
November 17, 2024
Landmark Belfast facility backed by UK Government shows strong returns and supply chain engagement
Ionic Rare Earths Limited (“IonicRE” or the “Company”) (ASX: IXR) wholly owned subsidiary Ionic Technologies is on track for the development of a unique commercial REO manufacturing facility in Belfast, UK, following the successful completion of a Feasibility Study that demonstrates both strong financial returns and environmental sustainability. The study positions Ionic Technologies as the ‘first mover’ in the development of a sustainable, traceable and sovereign UK/Europe supply chain, meeting the demands of the net-zero transition, advanced manufacturing and defence.
- Feasibility Study shows strong potential for profitable and unique commercial Rare Earth Oxide (REO) manufacturing facility in Belfast, UK, recycling pre- consumer rare earth magnet scrap and end-of-life (EOL) magnets and delivering sovereign capability to the UK;
- Key study outcomes:
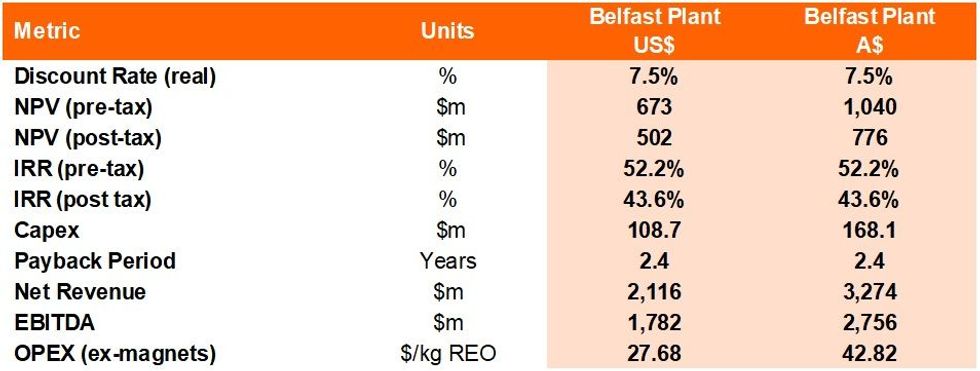
- NPV7.5 (post tax) of US$502m (A$776m, A$ = US$0.65);
- IRR (post tax) of 43.6%;
- Net revenue US$2.12b (A$3.26b);
- EDITDA US$1.78b (A$2.76b);
- Capital payback of 2.4 years, based on throughput of 1,200 tonnes per annum (tpa) of feed with production capacity of 400 tpa of separated magnet rare earth oxides (REO) over 20-year life of operation;
- IonicRE is progressing site permitting, with construction planned to be completed late 2026, delivering sovereign magnet REO for Western customers from early 2027; and
- Ionic Technologies set to submit application for a significant capital grant from the UK Government via the Automotive Transformation Fund (ATF), administered by the Advanced Propulsion Centre (APC), for automotive manufacturing and sovereign rare earth supply chain.
Commenting on the study, IonicRE’s Managing Director, Tim Harrison said: “The completion of this Feasibility Study is a major milestone in our Company’s development of a Western rare earths supply chain, initially centred on Belfast, UK. I congratulate our team at Ionic Technologies and all our partners for these outstanding results.
“The study confirms that the commercial case for magnet recycling is compelling, complementing the clear environmental and sustainability benefits, as well as the imminent need for REE production outside of China. Financially, this represents a low capital risk pathway to sovereign magnet REO production compared to alternative sources, offering strong financial returns based on a ‘circular economy’ model of sustainable production, backed by the UK Government and our project partners.
“Even at today’s REO spot prices, this study indicates a viable, positive NPV business due to our unique low cost, patented recycling process for separating magnet rare earths without requiring mining. Now that we have successfully delivered on this UK-Government supported study, we anticipate significant strategic and investor interest owing to the potential for the development to underpin UK and European net-zero ambitions, create supply certainty, reduce exposure to cost fluctuations and promote regional growth within the UK.
“The Company also intends to utilise this study to progress further opportunities in target markets – the US, Europe, Brazil and Asia – where we expect further improvement on the economics.
“We are now moving to secure feedstock and offtake agreements, enabling Ionic Technologies to capitalise on its leading market position and technical capability to deliver benefits for all stakeholders. With more than 50% of the global production of NdFeB magnets consumed for decades in the West, a sizeable inventory of material is available to recycle back into new supply chains now.”
Table 1 below highlights the Belfast facility’s positive projected financial returns.
Designed for a brownfield site located in Belfast Harbour, the planned commercial-scale plant would represent a 40-fold increase in production capacity (400 tpa) from the Demonstration Plant (10 tpa). The process design is modular, with the plant comprising of two 200 tpa production lines, allowing for scale-up flexibility and parallel REO separation activity.
The completion of the Feasibility Study, and ongoing completion of the FEED Study allows prioritisation of commercial offtake agreements for high purity, separated magnet REO products – didymium oxide ((NdPr)2O3), dysprosium oxide (Dy2O3) and terbium oxide (Tb4O7). Additionally, functionality for separated neodymium oxide (Nd2O3) and praseodymium oxide (Pr6O11) is also under further investigation driven by appetite in several industries beyond the magnet supply chain.
Given the nature of the design, and the potential to quickly replicate capacity in other target markets, a bare module cost has been developed independent of additional site-specific costs in Belfast. The study reflects a 20-year operational life for the Belfast magnet recycling facility.
Click here for the full ASX Release
This article includes content from Ionic Rare Earths, licensed for the purpose of publishing on Investing News Australia. This article does not constitute financial product advice. It is your responsibility to perform proper due diligence before acting upon any information provided here. Please refer to our full disclaimer here.
IXR:AU
The Conversation (0)
14 September 2023
Ionic Rare Earths
Low Capital Operations With the Potential for High Margins
Low Capital Operations With the Potential for High Margins Keep Reading...
Latest News
Interactive Chart
Latest Press Releases
Related News
TOP STOCKS
American Battery4.030.24
Aion Therapeutic0.10-0.01
Cybin Corp2.140.00
