December 03, 2024
S2 Resources Ltd (“S2” or the “Company”) advises that it has signed an earn-in agreement with Valkea Resources (“Valkea”, formerly Outback Goldfields Corp, TSXV:OZ) as per the terms agreed as part of the recently completed sale of S2’s Finnish assets to Valkea1.
Key Points
- S2 finalises earn-in terms for three Victorian gold projects from Valkea Resources (formerly Outback Goldfields)
- These projects were offered to S2 by Valkea as part of the sale of S2’s Finnish assets to Valkea
- This spreads S2’s gold exploration footprint in Victoria, supplementing its ground holdings around the prolific Fosterville gold mine owned by Agnico Eagle
- These projects have defined soil and aircore drilling anomalies requiring follow up
Under the terms of this agreement, S2 has the right to earn an 80% interest in three projects by sole funding a total expenditure of $1.2 million within 4 years. The agreement is subject to Valkea obtaining the approval of the TSX Venture exchange and also receiving Ministerial approval and registration under section 71 of the Mineral Resources (Sustainable Development) Act 1990 in Victoria, Australia.
The four year earnin period is deemed to start once the above conditions have been met. S2 can withdraw from any or all of the projects at any time providing the tenements are in good standing on a pro-rata expenditure commitment basis for a minimum of three months from the date of its withdrawal notice. In the event of S2 being unable to undertake exploration as a consequence of land access or permitting delays or restrictions outside of its reasonable control, then S2 will be entitled to a fair and reasonable extension to the earn-in term.
