November 12, 2024
Nevada Lithium Resources Inc. (CSE: NVLH; OTCQB: NVLHF; FSE: 87K) (“Nevada Lithium” or the “Company”) is pleased to provide an updated mineral resource estimate (“Mineral Resource Estimate”) at its 100% owned Bonnie Claire Lithium Project (the “Project” or “Bonnie Claire”), located in Nye County, Nevada. The Mineral Resource Estimate was prepared by Global Resource Engineering (“GRE”) in accordance with Canadian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy and Petroleum (“CIM”) definitions, as required under National Instrument 43-101 - Standards of Disclosure for Mineral Projects (“NI 43-101”) and has an effective date of September 24, 2024. Most notably, the Lower Zone (as defined below) gives an indicated resource of 275.85 million tonnes (“Mt”) at 3,519 parts per million (“ppm”) lithium (“Li”) (5.167 Mt lithium carbonate equivalent (“LCE”)) and 275.85 Mt at 8,404 ppm boron (“B”) (2.318 Mt B), together with an inferred resource of 1,561.06 Mt at 3,085ppm lithium (25.634 Mt LCE).
Nevada Lithium’s CEO, Stephen Rentschler, comments:
“We are excited to announce the impact of the new drilling in the Lower Zone of mineralized lithium and boron at Bonnie Claire. With the significantly increased tonnage and higher grades, Bonnie Claire is potentially unrivaled by other sediment hosted lithium projects in Nevada and is now amongst the largest lithium resources in the world and amongst the highest-grade in Nevada.
Compared to Bonnie Claire’s previous resource report, the new drilling in the Lower Zone has led to a 68% increase in LCE tonnage, at an average grade that has tripled from 1,000 ppm to over 3,000 ppm. It includes intervals where grades exceed 6,000ppm. These increases have occurred using a cut-off grade that has more than doubled to 1,800 ppm. For the first time, we are also able to report a significant high-grade boron resource that we believe further enhances the Project’s value.
The Lower Zone remains open to the NW, NE and SE, for future resource expansion. Furthermore, the new infill drilling has resulted in an indicated resource classification. We are confident that the continuity of the mineralization will allow us to easily upgrade additional resources from the inferred classification into indicated resources and add new inferred resources.
The results from this report will feed directly into ongoing work on an updated Preliminary Economic Assessment (“PEA”) that we are targeting for completion at the end of Q1 2025. This PEA will reflect the increased tonnages and grades reported today. The PEA will also include the metallurgical processes currently being developed by Fluor Enterprises Inc., as reported in our news release dated October 23, 2024.
I would like to offer my congratulations and thanks to Nevada Lithium’s technical team for this tremendous success. Their dedication and vision has led to results that are of global significance and, in my opinion, will lead to future increases in shareholder value.”
Highlights:
- Resources for the deposit have been separated into two zones; a Lower Zone (i.e., mineralization hosted by Lower Claystone and Lower Sandstone units) (the “Lower Zone”) and an Upper Zone (i.e., mineralization hosted by an Upper Claystone unit) (the “Upper Zone”).
- The updated Mineral Resource Estimate includes assays from eleven (11) additional exploration and infill drill holes completed since the 2021 maiden resource estimate. 2023 & 2024 drilling intersected the lower claystone which hosts the high grade (up to 7,160ppm) lithium, and which remains open in three directions. It is reasonably expected that the bulk of inferred resources can be upgraded to indicated through additional infill drilling.
