November 05, 2024
CleanTech Lithium PLC (AIM: CTL, Frankfurt:T2N, OTCQX:CTLHF), an exploration and development company advancing sustainable lithium projects in Chile, provides an operational update on progress with the Laguna Verde pre-feasibility study ("PFS"), the 2024 exploration programme and Direct Lithium Extraction ("DLE") pilot plant process work to produce battery-grade lithium carbonate.
Highlights:
Laguna Verde PFS Update
- Location of preferred sites for carbonation plant in Copiapó and port facilities for export of final lithium carbonate product have been selected
- Power supply study completed evaluating options for onsite renewables which provides a competitive alternative to the base case of a transmission line and grid connection
- Option to utilise electric truck transport identified, lowers emissions and noise pollution, and by hauling from high to low altitude regenerative charging reduces power consumption
- Decision to configure project based on locating DLE plant at Laguna Verde and carbonation plant in Copiapó has numerous advantages contributing to a more robust PFS
- Engineering for this configuration has extended the expected PFS delivery to Q1 2025
Exploration Programme and Pilot Plant Updates
- Results from two completed wells and pump tests for the 2024 field programme have been received increasing knowledge of the resource and providing additional information for the hydrogeological model
- Downstream processing work from our pilot plant is progressing well with lithium carbonate production expected in November
Investor webinar
- CTL to host investor webinar on Tuesday 5th November at 17:00 GMT. Register here: https://www.investormeetcompany.com/cleantech-lithium-plc/register
Steve Kesler, Executive Chairman and Interim Chief Executive Officer, CleanTech Lithium PLC, said:
"With the recent announcement by the Chilean Government to prioritise six salt flats, including Laguna Verde, to start the process of awarding Special Operating Lithium Contracts (CEOLs), we are focused on the key aspects to advance the project, being permitting, completion of the PFS and production of battery grade lithium carbonate from our pilot plant.
Progress has continued on central elements of the PFS with evaluation of plant location, power supply and transport options. As a leader in developing DLE based projects in Chile, we aim to enter production in 2027 when the lithium market is expected to rebalance, providing a strong long term growth outlook."
Further Information
Sites Selected for Carbonation Plant and Port for Export of Final Product
As part of the ongoing PFS for the Laguna Verde project, a trade-off analysis was completed which determined the DLE plant and eluate concentration stages should be located at the Laguna Verde site, and the carbonation plant at the nearby mining centre of Copiapó. This was reported to the market on July 2, 2024. The re-configuration required a change in pre-engineering design provided by Lanshen Technology, the Company selected to provide the lithium processing plant design and equipment. This has extended the expected PFS completion, which was originally targeted for Q4 2024, into Q1 2025.
The Company has since undertaken studies to determine the ideal location of the carbonation plant in Copiapó and selected a site. After evaluating several options, a site in an industrial zone which by-passes to the south-east of Copiapó was chosen, as shown in Figure 1. This location has existing power and water supply options and provides a direct route to port.
