September 03, 2025
Critical Metals Corp. (Nasdaq: CRML) (“Critical Metals Corp” or the “Company”), a leading critical minerals mining company, today announced for the first time three new assay results from the 2024 diamond drill hole program at the Fjord Deposit at the Tanbreez Rare Earth Project in Greenland.
Highlights – 2024 New Diamond Drill Hole Results
- Consistent high-grade rare earth mineralization intersected in all four reported holes, with Total Rare Earth Oxide (TREO) grades between 0.40% and 0.42%.
- High proportion of heavy rare earth oxides (HREO) ~26% of TREO, reinforcing the deposit’s potential strategic value.
- Significant zirconium oxide (ZrO₂) grades of 1.57–1.58% across all holes.
- Gallium oxide (Ga₂O₃) assays between 93–99 ppm, providing a potential additional economic credit.
- All holes drilled vertically (-90°) through sub-horizontal, stratiform kakortokite layers, intersecting mineralisation at approximately true thicknesses.
- Mineralisation remains open at depth in all reported holes.
- Drilling confirms continuity of grade and mineralogy across multiple sections of the Fjord Deposit, consistent with historical data.
- All the drill holes were collared within the Fjord Deposit with 23.6MT @ 0.42% TREO Maiden Mineral Resource.
- The holes are part of the ongoing 2024–2025 Fjord Resource Upgrade program, with over 1900 m drilled to date in 2025 and further assays pending.
Tony Sage, Executive Chairman of the Company, commented:
“These additional 2024 diamond drill hole results indicate the consistent grades of rare earth and gallium, with a high proportion of critical heavy rare earths. Our rare earth grades and gallium concentration, position Tanbreez as a strategically important asset for Western supply chains. With China's control over the rare earth market and gallium, securing sources of these critical minerals has become paramount for U.S. defense capabilities and national security. The progress we've made, with 1,316 meters of diamond core drilling completed in 2024, and over 1,850 meters of drilling as part of our 2025 Fjord Resource Upgrade resource extension program, significantly strengthens our ability to build on our substantial resource base. With further assays pending and more drilling underway, we see strong potential to grow the scale and nature of the project's mineral inventory.”
Summary New Drill Hole Results
Drill hole collars and assay Tables 1 and 2 and Figure 1 and Appendix 1, 2 and 3.
| Hole ID | Depth (m) | TREO (%) | HREO (% of TREO) | ZrO₂ (%) | Ga₂O₃ (ppm) | ||||||
| D-24 | 85.70 | 0.42 | 26.3% | 1.58 | 99 | ||||||
| E-24 | 62.30 | 0.40 | 26.5% | 1.57 | 93 | ||||||
| F-24 | 107.45 | 0.40 | 25.5 | 1.57 | 93 | ||||||
| Cut-off | 0.30 |
Table 1 – 2024 New assay results summary for D-24, E-24, F-24
New Drill Hole Results
Drill Hole D-24
Drilled vertically to 85.7m from surface and intersected high-grade rare earths and metal oxides mineralisation averaging:
- 0.42% TREO (including 25.9%,HREO)
- 1.57% ZrO2 zirconium oxide,
- 100ppm Ta2O5 tantalum pentoxide,
- 1340ppm Nb2O5 niobium pentoxide,
- 99ppm Ga2O3 gallium oxide,
- Mineralisation open at bottom of the hole,
- Mineralisation average from surface to 63m downhole.
Drill Hole E-24
Drilled vertically to 62.3m from surface and intersected high-grade rare earths and metal oxides mineralisation averaging:
- 0.39% TREO (including 26.2%,HREO)
- 1.56% ZrO2 zirconium oxide,
- 100ppm Ta2O5 tantalum pentoxide,
- 1330ppm Nb2O5 niobium pentoxide,
- 90ppm Ga2O3 gallium oxide,
- Mineralisation open at bottom of the hole,
- Mineralisation average from surface to 61.3m downhole.