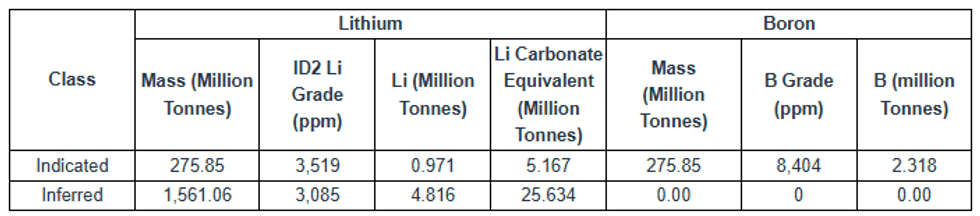
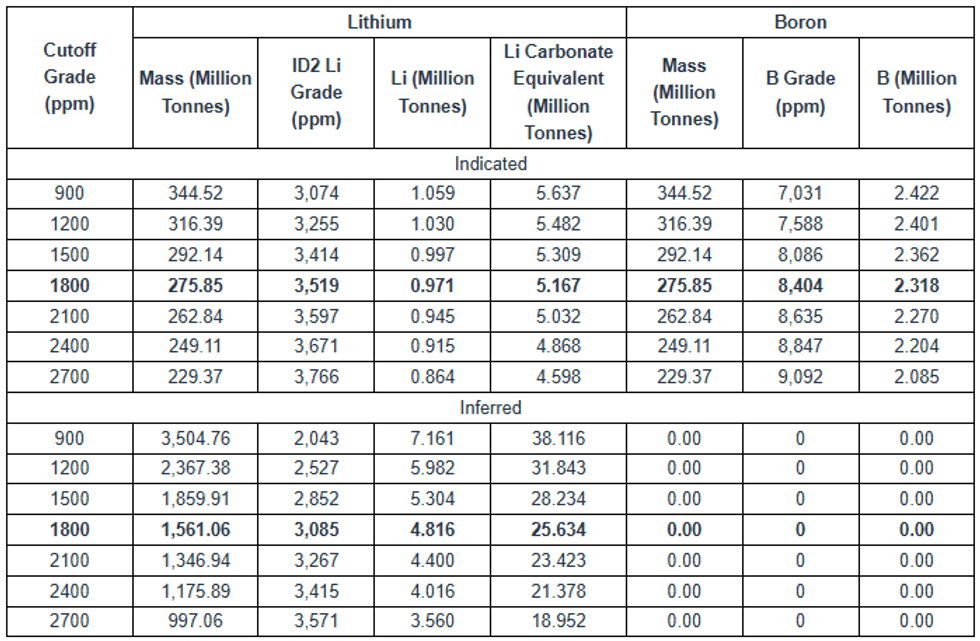
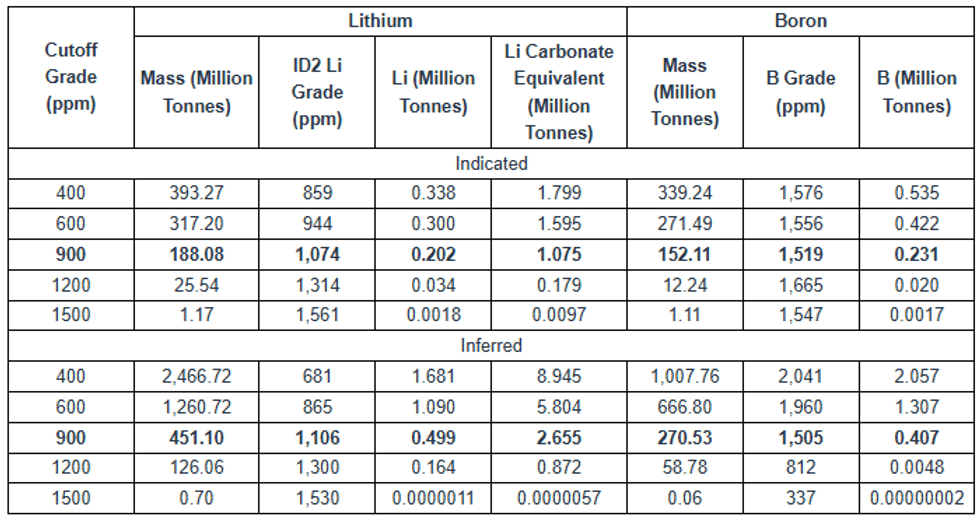
- The Lower Zone gives an indicated resource of 275.85 Mt at 3,519 ppm lithium (5.167 Mt LCE) and 275.85 Mt at 8,404 ppm Boron (2.318 Mt B), together with an inferred resource of 1,561.06 Mt at 3,085ppm lithium (25.634 Mt LCE). This base-case resource is based on a 1,800ppm lithium cutoff, constrained by hydraulic borehole mining (“HBHM”) parameters, and an assumed 60% recovery of the host strata.