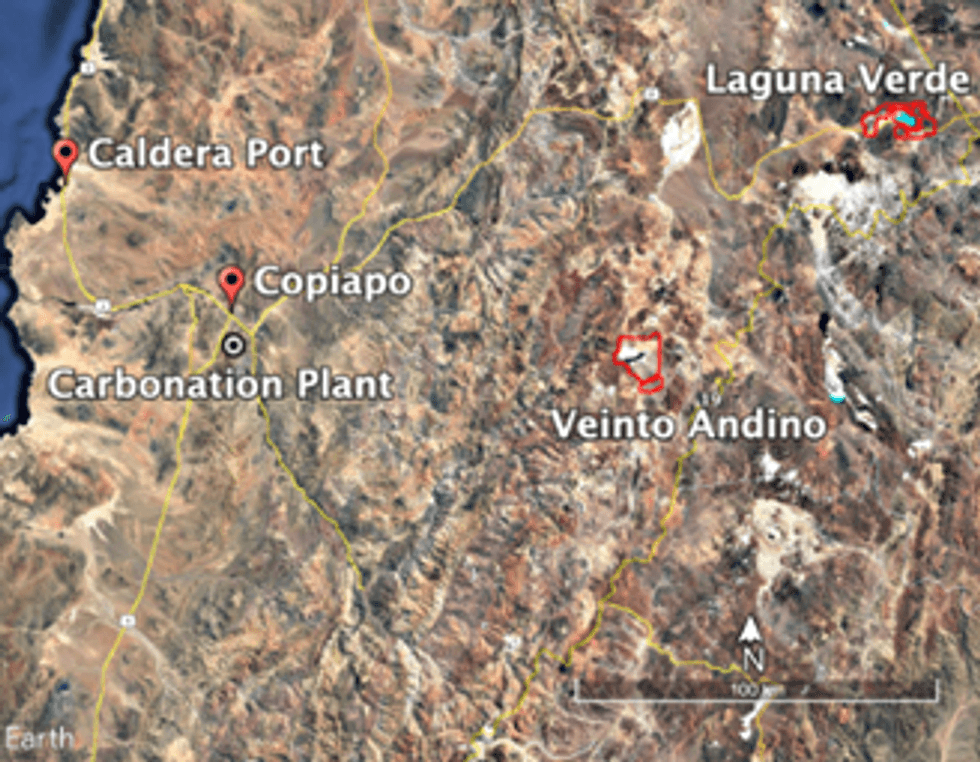
Figure 1: Carbonation Plant Location Map
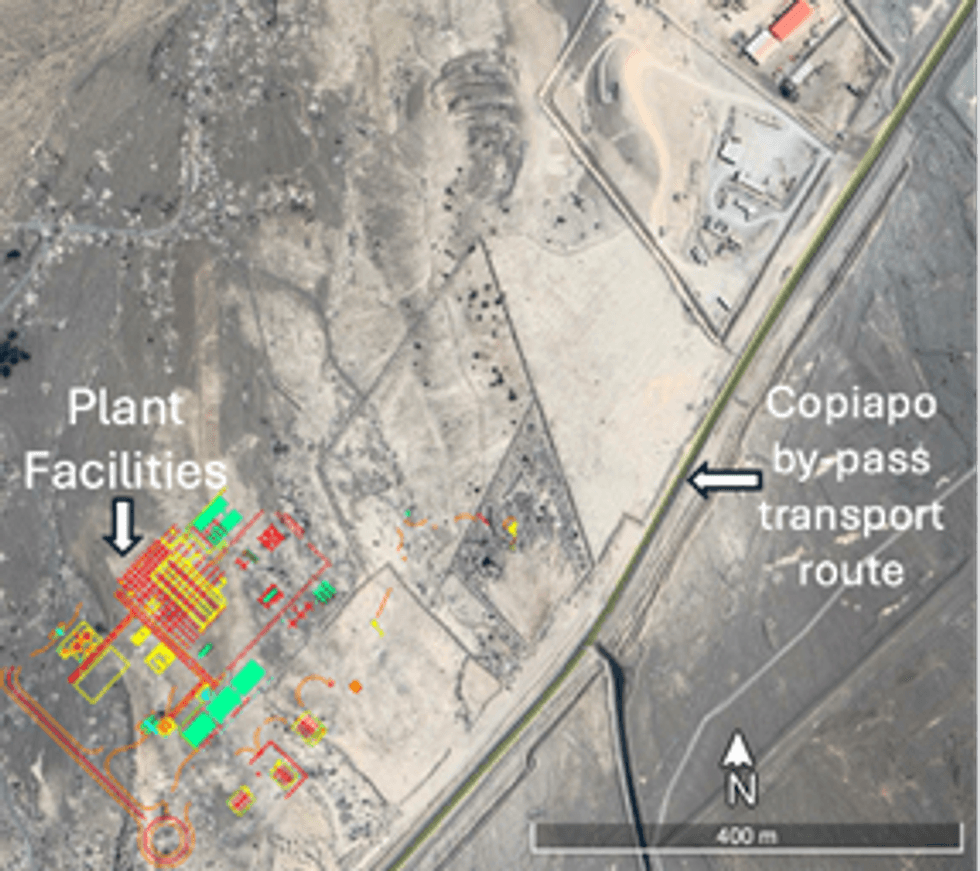
Figure 2: Carbonation Plant Design Layout
A trade-off analysis was undertaken to evaluate transport corridors and port facilities providing four different options for export of final lithium product. The study indicated that the nearby Caldera Port provides the most suitable option either utilising existing infrastructure which is currently utilised for seasonal shipment of agricultural products, shown in Figure 3. Other port options are also available and may come into consideration however Caldera Port is the current preference.
