- WORLD EDITIONAustraliaNorth AmericaWorld
May 30, 2024
Gladiator Resources (ASX:GLA) focuses on uranium assets covering 1,811 square kilometres located in Tanzania. The company’s key projects include – Mkuju, Minjingu, Liwale, Foxy and Eland. The flagship Mkuju has the potential to host world-class uranium deposits given its proximity to the Nyota deposit, which contains 124.6 million pounds (Mlbs) U3O8. Nyota is regarded as one of the largest uranium deposits in the world.
The company is planning a 2024 drill program at Mkuju focusing on the South West Corner (SWC), Mtonya and Likuyu North targets. The 2024 drilling program will commence with initial core drilling at the SWC target, where 2023 trenching revealed up to 7,139 parts per million (ppm) U3O8. Drilling at Mtonya and Likuyu North aims to explore potential extensions and new zones of the existing uranium deposits.
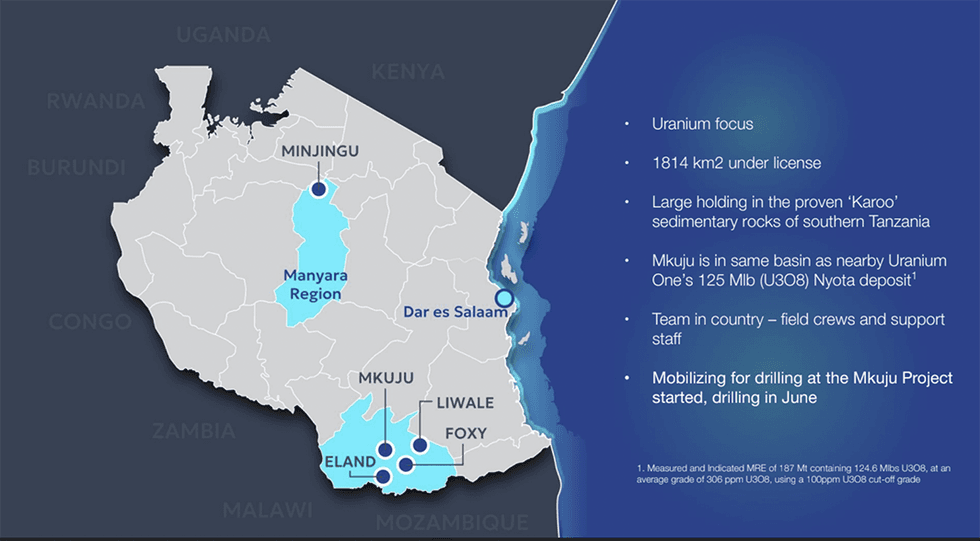
The Mkuju project spans over 725 sq kms and is located 20 kms south of Uranium One’s Nyota deposit, regarded as one of the largest uranium deposits in the world. Nyota hosts a measured and indicated mineral resource estimate of 187 metric tons (MT) at 306 ppm U3O8, containing 124.6 Mlbs U3O8. The deposit is being developed by global uranium company Uranium One. The Nyota deposit and the Mkuju project are underlain by sediments of the lower Karoo, which are considered highly prospective for uranium.
Company Highlights
- Gladiator Resources is an ASX-listed exploration and mining company focused on uranium. The company operates eight exploration projects, mainly in Tanzania, covering a total area of 1,811 sq kms.
- The company’s key projects include – Mkuju, Minjingu, Liwale, Foxy and Eland.
- Gladiator’s primary short term focus is on advancing the Mkuju project, located only 20 kms south of Uranium One’s Nyota deposit, regarded as one of the largest uranium deposits in the world.
- The 2024 drill program at Mkuju will focus on the South West Corner (SWC) initially, where trench assay results received Dec/Jan 2023/24 confirmed high-grade uranium in sandstone, 1000’s ppm U3O8 in places.
- Further work is also planned at Mtonya and Likuyu North – also located within the promising Mkuju area.
- Tanzania is endowed with many uranium-bearing deposits and is known for its mining-friendly policies. The government offers attractive tax policies and quick permitting processes to encourage investment in the sector.
- The presence in relatively attractive uranium mining jurisdictions such as Tanzania positions the company to capitalize on opportunities in the uranium sector and deliver superior returns to its shareholders.
This Gladiator Resources profile is part of a paid investor education campaign.*
Click here to connect with Gladiator Resources (ASX:GLA) to receive an Investor Presentation
GLA:AU
The Conversation (0)
29 May 2024
Gladiator Resources
Capitalizing on the uranium momentum with prolific assets in Tanzania
Capitalizing on the uranium momentum with prolific assets in Tanzania Keep Reading...
04 March
Cameco Signs US$2.6 Billion Uranium Deal With India to Fuel Nuclear Expansion
Cameco (TSX:CCO,NYSE:CCJ) has secured a nine-year uranium supply agreement with India worth an estimated US$2.6 billion, accelerating its nuclear power expansion as it deepens critical mineral ties with the country.The Saskatoon-based uranium producer will supply nearly 22 million pounds of... Keep Reading...
26 February
Definitive Agreement for the Sale of the Marshall Project
Basin Energy (BSN:AU) has announced Definitive agreement for the sale of the Marshall projectDownload the PDF here. Keep Reading...
26 February
Denison Greenlights First Major Canadian Uranium Mine in 20 Years
Denison Mines (TSX:DML,NYSEAMERICAN:DNN) has approved construction of what it says will be Canada’s first new large-scale uranium mine in more than 20 years, setting the stage for work to begin next month at its flagship Phoenix project in northern Saskatchewan.The company announced that its... Keep Reading...
25 February
Uranium American Resources
Uranium American Resources Inc. is a mining company. The Company maintains mining leases on properties in Nevada. The Company is engaged in mining activities in the mineable resource of gold and silver remains in the Comstock Mining District. Its Comstock project is located in northwestern... Keep Reading...
25 February
US Nuclear Growth at Risk as Enrichment Supply Gap Looms
A looming shortage of uranium enrichment services could threaten US nuclear expansion plans, according to the leader of Centrus Energy (NYSE:LEU), one of the country’s largest suppliers of enriched uranium.Amir Vexler, president and CEO of Centrus, is warning that rising demand from existing... Keep Reading...
24 February
Eagle Energy Metals and Spring Valley Acquisition Corp. II Announce Closing of Business Combination
Eagle Energy Metals Corp. (“Eagle”), a next-generation nuclear energy company with rights to the largest conventional, measured and indicated uranium deposit in the United States, today announced that it has completed its business combination with Spring Valley Acquisition Corp. II (OTC: SVIIF)... Keep Reading...
Latest News
Interactive Chart
Latest Press Releases
Related News
TOP STOCKS
American Battery4.030.24
Aion Therapeutic0.10-0.01
Cybin Corp2.140.00