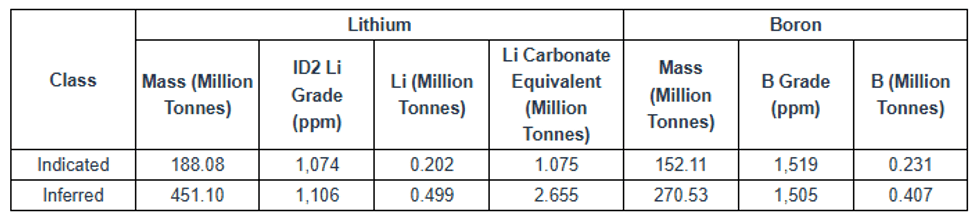
- The Upper Zone gives an indicated resource of 188.08 Mt at 1,074 ppm lithium (1.075 Mt LCE) and 152.11 Mt at 1,519 ppm boron (0.231 Mt B), together with an inferred resource of 451.10 Mt at 1,106 ppm lithium (2.655 Mt LCE) and 270.53 Mt at 1,505 ppm boron (0.407 Mt B). This resource is calculated at a 900 ppm lithium cut-off, within a constraining pit shell, and would be mined by conventional open-pit methods
- The 60% HBHM recovery is based purely on a cylindrical cavity and does not account for any improved recoveries from the expected plastic deformation of the deep zone material.
- The updated Mineral Resource Estimate will be included into ongoing work on an updated PEA expected for completion at the end of Q1 2025.
Join Stephen Rentschler, CEO of Nevada Lithium for a LIVE virtual event
to learn more about the Company’s findings and ask questions during the interactive Q&A.
Date and time: Tuesday, November 19th at 1 pm ET / 10 am PT
to learn more about the Company’s findings and ask questions during the interactive Q&A.
Date and time: Tuesday, November 19th at 1 pm ET / 10 am PT
Results and Interpretation
Bonnie Claire consists of a sedimentary package of volcaniclastic origin, laid down in a NW-SE basin striking basin. Lithium and boron mineralization are located within an Upper Zone, hosted within an upper claystone unit encountered by drilling from surface to about 425 ft (130m), and a Lower Zone, hosted within lower claystone and lower sandstone units intersected from 1,500-2,850ft (457-853m). Lithium mineralization appears to be hosted within non-swelling clay phases such as illite, or as lithium carbonate or salt within the sedimentary matrix. Boron mineralization appears to be associated with searlesite, a sodium borosilicate mineral.
While the Upper Zone and Lower Zones exhibit lithium and boron mineralization, they are separated spatially, and exhibit differences in metallurgical behaviour, leading the Company to treat them as two distinct deposits with different mining methods.
Lower Zone
While early exploration concentrated on mineralization in the Upper Zone, the Company has shifted its focus to mineralization in the Lower Zone, hosted in the lower claystone and sandstone units and containing the bulk of lithium and boron. This Lower Zone remains open to the NW, NE and SE. The current plan is to use an underground HBHM method, with a higher 1,800ppm cut-off. The Mineral Resource Estimate for the Lower Zone is presented in Table 1-1 and the sensitivity of the Lower Zone to cutoff grade is presented in Table 1-2.
Table 1-1: Bonnie Claire Lower Zone Mineral Resource Estimate With 60% Hydraulic Borehole Mining Recovery
- The effective date of the Mineral Resource Estimate is September 24, 2024.
- The Qualified Person (as such term is defined in NI 43-101) for the estimate is Terre Lane of GRE.
- Mineral resources are not mineral reserves and do not have demonstrated economic viability.
- Mineral resources are reported at an 1,800 ppm Li cutoff, an assumed lithium carbonate (Li2CO3) price of $20,000/tonne, 5.323 tonnes of Li2CO3 per tonne Li.
- Numbers in the table have been rounded to reflect the accuracy of the estimate and may not sum due to rounding.