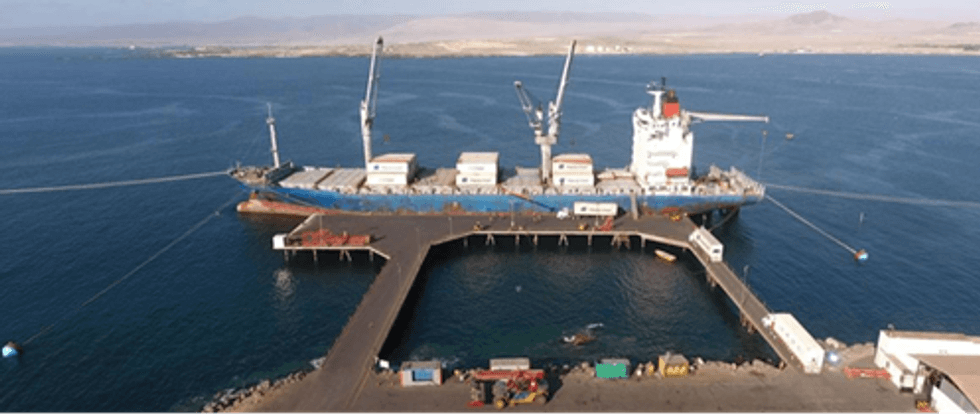

Figure 3: Caldera Port Existing Facilities
Power Supply Alternative of Onsite Renewable Generation
The Company engaged Chilean consultant Clean Power Hunters to undertake a power supply study to evaluate the option of using renewable power generated at the project site as an alternative to the base case of a transmission line and grid connection. Laguna Verde is located in the region with the highest solar irradiance in the world, as shown in Figure 4. Analysis of estimated Capex and Opex was provided based on different configurations of onsite renewables, either solar plus a battery energy storage system (BESS) or solar plus wind plus BESS. Figure 5 shows the lowest Capex corresponds to combining solar with three wind turbines plus BESS.
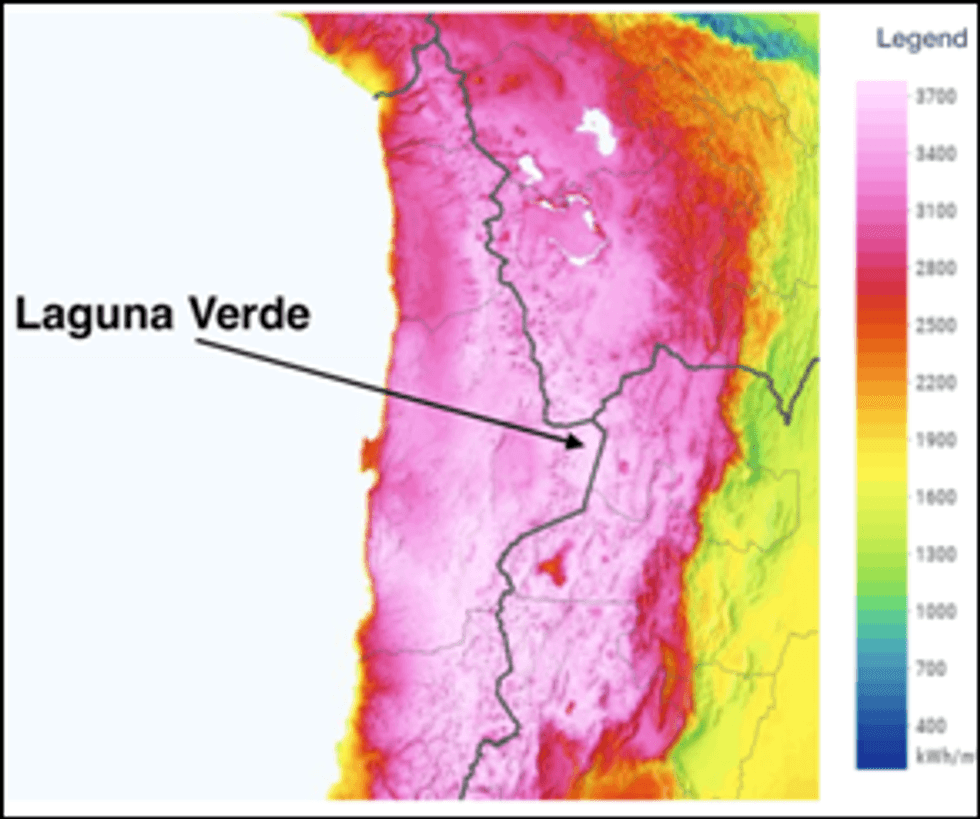
Figure 4: Solar Irradiance Map
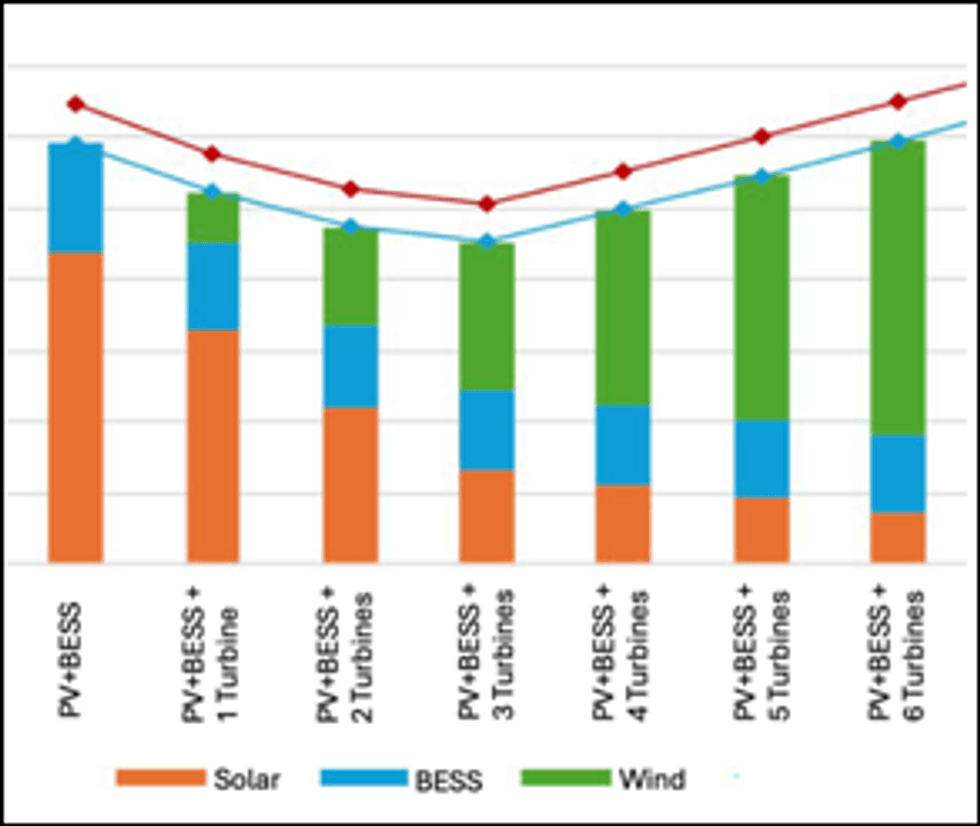
Figure. 5: Solar + Wind + BESS Scenarios Capex Split
The Company has received proposals including from major global solar plus BESS suppliers, consistent with the costs estimated in the study and competitive with the grid connection option. The financing model for both the grid connection model or the alternative of onsite renewables is expected to be based on a power purchase agreement and a build own operate basis by established suppliers. These proposals will be built into the PFS and the commercial analysis of the project.
Truck Transport Study
Based on the outcome of the plant location study the Company will transport 6% Li in solution post the DLE and concentration stages at Laguna Verde to the carbonation plant. Use of standard and electric trucks is being compared with the latter providing several potential benefits in addition to cutting CO2 emissions. Electric trucks are well suited to hauling loads from high to low altitudes by taking advantage of regenerative charging to reduce power consumption and required battery capacity. Minimal noise and elimination of tailpipe emissions is particularly attractive considering the transport route traverses an indigenous community settlement approximately 100km from the project site, a community the company has been working with closely.