Should S2 complete its earnin, Valkea can elect to contribute its share of expenditure or dilute. In the latter circumstance, should Valkea’s participating interest decrease to less than 10% it will revert to a 2% Net Smelter Return (NSR) royalty, which S2 can buy back for C$1.5 million at any time.
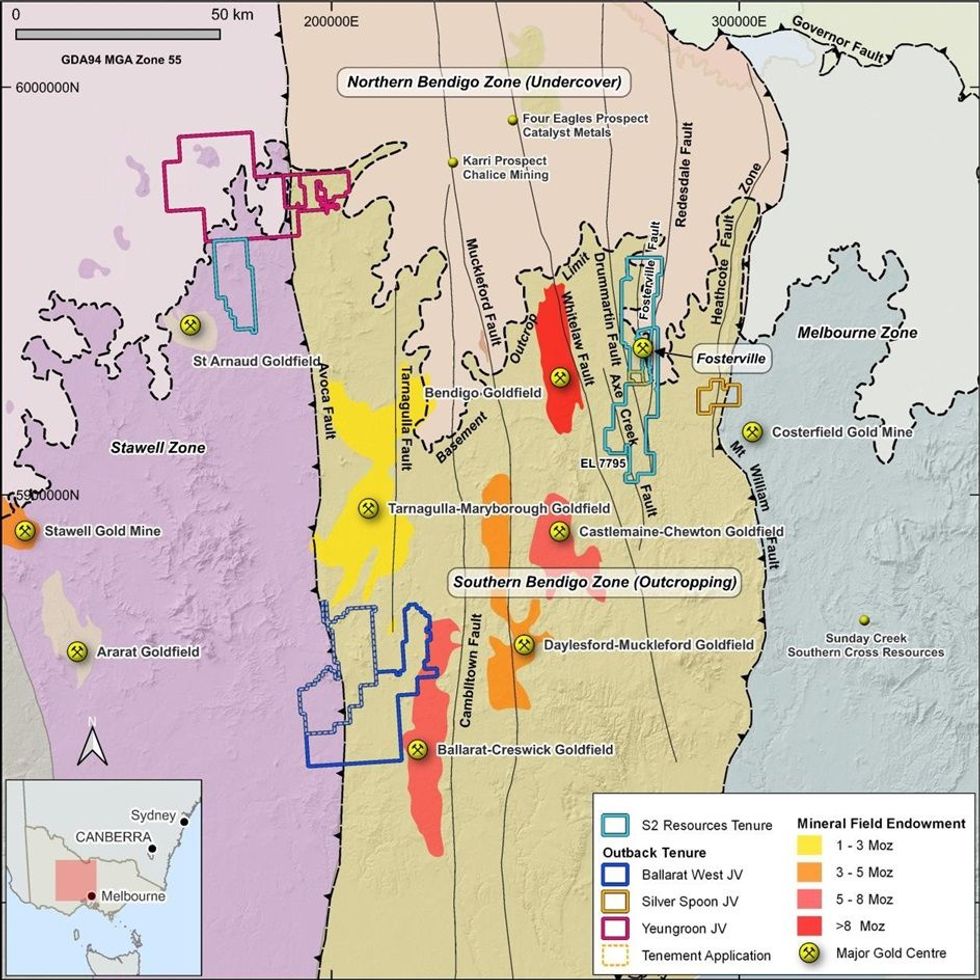
The three projects comprise the Silverspoon, Yeungroon and Ballarat West exploration projects, which are all located in the central Victorian Goldfields (see Figure 1) and which provide the Company with a variety of gold exploration options, as summarised below.
Yeungroon
The Yeungroon project covers an area of 728 square kilometres near Charlton and Wedderburn in north central Victoria, and comprises three granted exploration licences (EL6897, EL7280 and EL7701). The project area straddles the Avoca Fault, which is the major crustal boundary between the Bendigo Zone (to the east) and the Stawell Zone (to the west). Previous soil sampling and reconnaissance aircore drilling undertaken by Valkea has defined several district-scale gold-arsenic anomalies that require follow up (see Figure 2).
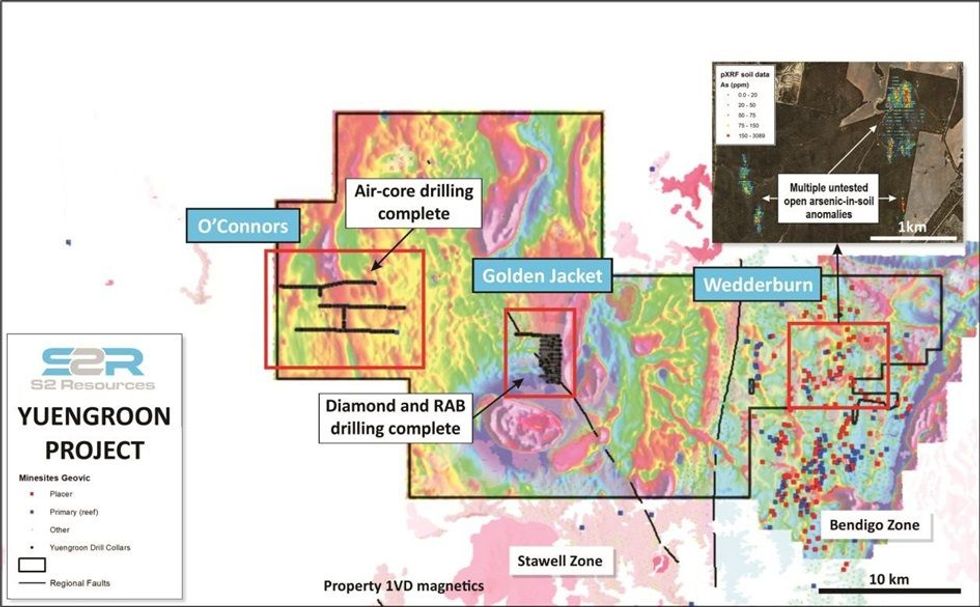
The O’Connors anomaly, located within the Stawell Zone, is a 3 kilometre long zone of north- northwest striking strong arsenic-gold anomalism that is open along strike in both directions and is coincident with the O’Connors fault zone. The anomalism intersected in the shallow aircore drilling is comparable with alteration haloes observed at other central Victorian gold systems and the drilling to date may have intersected the low-grade haloes proximal to the high-grade bearing quartz reef lodes.