Table 1-2: Bonnie Claire Lower Zone Resource Estimate Sensitivity to Cutoff Grade With 60% Hydraulic Borehole Mining Recovery
Upper Zone
The Upper Zone extends from surface to about 425ft (130m) depth and would be mined by conventional open-pit methods, reflected in a lower 900 ppm cutoff. The Mineral Resource Estimate for the Upper Zone is presented in Table 1-3, and the Upper Zone sensitivity to cutoff grade is presented in Table 1.4
Table 1-3: Bonnie Claire Upper Zone Mineral Resource Estimate Within a Constraining Pit Shell
- The effective date of the Mineral Resource Estimate is September 24, 2024.
- The Qualified Person for the estimate is Terre Lane of GRE.
- Mineral resources are not mineral reserves and do not have demonstrated economic viability.
- Mineral Resources are reported at a 900 ppm Li cutoff, an assumed lithium carbonate (Li2CO3) price of $20,000/tonne, 5.323 tonnes of Li2CO3 per tonne Li, 75% recovery, a slope angle of 18 degrees, no royalty, processing and general and administrative cost of $26.52/tonne, mining cost of $3.52/tonne, and selling costs of $100/tonne Li2CO3.
- Numbers in the table have been rounded to reflect the accuracy of the estimate and may not sum due to rounding.
Table 1.4: Bonnie Claire Upper Zone Resource Estimate Sensitivity to Cutoff Grade Within a Constraining Pit Shell
Cautionary Statements Regarding Mineral Resource Estimates:
Mineral resources are not mineral reserves and do not have demonstrated economic viability. There is no certainty that all or any part of the mineral resources will be converted into mineral reserves. Inferred mineral resources are that part of a mineral resource for which quantity and grade or quality are estimated on the basis of limited geological evidence and sampling. Geological evidence is sufficient to imply but not verify geological and grade or quality continuity. It is reasonably expected that the majority of inferred mineral resources could be upgraded to indicated mineral resources with continued exploration.
Resource Estimation Parameters
The updated Mineral Resource Estimate for Bonnie Claire was performed using Leapfrog® Geo and Leapfrog® Edge software. Leapfrog® Geo was used to update the geologic model, and Leapfrog® Edge was used for geostatistical analysis and grade modeling in the block model. An oblique view of the block model at Bonnie Claire is illustrated by Figure 1.1
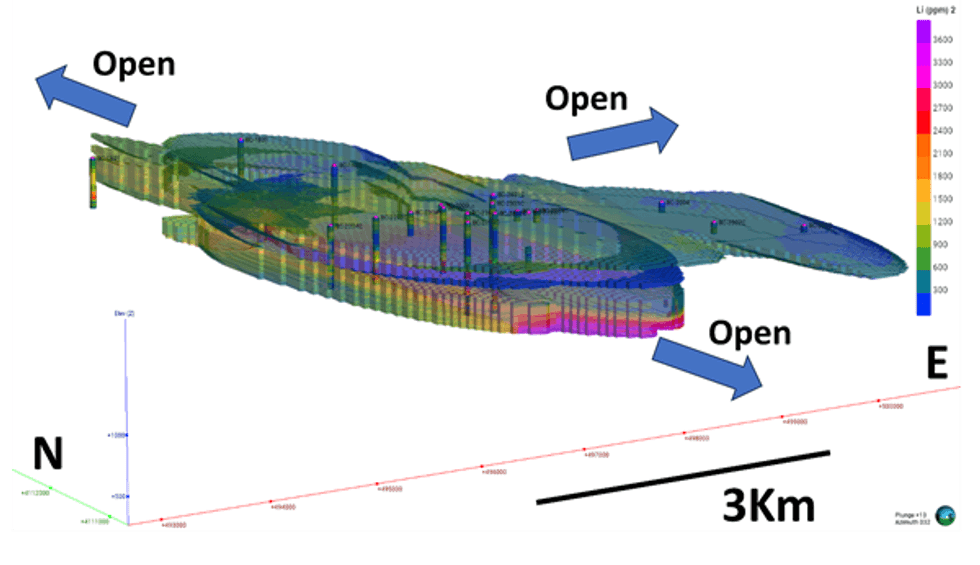
Figure 1.1: Oblique view from southwest of block model for Bonnie Claire generated by Leapfrog® Edge software. Lithium ppm legend to right.