The Company has gathered insight from several potential suppliers. Chinese company XCMG is a leader in electric trucks and is actively expanding its offering in Chile, with its E7-49T model which has a haulage load of 49 tonnes potentially providing a suitable option. The technology is evolving rapidly and is expected to provide a strongly cost competitive option in line with the project development timeline.

Figure. 6: XCMG´s range of electric transport trucks

Figure. 7: Paved Highway to Laguna Verde
2024 Exploration Programme Update
CleanTech Lithium´s 2024 drilling programme anticipated to drill five new resource wells, as shown in Figure 8, with the aim of upgrading the existing Measured and Indicated resource into maiden Reserves for the Laguna Verde project. The existing JORC compliant resource estimate of 1.8 million tonnes of lithium carbonate equivalent (LCE) is based on six wells completed in 2022 and 2023. The Company engaged Montgomery & Associates Consultores Limitada ("Montgomery" or "M&A"), a leading hydrogeological consultant, for the programme. During 1H 2024, two of the five resource wells were completed being LV07 and LV11, along with three observation wells drilled to support observations during pumping tests, before winter conditions curtailed the programme in June 2024. The full 2024 programme is paused until further funding is available following the Company´s planned ASX fund raising and as a result Montgomery has produced an interim report on work completed.
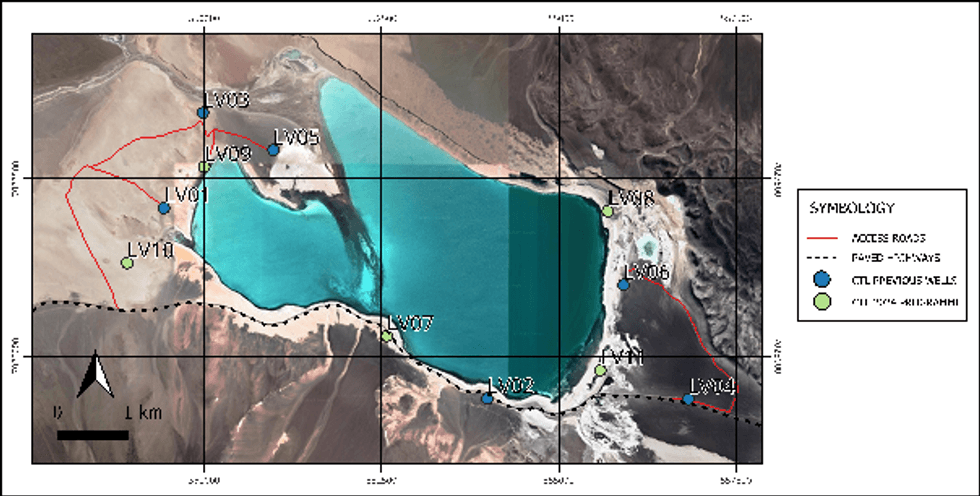
Figure 8: Laguna Verde Drilling Wells Map - Show original figure
Drilling activities for exploration borehole LV07 reached a final depth of 650m below land surface. This well was drilled with PQ3 diameter from land surface to 300m, and with HQ3 diameter from 300m to 650m. Packer samples were obtained during drilling for 2-meter packer intervals and the volume of the well was purged at least one time before obtaining the sample. Assuming a lithium cut-off grade of 100 mg/L, the average lithium grade of the packer samples corresponds to 139 mg/L with the well encountering lower density water in the upper 150m.
In contrast to LV07, drilling at LV11 did not reach the anticipated depth due to the presence of hydrothermal waters (under pressure) which were encountered during drilling, with a final depth of 412.8m below land surface. Assuming a lithium cut-off grade of 100 mg/L, the average lithium grade of the packer results would correspond to 131 mg/L. In general, it is believed that lithium grades decrease below 220m at LV11 due to the presence of dilute hydrothermal waters which were encountered during drilling. The presence of hydrothermal waters in the eastern portion of the Project are more dilute than the average lithium grade measured in other exploration wells.
