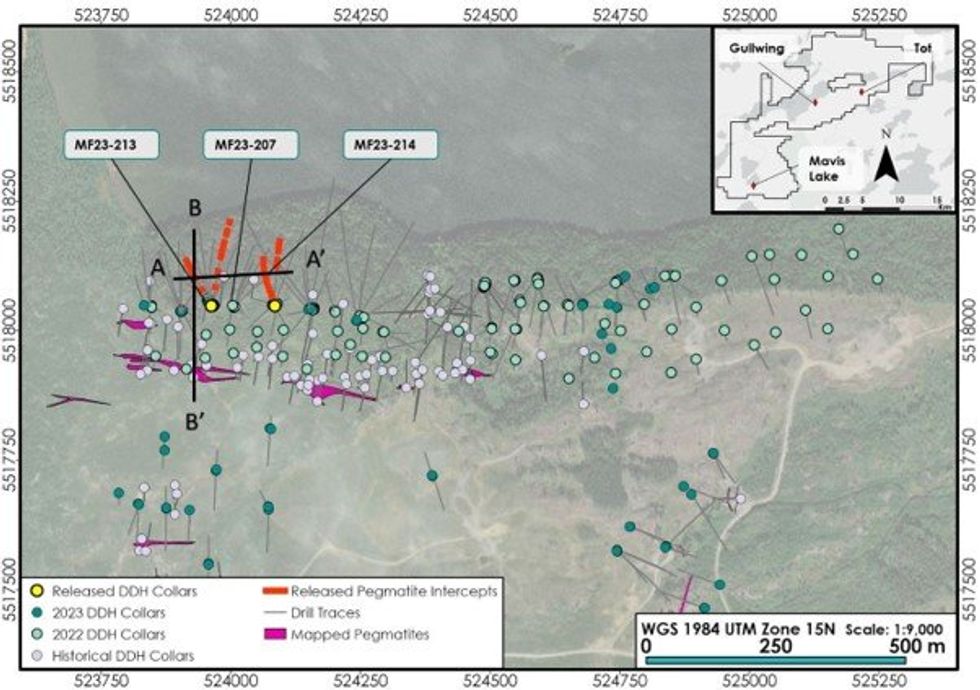
MF23-213 intersected the Swell Zone approximately 115m west from MF23-207’s 74.4m @ 1.18% Li2O pegmatite intercept. Drill hole MF23-213 provides a high level of confidence in the continuity of the large widths and high grades intersected so far in the Swell Zone while also delineating the trend and geometry of this important new structure towards the West, as shown in figure 2. The Swell Zone trend has a shallow plunge of approximately 10 degrees, trending at 280Az.
Click here for the full ASX Release
This article includes content from Critical Resources, licensed for the purpose of publishing on Investing News Australia. This article does not constitute financial product advice. It is your responsibility to perform proper due diligence before acting upon any information provided here. Please refer to our full disclaimer here.
CRR:AU
The Conversation (0)
21 June 2022
Critical Resources
High-grade Lithium Portfolio, in a Tier 1 Location, Aligned with the World’s Green Energy Transition
High-grade Lithium Portfolio, in a Tier 1 Location, Aligned with the World’s Green Energy Transition Keep Reading...
19 February
Top Australian Mining Stocks This Week: Lithium Valley Results Boost Gold Mountain
Welcome to the Investing News Network's weekly round-up of the top-performing mining stocks listed on the ASX, starting with news in Australia's resource sector.Mining giant BHP (ASX:BHP,NYSE:BHP,LSE:BHP) reported strong half-year copper results, saying that its copper operations accounted for... Keep Reading...
17 February
Howard Klein Doubles Down on Strategic Lithium Reserve as Project Vault Takes Shape
Before the Trump administration revealed plans for Project Vault, Howard Klein, co-founder and partner at RK Equity, proposed the idea of a strategic lithium reserve. “The goal of a strategic lithium reserve is to stabilize prices and allow the industry to develop,” he told the Investing News... Keep Reading...
17 February
Sigma Lithium Makes New Lithium Fines Sale, Unlocks US$96 Million Credit Facility
Sigma Lithium (TSXV:SGML,NASDAQ:SGML) has secured another large-scale sale of high-purity lithium fines and activated a production-backed revolving credit facility as it ramps up operations in Brazil.The lithium producer announced it has agreed to sell 150,000 metric tons (MT) of high-purity... Keep Reading...
12 February
Albemarle Lifts Lithium Demand Forecast as Energy Storage Surges
Albemarle (NYSE:ALB) is raising its long-term lithium demand outlook after a breakout year for stationary energy storage, underscoring a shift in the battery materials market that is no longer driven solely by electric vehicles.The US-based lithium major reported fourth quarter 2025 net sales of... Keep Reading...
21 January
Official signing of the Portuguese State Grant
Savannah joins other grant recipient companies at official signing ceremony
Savannah Resources Plc, the developer of the Barroso Lithium Project in Portugal, a 'Strategic Project' under the European Critical Raw Materials Act and Europe's largest spodumene lithium deposit (the 'Project'), was delighted to join with other recipients of State grants yesterday at the... Keep Reading...
21 January
Excellent Results from 2025 Core Drilling Program at McDermitt
Jindalee Lithium Limited (Jindalee, or the Company; ASX: JLL, OTCQX: JNDAF) is pleased to report assay results from the drilling program at the McDermitt Lithium Project completed late 2025. All holes returned strong lithium and magnesium intercepts from shallow depths, including:R92: 36.5m @... Keep Reading...
Latest News
Interactive Chart
Latest Press Releases
Related News
TOP STOCKS
American Battery4.030.24
Aion Therapeutic0.10-0.01
Cybin Corp2.140.00