The drill hole database used for the estimation included:
- 21 exploration drill holes, including 8 reverse circulation holes and 11 vertical diamond core holes
- 9,159.54 meters of drilling in exploration drill holes
- 1,898 assay intervals in exploration drill holes
- Minimum grade of 18 ppm Li in exploration drill holes
- Maximum grade of 7,160 ppm Li in exploration drill holes
Cumulative probability plots of lithium and boron assay values did not exhibit grade breaks that would indicate the presence of outlier data, so the data were not capped or clipped. A specific gravity of 1.7 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm3) for all lithological units, comparable to other similar lithium deposits. Drill hole assay values were composited to intervals of equal length to ensure that the samples used in statistical analysis and estimations were equally weighted. The majority of samples were collected at 6.096-meter (20-foot) intervals, with some samples collected at other intervals up to a maximum of 12.192 meters (40 feet). Down-the-hole composites were created from the Li and B assays within upper claystone, lower claystone, and lower sandstone mineralized domains, with the following specifications: 6.096-meter (20-foot) intervals, with anything less than 3.048 meters (10 feet) added to the previous interval. This resulted in 1,313 Li composite intervals with Li grades from 40.37 ppm to 5,764.48 ppm and 857 B composite intervals with B grades from 10 ppm to 14,658.8 ppm.
Qualified Person Terre Lane estimated Li and B grades into the block model using inverse distance to the second power (“ID2”) and for each method, a single pass was conducted at the ellipsoid ranges (1,600 meters x 900 meters x 150 meters). All blocks with modeled grade were coded as inferred resources. The search was restricted to a minimum of four samples and a maximum of 12 samples per block and a maximum of three samples per drill hole, thereby requiring data from a minimum of two drill holes to populate a block. For statistical comparison, nearest neighbor (“NN”) and ordinary kriging (“OK”) models were run to serve as comparisons with the estimated results from the ID2 method. The estimate means for the global population as well as the means for the estimation domains are similar, suggesting the ID2 estimate is not biased or overestimating the grades. The reduction in mean, coefficient of variation, and maximum from composites to the ID2 estimate shows an appropriate amount of smoothing. Swath plots and visual comparison of composites versus block model values by section and plan show good correlation.
Mining Methods
Hydraulic Borehole Mining of Lower Zone
As disclosed in their April 16, 2024, news release, Nevada Lithium contracted Kinley Exploration LLC (“Kinley”) to provide a preliminary evaluation of HBHM for Bonnie Claire.
Kinley was asked to establish a reasonable and economic mining strategy utilizing HBHM within the Bonnie Claire Lithium resource deposit to extract lithium in a continuous, efficient, cost effective and safe manner in the targeted higher grade zone from 1,500-2,800ft (457-853m) deep.
Kinley’s analysis took into consideration that the mineralization is highly plastic and with the assistance of jetting and pumping would likely flow. With this information, coupled with the significant cost of backfilling and then the consideration of subsidence, Kinley evaluated HBHM without backfilling and using directional drilling from a stable position.
The Kinley model assumed the highly mobile mineralization within the target section would behave plastically and flow in a fluid state or caving condition to the mining system intake. This relies on flow of the mobilized mineralization, accelerated by high pressure jetting to a centralized well, then pumped back to surface. GRE assumes a more conservative recovery of 60% because of potential mass flow issues that need to be evaluated during test mining.
Open Pit Mining of Upper Zone
Open pit mining of the Upper Zone at Bonnie Claire would likely use conventional mining equipment of hydraulic shovels and mining haul trucks but could possibly use scrapers. The soil is extremely soft and typically saturated. As a result, pit wall slopes would need to be relatively shallow; for the Lerchs-Grossman pit exercise in Section 14, the GRE Qualified Person used 18° side wall slopes. Additional geotechnical testing would need to be completed to determine stable side wall slope angles, bench heights, and catch bench widths. Dewatering portions of the pit, freezing, or other forms of stabilizing pit slopes and bottom may be required.