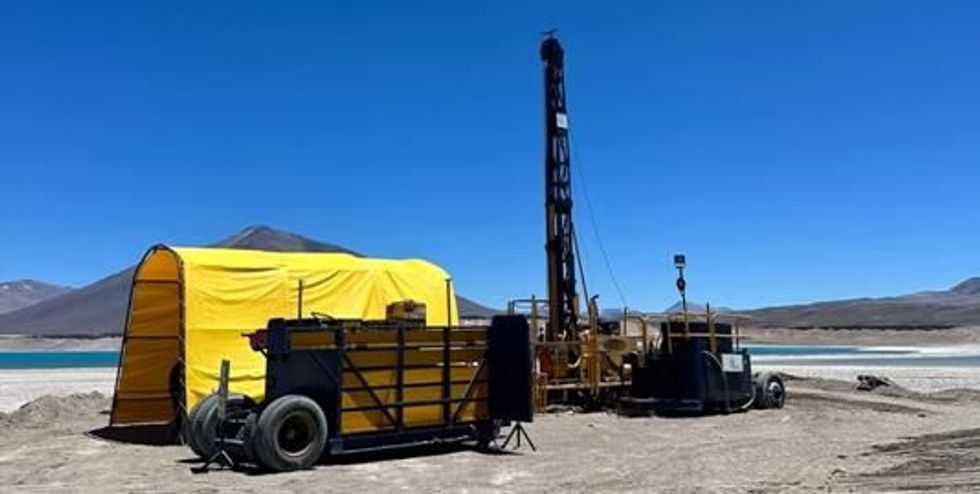

Figure 9: Drilling at LV07 in 1H 2024
Lithology and Drainable Porosity
Based on core retrieved from drilling, the most predominant lithology encountered corresponds to a volcanic tuff with variable levels of consolidation and welding based on the depth and location. As determined by relative brine release testing at Geosystems Analysis (GSA) laboratory in Tuscon, USA, drainable porosity values of collected core samples from LV07 and LV11 range from 0.3% to 9.2%, with an arithmetic average of approximately 4%; this is considered by Montgomery to be reasonable for the encountered lithologic units based on visual inspection of the core.
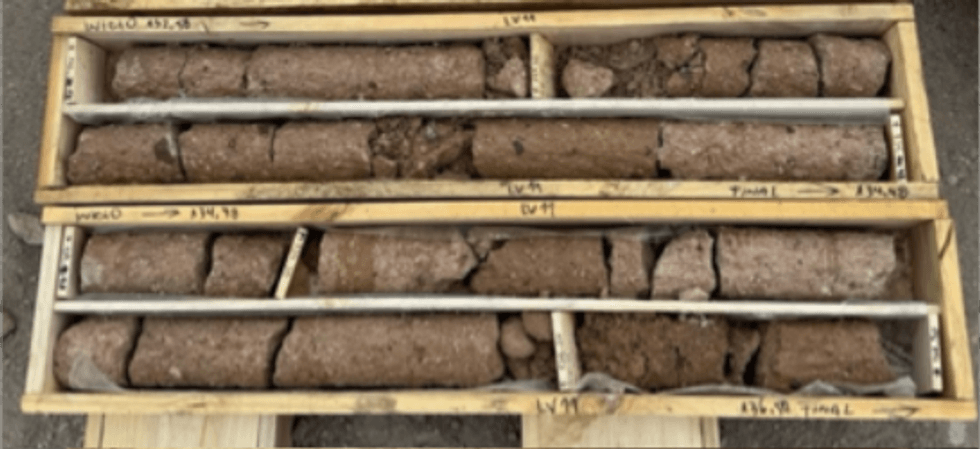

Figure 10: Example of Drill Core from Exploration Borehole LV11 (132 to 136m)
Hydrogeological Evaluation
In addition to resource drilling, the 2024 campaign aimed to complete pump tests to evaluate the feasibility of lithium brine extraction for the Project and to also estimate aquifer parameters. Prior to the winter break, three observation wells were completed and initial variable rate step tests and a constant rate flow test undertaken. The intended long duration pump tests at well LV05 was not able to be completed, however a 7-day pumping test was successfully completed at LV06. With data obtained to date, Montgomery is able to continue refining the hydrogeological modelling that will feed into the design of the extraction and reinjection well fields for the PFS. A key aspect is to ensure no impact on surface water bodies.
