June 23, 2024
Abundant Lepidolite Pegmatite Zone Identified – 1.5km x 500m
Battery and critical metals explorer and developer Pan Asia Metals Limited (ASX: PAM) (‘PAM’ or ‘the Company’) is pleased to report that field work at the KT East Lithium Prospect continues to deliver strong results and expand the potential for the prospect.
- Rock-chip sampling continues to enhance prospectivity
- Zone of abundant lepidolite pegmatites 1.5km long and 500m wide define
- Individual dykes up to 20m wide, many 7-10m wide, ranging down to 1m or less
- Old mine dumps containing extensive lepidolite pegmatite enhance potential to north
- Hand held XRF (hhXRF) of rock-chip samples return highly elevated Li pathfinder elements such as rubidium (Rb) and ceasium (Cs)
- Modelled Li2O grades using Rb regression are supported by the presence of lepidolite and white mica in many samples
- KTE prospect has larger footprint than the RK and BT Lithium Prospects combined
- Soil sampling on 100m x 25m grid has begun, with associated rock-chip sampling and mapping
- Preliminary drill sites identified, several walk-up targets identified, many more sites to assess
- Drilling scheduled for later this year
Pan Asia Metals’ Managing Director, Paul Lock, said: “The KT Lithium Prospect is proving to be extensive, and the Li2O mod grades continue to impress. PAM’s field team has begun a grid-based soil and rock-chip sampling and geological mapping program, with soil sampling being conducted on a 100m x 25m grid. Initial gridding reports have been very encouraging, and we await formal results before providing an update on the program in a week or so. We are also investigating drill sites, with several walk-up drill targets identified. Drilling is expected to start later this year. KT presents PAM a substantial extension to RK and BT prospects and, with the KT footprint already larger than RK and BT combined, KT has the potential to add substantial tonnes, which means potential for an extended project life and/or increased annual LCE production. These results are feeding into discussions with strategic partners, so the KT exploration success is timely.”
PAM is pleased to provide this update as its field team continues its exploration program at the KT East Lithium Prospect. This highly prospective zone continues to deliver, with additional pegmatites discovered during the ongoing rock-chip and mapping program. This update follows on from PAM’s recent ASX announcement dated May 22, 2024 and titled “RK Lithium Project - KT East Lithium Prospect Lepidolite Pegmatite Dyke Swarm – Discovery Footprint Expands”. The lithium pegmatite field is identified over a strike length of approximately 2.4km and a width of at least 2.4km
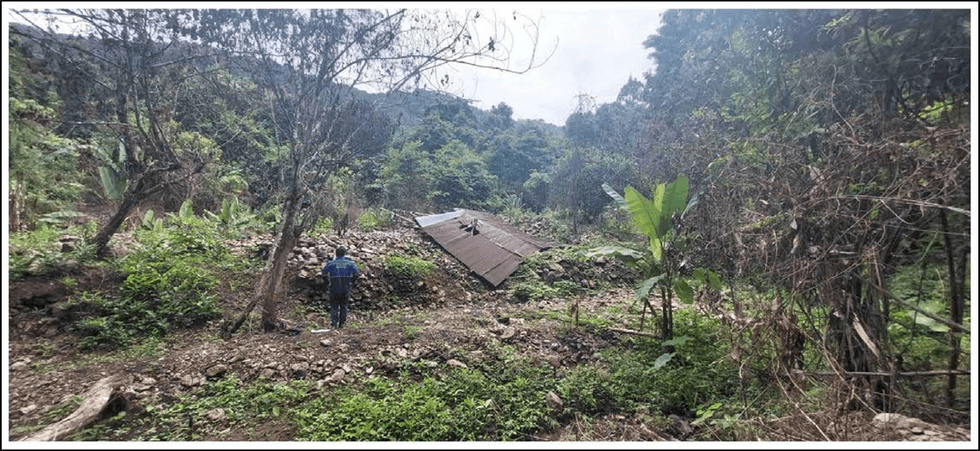
The pegmatite dyke swarm remains open and is now larger than the aggregate area of the RK and BT Lithium Prospects combined. Additional pegmatites, or extensions to previously mapped pegmatites, have been discovered, and the field team identified a historic alluvial/eluvial dump, remnants from historic tin mining, where rock-chips grading 1.74% and 1.64% Li2O mod were taken. The dump is about 70% Lepidolite pegmatites (see Figure 1 and Picture 1). Other dumps and samples are also located immediately to the west.