In addition to the O’Connors trend, the aircore drilling is has intersected a number of other zones, which may represent sub-parallel mineralised structures.
Follow-up bedrock drilling is required to test for the presence of high grade lodes within the mineralised system.
The Golden Jacket anomaly, defined in top of bedrock RAB/aircore drilling, is a strong, broad arsenic anomaly that extends at least 600 metres southwest of the historic Golden Jacket Mine. Drilling to date has intersected low-level gold associated with the arsenic anomaly. Anomalous gold values intersected extend approximately 800 metres south of the mine, indicating the potential for a system with significant strike potential.
In addition, drilling has defined several parallel northwest striking trends of strong arsenic (with anomalous gold) to the north of the of the Golden Jacket mine. Deeper drilling is warranted to test for high-grade, structurally controlled quartz reefs associated with the anomalous top-of bedrock sampling.
Click here for the full ASX Release
This article includes content from S2 Resources Ltd, licensed for the purpose of publishing on Investing News Australia. This article does not constitute financial product advice. It is your responsibility to perform proper due diligence before acting upon any information provided here. Please refer to our full disclaimer here.
The Conversation (0)
18h
Aurum Hits High-Grade Gold at Napie, Cote d'Ivoire
Aurum Resources (AUE:AU) has announced Aurum Hits High-Grade Gold at Napie, Cote d'IvoireDownload the PDF here. Keep Reading...
19h
Precious Metals Price Update: Gold, Silver, PGMs Fall on Escalating US-Iran War
Precious metals prices are down on potential for economic fallout from escalating US-Iran War.Volatility has returned to the precious metals market this past week. All eyes are on the breakout of a full-scale war across the Middle East prompted by a coordinated assault on Iran by the United... Keep Reading...
04 March
SSR Mining to Sell Çöpler Gold Mine Stake in US$1.5 Billion Deal
SSR Mining (NASDAQ:SSRM,TSX:SSRM,OTCPL:SSRGF) has agreed to sell its majority stake in the Çöpler gold mine in Turkey for US$1.5 billion in cash, shifting the company’s portfolio towards the Americas as the yellow metal continues to surge amid rising geopolitical tensions.The Denver-based miner... Keep Reading...
04 March
Blackrock Silver Announces the Appointment of Bernard Poznanski and Susan Mathieu to the Board of Directors
Blackrock Silver Corp. (TSXV: BRC,OTC:BKRRF) (OTCQX: BKRRF) (FSE: AHZ0) ("Blackrock" or the "Company") is pleased to announce the appointment of Bernard Poznanski and Susan Mathieu as independent directors to the Board of Directors of the Company (the "Board of Directors").In conjunction with... Keep Reading...
03 March
Fortune Bay: Exploration Underway, Fully Funded Program at the Goldfields Project in Saskatchewan
While Saskatchewan has long been recognized for uranium, its geology and historical exploration also make it a promising place for gold. Canadian company Fortune Bay (TSXV:FOR,OTCQB:FTBYF) seeks to maximize this potential with its flagship Goldfields project. Fortune Bay’s 100 percent owned... Keep Reading...
03 March
RUA GOLD Files 43-101 Technical Reports for the Reefton and Glamorgan Projects in New Zealand
Rua Gold INC. (TSX: RUA,OTC:NZAUF) (NZX: RGI) (OTCQX: NZAUF) ("Rua Gold" or the "Company") is pleased to announce the filing on SEDAR+ of independent Technical Reports for its Reefton Project ("Reefton Technical Report") on the South Island and Glamorgan Project ("Glamorgan Technical Report") on... Keep Reading...
Latest News
Interactive Chart
Latest Press Releases
Related News
TOP STOCKS
American Battery4.030.24
Aion Therapeutic0.10-0.01
Cybin Corp2.140.00