Recommendations and Next Steps
Based on the obtained results from the 2024 exploration programme, recommended priorities for continued exploration include additional drilling and testing in the western portion of the Project concessions. A long-term pump test at LV05 (as part of the planned reinjection test) will also aid in demonstrating feasible extraction and reinjection to the west of the basin. A long-term test at LV05 will also allow for a better understanding of the hydraulic connection between the deep and shallow aquifers in that area.
On the completion of the 5 well programme as originally planned for 2024, the existing JORC compliant resource estimate of 1.8 million tonnes will be updated and a Reserve estimate will be calculated for the project. The Reserve calculation is the economically mineable part of the Measured and/or Indicated resource and this will be defined by the PFS data demonstrating that extraction could reasonably be justified. Progress continues on the PFS and the remaining planned wells will be completed as funds are available following completion of the planned ASX capital raising.
Pilot Plant Update
Downstream conversion of concentrated eluate from the Company´s pilot plant into battery grade lithium commenced last week at the facilities of Conductive Energy in Chicago, USA. The initial volume of 88m3 of concentrated eluate from Laguna Verde, equal to approximately one tonne of lithium carbonate equivalent ("LCE"), will be processed in four batches with the first batch expected to produce a volume of battery-grade sample product in November. With this product, the Company plans to engage with strategic partners for product qualification.
For further information contact: | |
CleanTech Lithium PLC | |
Steve Kesler/Gordon Stein/Nick Baxter | Jersey office: +44 (0) 1534 668 321 Chile office: +562-32239222 |
Or via Celicourt | |
Celicourt Communications Felicity Winkles/Philip Dennis/Ali AlQahtani | +44 (0) 20 7770 6424 |
Beaumont Cornish Limited (Nominated Adviser) Roland Cornish/Asia Szusciak | +44 (0) 20 7628 3396 |
Fox-Davies Capital Limited (Joint Broker) Daniel Fox-Davies | +44 (0) 20 3884 8450 |
Canaccord Genuity (Joint Broker) James Asensio | +44 (0) 20 7523 4680 |
Competent Persons
The following professionals act as Competent Persons (CPs), as defined in the AIM Note for Mining, Oil and Gas Companies (June 2009) and JORC Code (2012):
Mike Rosko and Brandon Schneider of M&A are Registered Members of the Society of Mining, Metallurgy, and Exploration and have functioned as CPs for lithium brine projects under Canadian, Australian, and United States technical reporting standards. Their relevant experience includes:
· Mike Rosko has been estimated lithium brine resources since 2010, and has functioned as a CP for Lithium One's Sal de Vida project, Millennial Lithium's Pastos Grandes project, Lithium Chile's Salar de Arizaro project, NOA Lithium's Rio Grande project, Lithium America's Cauchari project, Wealth Minerals' Salar de Ollague project, Gangfeng's Mariana project, Eramine's Centenario/Ratones project, Posco Lithium's Sal de Oro project, Pepennini's Salar de Pular project, and others, and has prepared numerous third party due diligence and independent geologist reports in Argentina, Chile, and the United States.
· Brandon Schneider specializes in lithium brine reserve estimates, variable density flow modeling, and optimization of brine pumping in salt flats of Argentina and Chile. He has functioned as a CP for the Sal de Vida Project of Arcadium Lithium and Salar de Arizaro Project of Lithium Chile and was responsible for the reserve estimate and projected wellfield design. He also collaborates on the lithium brine exploration phases, resource estimation, and due diligence reviews for lithium brine projects.
Beaumont Cornish Limited ("Beaumont Cornish") is the Company's Nominated Adviser and is authorised and regulated by the FCA. Beaumont Cornish's responsibilities as the Company's Nominated Adviser, including a responsibility to advise and guide the Company on its responsibilities under the AIM Rules for Companies and AIM Rules for Nominated Advisers, are owed solely to the London Stock Exchange. Beaumont Cornish is not acting for and will not be responsible to any other persons for providing protections afforded to customers of Beaumont Cornish nor for advising them in relation to the proposed arrangements described in this announcement or any matter referred to in it.