Mineral Processing and Metallurgical Testing
The mineral assemblage changes with depth. The Upper Zone generally shows lower grade lithium and boron and higher calcite content, while the Lower Zone tends to be significantly higher-grade lithium and boron and lower calcite content. The final mine design has not been completed, and the project may have several options: mine the upper portion, mine the lower portion, or mine the entire deposit. As a result, two distinct treatment options have been evaluated.
For the Upper Zone, a thermal treatment was developed that involved a sulfate calcination followed by a hot water leach. This process had the advantage of not solubilizing as many impurities, particularly iron. High lithium extractions (up to 80%) were achieved.
New drill samples from the Lower Zone were tested, and the calcination process was not effective due to the low melting point of the boron minerals (searlesite). Subsequently, sulfuric acid leaching was evaluated to treat the deeper deposit material. The acid treatment demonstrated that the lithium host is readily soluble in a strong sulfuric acid solution, achieving extractions of approximately 85%. The conventional downstream purification of the acid liquor had challenges for the upper sections of the deposit due to high iron solubilization.
Boron concentrations in the Lower Zone warrant a separate boron recovery circuit. Boron is recovered from the leach liquor after primary impurity removal via ion exchange to produce a boric acid product.
Quality Assurance / Quality Control
A quality assurance / quality control protocol following industry best practice was incorporated into the drill program by Nevada Lithium. Drilling was conducted by Major Drilling Group International Inc. (“Major Drilling”). Core was transported by Major Drilling from the collar location and received by Nevada Lithium staff at the Company storage facility in Beatty, Nevada. The facility is only accessible to Nevada Lithium staff and remains otherwise locked. Received core was logged and cut at the facility by Nevada Lithium staff. Logging and sampling included the systematic insertion of blanks, duplicates and certified reference material (“CRM”) MEG Li.10.12 and OREAS 750 into sample batches at an insertion rate of approximately 10%. All core samples collected were transported by Company staff to ALS USA Inc.’s laboratory in Reno, Nevada. for sample preparation. Sample preparation comprises initial weighing (Code WEI-21), crushing quality control test (CRU-QC), pulverizing quality control test (PUL-QC), fine crushing at 70% <2mm (CRU-31), sample split using Boyd rotary splitter ((SPL-22Y), pulverizing up to 250g 85% <75 µm (PUL-31), crush entire sample (CRU-21), pulp login (LOG-24) and a crusher wash (final crusher wash between samples (WSH-21). Samples were shipped to ALS USA Inc.’s Vancouver laboratory in Burnaby British Columbia, where the samples were analyzed using 48-element four-acid inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ME-MS61) and B/Li N₂O₂ fusion inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy high-grade (ME-ICP82b) procedures.
Data verification by GRE staff included: an on-site inspection of the Project site and core, reverse circulation and chip tray storage facilities, check sampling, geologic maps and reports, and manual auditing of the Project drill hole database. GRE’s Qualified Persons have been involved with the project since 2018. They visited the site in 2018 after drilling, during drilling in 2020 and 2022. The results from the site inspection, visual sample inspection and check sampling for each drilling campaign are given below. Based on the results of GRE’s Qualified Persons check of the sampling practices, verification of drill hole collars in the field, results of the check assay analysis, visual examination of selected core intervals, and the results of both manual and mechanical database audit efforts, GRE considers the collar, lithology, and assay data contained in the project database to be reasonably accurate and suitable for use in estimating mineral resources.
The data verification of the drilling campaigns shows that data from the rotary mud drilling was suspect and not used in the resource estimate. Open pit mining and processing methods, costs and infrastructure needs were verified by Ms. Lane in comparison to other similar sized open pit mines operating in the western USA. Borehole mining costs were developed by Kinley with coordination with GRE. Other cost data used in the report was sourced from the most recent infomine cost data report. All costs used to determine reasonable prospects for economic extraction were verified and reviewed by GRE and were assessed to be current and appropriate for use.