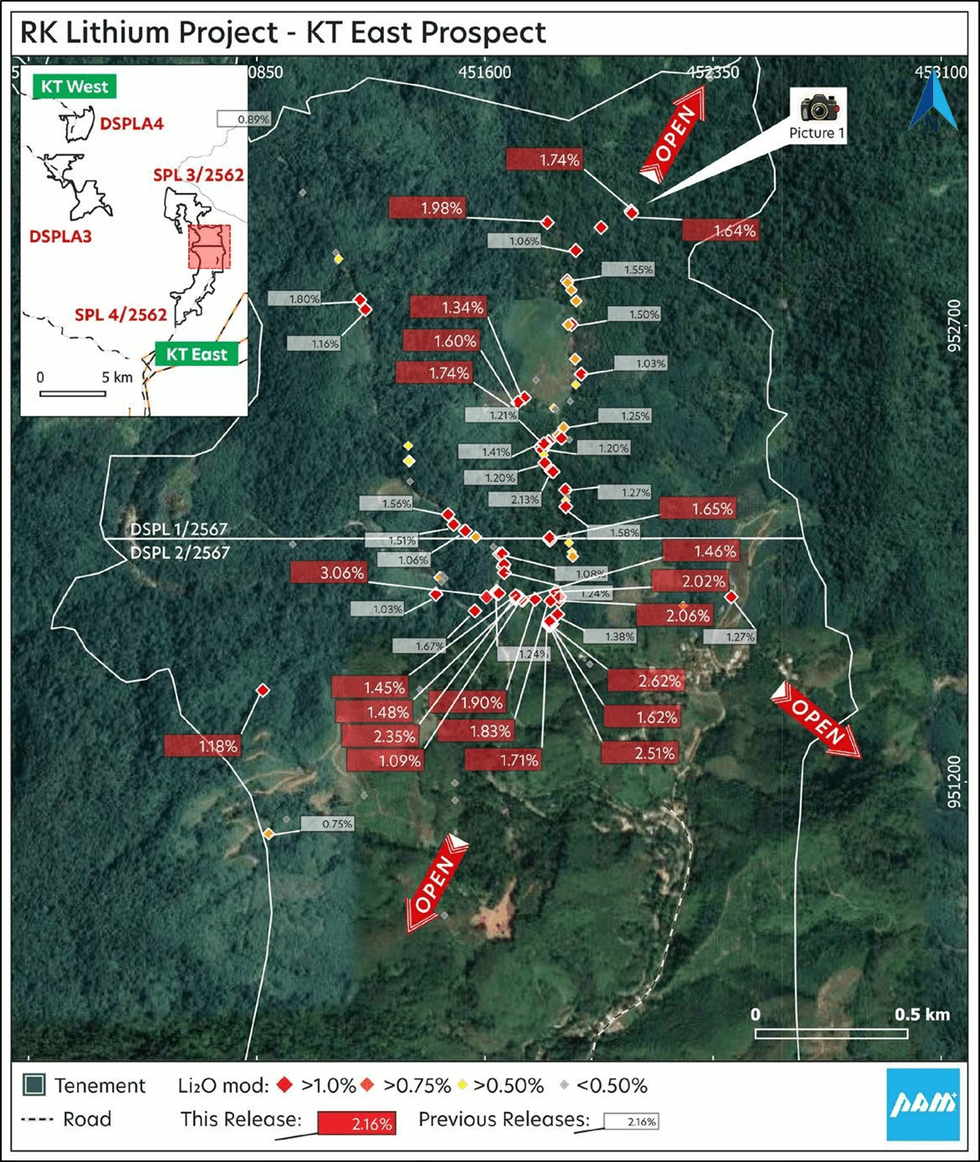

In this report, sample details and pertinent hhXRF results are presented in Appendix 2 – “Table 3, KT East Lithium Prospect – hhXRF Rb and Li2O% mod”. Further technical details are provided in Appendix 3, being JORC Table 1. Appropriate plans are provided in this report.
Rock-chip sampling and mapping has been conducted within the KT East prospect area, collecting samples of outcrop, subcrop and float for analysis. Most of these samples are described as pegmatite, with varying amounts of lepidolite and white mica. Many of the samples are described as weathered. Hand-held X-Ray fluorescence analysis (hhXRF) was carried out on an informally powdered sample that reports to the bottom corner of the calico sample bag. Two separate analysis per sample are taken in different locations, with the average result used to report grades. The analysis was performed using an Olympus Delta 400hhXRF in Geochem mode with dual beam analysis for 30 seconds each. The hhXRF reports 43 elements, but not lithium. Reported elements include lithium pathfinders and associated elements such as Rb, Cs, Mn, K, Ba, Sn, Ta and Nb. Rb (rubidium) exhibits a very strong correlation with Li in hhXRF rubidium v laboratory results for Li. This Rb:Li correlation has an R2 of 0.82 based upon 162 previous rockchip samples from the RK and BT prospects (see Appendix 3, Table 1). This technique has been practiced by PAM for many years as an accurate and cost effective means of identifying target zones quickly and efficiently.