Notes
CleanTech Lithium (AIM:CTL, Frankfurt:T2N, OTCQX:CTLHF) is an exploration and development company advancing lithium projects in Chile for the clean energy transition. Committed to net-zero, CleanTech Lithium's mission is to become a new supplier of battery grade lithium using Direct Lithium Extraction technology powered by renewable energy.
CleanTech Lithium has two key lithium projects in Chile, Laguna Verde and Viento Andino, and exploration stage projects in Llamara and Arenas Blancas (Salar de Atacama), located in the lithium triangle, a leading centre for battery grade lithium production. The two most advanced projects: Laguna Verde and Viento Andino are situated within basins controlled by the Company, which affords significant potential development and operational advantages. All four projects have good access to existing infrastructure.
CleanTech Lithium is committed to utilising Direct Lithium Extraction with reinjection of spent brine resulting in no aquifer depletion. Direct Lithium Extraction is a transformative technology which removes lithium from brine with higher recoveries, short development lead times and no extensive evaporation pond construction. www.ctlithium.com

Sign up to get your FREE
Homerun Resources Investor Kit
and hear about exciting investment opportunities.
- Corporate info
- Insights
- Growth strategies
- Upcoming projects
GET YOUR FREE INVESTOR KIT
The Conversation (0)
23 February
Homerun Resources
Establishing a vertically integrated leader in high-purity silica for solar & energy markets
Establishing a vertically integrated leader in high-purity silica for solar & energy markets Keep Reading...
19 February
Top Australian Mining Stocks This Week: Lithium Valley Results Boost Gold Mountain
Welcome to the Investing News Network's weekly round-up of the top-performing mining stocks listed on the ASX, starting with news in Australia's resource sector.Mining giant BHP (ASX:BHP,NYSE:BHP,LSE:BHP) reported strong half-year copper results, saying that its copper operations accounted for... Keep Reading...
17 February
Howard Klein Doubles Down on Strategic Lithium Reserve as Project Vault Takes Shape
Before the Trump administration revealed plans for Project Vault, Howard Klein, co-founder and partner at RK Equity, proposed the idea of a strategic lithium reserve. “The goal of a strategic lithium reserve is to stabilize prices and allow the industry to develop,” he told the Investing News... Keep Reading...
17 February
Sigma Lithium Makes New Lithium Fines Sale, Unlocks US$96 Million Credit Facility
Sigma Lithium (TSXV:SGML,NASDAQ:SGML) has secured another large-scale sale of high-purity lithium fines and activated a production-backed revolving credit facility as it ramps up operations in Brazil.The lithium producer announced it has agreed to sell 150,000 metric tons (MT) of high-purity... Keep Reading...
12 February
Albemarle Lifts Lithium Demand Forecast as Energy Storage Surges
Albemarle (NYSE:ALB) is raising its long-term lithium demand outlook after a breakout year for stationary energy storage, underscoring a shift in the battery materials market that is no longer driven solely by electric vehicles.The US-based lithium major reported fourth quarter 2025 net sales of... Keep Reading...
21 January
Official signing of the Portuguese State Grant
Savannah joins other grant recipient companies at official signing ceremony
Savannah Resources Plc, the developer of the Barroso Lithium Project in Portugal, a 'Strategic Project' under the European Critical Raw Materials Act and Europe's largest spodumene lithium deposit (the 'Project'), was delighted to join with other recipients of State grants yesterday at the... Keep Reading...
21 January
Excellent Results from 2025 Core Drilling Program at McDermitt
Jindalee Lithium Limited (Jindalee, or the Company; ASX: JLL, OTCQX: JNDAF) is pleased to report assay results from the drilling program at the McDermitt Lithium Project completed late 2025. All holes returned strong lithium and magnesium intercepts from shallow depths, including:R92: 36.5m @... Keep Reading...
Latest News

Sign up to get your FREE
Homerun Resources Investor Kit
and hear about exciting investment opportunities.
- Corporate info
- Insights
- Growth strategies
- Upcoming projects
GET YOUR FREE INVESTOR KIT
Interactive Chart
Latest Press Releases
Related News
TOP STOCKS
American Battery4.030.24
Aion Therapeutic0.10-0.01
Cybin Corp2.140.00