Metallurgical testing was completed for Bonnie Claire by a well-known commercial metallurgical laboratory. GRE reviewed all available metallurgical reports. GRE confirmed that the mineralization found at the Project is similar to another project where GRE has performed other consulting work and finds that the test work for Bonnie Claire shows that the material behaves in a similar manner, specifically in lithium extraction and recovery and reagent consumption. Given the similarities of the Bonnie Claire material to other similar projects, this provides a good basis for benchmarking the metallurgical test. The work appears to be professionally completed and is well documented and is suitable for estimation of lithium extraction and recovery calculations in the Mineral Resource Estimate.
About Nevada Lithium Resources Inc.
Nevada Lithium Resources Inc. is a mineral exploration and development company focused on shareholder value creation through its core asset, the Bonnie Claire Lithium Project, located in Nye County, Nevada, where it holds a 100% interest.
For further information on Nevada Lithium and to subscribe for updates about Nevada Lithium, please visit its website at: https://nevadalithium.com/
Qualified Person Disclosure
The technical information in the above disclosure has been reviewed and approved by the designated Qualified Person under NI 43-101, Dr. Jeff Wilson, PhD, P.Geo, Vice President of Exploration for Nevada Lithium. Dr. Wilson is not independent of Nevada Lithium, as he is Vice President of Exploration for Nevada Lithium.
The technical information in the above disclosure has also been reviewed and approved by Terre Lane, a ‘Qualified Person’ as defined under NI 43-101. Ms. Lane is Principal Mining Engineer with GRE and considered to be “independent” of the Company under Section 1.5 of NI 43-101.
On behalf of the Board of Directors of Nevada Lithium Resources Inc.
“Stephen Rentschler”
Stephen Rentschler, CEO
For further information, please contact:
Nevada Lithium Resources Inc.
Stephen Rentschler
CEO and Director
Phone: (647) 254-9795
E-mail: sr@nevadalithium.com
Media Inquiries
E-mail: info@nevadalithium.com
Find Nevada Lithium on Twitter and LinkedIn
The Canadian Securities Exchange does not accept responsibility for the adequacy or accuracy of this news release. The Canadian Securities Exchange has not approved or disapproved of the contents of this news release.
Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements
This news release contains forward-looking statements and forward-looking information (collectively, “forward-looking statements”) within the meaning of applicable Canadian securities legislation. These statements relate to matters that identify future events or future performance. Often, but not always, forward looking information can be identified by words such as “could”, “pro forma”, “plans”, “expects”, “may”, “will”, “should”, “budget”, “scheduled”, “estimates”, “forecasts”, “intends”, “anticipates”, “believes”, “potential” or variations of such words including negative variations thereof, and phrases that refer to certain actions, events or results that may, could, would, might or will occur or be taken or achieved.
The forward-looking statements contained herein include, but are not limited to, statements regarding: the performance of the Project; results of the 2023 Exploration and Development Plan (including, without limitation, its mineral resources, current claims and its ability to utilize global lithium needs); any plans following the Mineral Resource Estimate; the preparation of an updated PEA in 2025; and the performance of lithium as a commodity, including the sustained lithium demand and prices.
In making the forward looking statements in this news release, Nevada Lithium has applied several material assumptions, including without limitation: market fundamentals that result in sustained lithium demand and prices; the receipt of any necessary permits, licenses and regulatory approvals in connection with the future development of Bonnie Claire in a timely manner; the availability of financing on suitable terms for the development; construction and continued operation of Bonnie Claire; the Project containing mineral resources; and Nevada Lithium’s ability to comply with all applicable regulations and laws, including environmental, health and safety laws.