The strong Rb:Li correlation enables a regression formula to be used to estimate an Li2O grade, herein referred to as “Li2O% mod”. The regression formula is simplified to 3 x Rb (ppm) = Li2O mod (ppm). The results for Rb and Li2O% mod for new samples (20553-20602) collected at KT East are reported in Appendix 2. The Li2O% mod values of these samples range from 0.01% to 3.06% % Li2O, with an average of 1.14%. Of all 132 samples so far collected at the prospect, 96 have returned values greater than 0.50% Li2O mod, with an average of 1.19% Li2O mod. The Li2O% mod values are supported by other Li pathfinders identified by hhXRF, as well as the presence of variable, but commonly abundant lepidolite and white mica.
Readers are cautioned that the Li2O% mod values reported are estimates of potential lithium grade based upon the strong correlation between Rb and Li, and a simple regression formula applied to hhXRF results for Rb. The derived Li2O% mod values are supported by the presence of lithium micas in the samples tested. Readers should note the Li2O% mod values are not laboratory quality results and actual Li2O contents for these samples await confirmation by laboratory analysis to be undertaken at a later date.
Click here for the full ASX Release
This article includes content from Pan Asia Metals, licensed for the purpose of publishing on Investing News Australia. This article does not constitute financial product advice. It is your responsibility to perform proper due diligence before acting upon any information provided here. Please refer to our full disclaimer here.
PAM:AU
The Conversation (0)
09 July 2023
Pan Asia Metals
First-mover Advantage in Critical Metals for Southeast Asia Market
First-mover Advantage in Critical Metals for Southeast Asia Market Keep Reading...
27 February
UK Enters Commercial Lithium Production with Geothermal Plant Launch
The UK has entered commercial lithium production for the first time as Geothermal Engineering Ltd (GEL) began operations in its plant at Cornwall, anchoring the government's hopes of a domestic battery metals supply chain.The Redruth-based facility marks the country’s first commercial-scale... Keep Reading...
26 February
Zimbabwe Imposes Immediate Ban on Raw Mineral and Lithium Exports
Zimbabwe has imposed an immediate ban on exports of all raw minerals and lithium concentrates, halting shipments already in transit as the government tightens control over the country’s mining sector.Mines and Mining Development Minister Polite Kambamura announced Wednesday that the suspension... Keep Reading...
19 February
Top Australian Mining Stocks This Week: Lithium Valley Results Boost Gold Mountain
Welcome to the Investing News Network's weekly round-up of the top-performing mining stocks listed on the ASX, starting with news in Australia's resource sector.Mining giant BHP (ASX:BHP,NYSE:BHP,LSE:BHP) reported strong half-year copper results, saying that its copper operations accounted for... Keep Reading...
17 February
Howard Klein Doubles Down on Strategic Lithium Reserve as Project Vault Takes Shape
Before the Trump administration revealed plans for Project Vault, Howard Klein, co-founder and partner at RK Equity, proposed the idea of a strategic lithium reserve. “The goal of a strategic lithium reserve is to stabilize prices and allow the industry to develop,” he told the Investing News... Keep Reading...
17 February
Sigma Lithium Makes New Lithium Fines Sale, Unlocks US$96 Million Credit Facility
Sigma Lithium (TSXV:SGML,NASDAQ:SGML) has secured another large-scale sale of high-purity lithium fines and activated a production-backed revolving credit facility as it ramps up operations in Brazil.The lithium producer announced it has agreed to sell 150,000 metric tons (MT) of high-purity... Keep Reading...
12 February
Albemarle Lifts Lithium Demand Forecast as Energy Storage Surges
Albemarle (NYSE:ALB) is raising its long-term lithium demand outlook after a breakout year for stationary energy storage, underscoring a shift in the battery materials market that is no longer driven solely by electric vehicles.The US-based lithium major reported fourth quarter 2025 net sales of... Keep Reading...
Latest News
Interactive Chart
Latest Press Releases
Related News
TOP STOCKS
American Battery4.030.24
Aion Therapeutic0.10-0.01
Cybin Corp2.140.00