Investors are cautioned that forward-looking statements are not based on historical facts but instead reflect Nevada Lithium’s management’s expectations, estimates or projections concerning future results or events based on the opinions, assumptions and estimates of managements considered reasonable at the date the statements are made. Although Nevada Lithium believes that the expectations reflected in such forward- looking statements are reasonable, such information involves risks and uncertainties, and under reliance should not be placed on such information, as unknown or unpredictable factors could have material adverse effects on future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by Nevada Lithium. Among the key risk factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those projected in the forward- looking statements are the following: operating and technical difficulties in connection with mineral exploration and development and mine development activities at the Project; estimation or realization of mineral reserves and mineral resources, requirements for additional capital; future prices of precious metals and lithium; changes in general economic, business and political conditions, including changes in the financial markets and in the demand and market price for commodities; possible variations in ore grade or recovery rates; possible failures of plants, equipment or processes to operate as anticipated; accidents, labour disputes and other risks of the mining industry; delays or the inability of Nevada Lithium to obtain any necessary approvals, permits, consents or authorizations, financing or other planned activities; changes in laws, regulations and policies affecting mining operations; currency fluctuations, title disputes or claims limitations on insurance coverage and the timing and possible outcome of pending litigation, environmental issues and liabilities; risks relating to epidemics or pandemics such as COVID-19, including the impact of COVID-19 on Nevada Lithium’s business; as well as those factors discussed under the heading “Risk Factors” in Nevada Lithium’s latest Management Discussion and Analysis and other filings of Nevada Lithium filed with the Canadian securities authorities, copies of which can be found under Nevada Lithium’s profile on the SEDAR+ at www.sedarplus.ca.
Should one or more of these risks or uncertainties materialized, or should assumptions underlying the forward-looking statements prove incorrect, actual results may vary materially from those described herein as intended, planned, anticipated, believed, estimated or expected. Although Nevada Lithium has attempted to identify important risks, uncertainties and factors which could cause actual results to differ materially, there may be others that cause results not to be as anticipated, estimated or intended. Nevada Lithium does not intend, and does not assume any obligation, to update this forward-looking information except as otherwise required by applicable law.
NVLH:CC
The Conversation (0)
19h
Albemarle Lifts Lithium Demand Forecast as Energy Storage Surges
Albemarle (NYSE:ALB) is raising its long-term lithium demand outlook after a breakout year for stationary energy storage, underscoring a shift in the battery materials market that is no longer driven solely by electric vehicles.The US-based lithium major reported fourth quarter 2025 net sales of... Keep Reading...
21 January
Official signing of the Portuguese State Grant
Savannah joins other grant recipient companies at official signing ceremony
Savannah Resources Plc, the developer of the Barroso Lithium Project in Portugal, a 'Strategic Project' under the European Critical Raw Materials Act and Europe's largest spodumene lithium deposit (the 'Project'), was delighted to join with other recipients of State grants yesterday at the... Keep Reading...
21 January
Excellent Results from 2025 Core Drilling Program at McDermitt
Jindalee Lithium Limited (Jindalee, or the Company; ASX: JLL, OTCQX: JNDAF) is pleased to report assay results from the drilling program at the McDermitt Lithium Project completed late 2025. All holes returned strong lithium and magnesium intercepts from shallow depths, including:R92: 36.5m @... Keep Reading...
08 January
Top 5 US Lithium Stocks (Updated January 2026)
The global lithium market enters 2026 after a punishing 2025 marked by oversupply, weaker-than-expected EV demand and sustained price pressure, although things began turning around for lithium stocks in Q4. Lithium carbonate prices in North Asia fell to four-year lows early in the year,... Keep Reading...
07 January
5 Best-performing ASX Lithium Stocks (Updated January 2026)
Global demand for lithium presents a significant opportunity for Australia and Australian lithium companies.Australia remains the world’s largest lithium miner, supplying nearly 30 percent of global output in 2024, though its dominance is easing as other lithium-producing countries such as... Keep Reading...
05 January
CEOL Application for Laguna Verde Submitted
CleanTech Lithium PLC ("CleanTech Lithium" or "CleanTech" or the "Company") (AIM: CTL, Frankfurt:T2N), an exploration and development company advancing sustainable lithium projects in Chile, is pleased to announce it has submitted its application (the "Application") for a Special Lithium... Keep Reading...
Latest News
Interactive Chart
Latest Press Releases
Related News
TOP STOCKS
American Battery4.030.24
Aion Therapeutic0.10-0.01
Cybin Corp2.140.00