Drill Hole F-24
Drilled vertically to 107.45m from surface and intersected high-grade rare earths and metal oxides mineralisation averaging:
- 0.40% TREO (including 25.6%,HREO)
- 1.57% ZrO2 zirconium oxide,
- 100ppm Ta2O5 tantalum pentoxide,
- 1260ppm Nb2O5 niobium pentoxide,
- 93ppm Ga2O3 gallium oxide,
- Mineralisation open at bottom of the hole,
- Mineralisation average from surface to 72m downhole.

Figure 1 - Tanbreez Site Visit August 29 Malcolm Day Director CRML, Greg Barnes JV Partner, George Karageorge CTO, Anna Wingle Tanbreez Mining Greenland
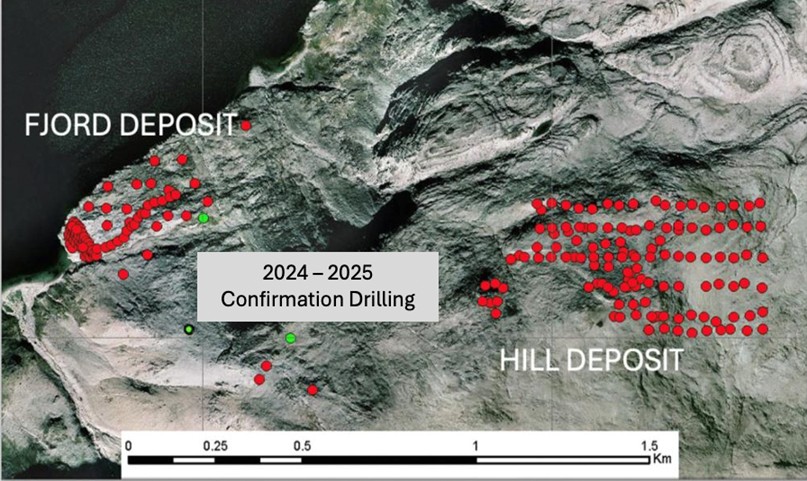
Figure 2 - Fjord and Hill Deposit drill hole locations for 2007, 2010, 2013, 2024 in red with 2025 drill hole collars completed in July with 9 diamond holes awaiting drilling.
Drill Hole Statistics
Drill hole collars and assay Tables 1 and 2 and Figure 1 and Appendix 1, 1A , 2 and 3.
| Hole ID | Depth From | Depth To | Interval | TREO% | HREO% | ZrO2 % | Ta2O5 ppm | Nb2O5 ppm | Ga2O5 ppm | |
| A1-24 | - | 40.00 | 40.00 | 0.48 | 0.13 | 1.86 | 134 | 1513 | 103 | |
| A2-24 | - | 41.00 | 41.00 | 0.51 | 0.14 | 1.96 | 145 | 1685 | 96 | |
| B-24 | - | 58.00 | 58.00 | 0.49 | 0.13 | 1.99 | 144 | 1651 | 101 | |
| C-24 | - | 65.00 | 65.00 | 0.54 | 0.14 | 1.98 | 156 | 1741 | 89 | |
| D-24 | 1.00 | 63.00 | 62.00 | 0.42 | 0.11 | 1.58 | 112 | 1344 | 99 | |
| E-24 | 1.00 | 62.30 | 61.30 | 0.40 | 0.11 | 1.57 | 105 | 1336 | 93 | |
| F-24 | 0.00 | 72.00 | 72.00 | 0.40 | 0.10 | 1.57 | 103 | 1256 | 93 |
Table 2 - 2024 Drill Hole Assay results summary to date 2024 diamond drill hole program in the Fjord Area. Assay results are reported for drill holes D, E and F. A1, A2, B and C were reported on 22 August 2025. Remaining assay results for holes G to Z are expected to be reported in Q3, 2025.
Background – Fjord Deposit Drilling
The 2024–2025 drilling campaign in the Fjord area has targeted confirmatory and step-out holes to:
- Validate historical drilling data.
- Refine the geological model for resource estimation.
- Provide material for metallurgical and environmental test work.
All drill holes in this program are vertical, intersecting the sub-horizontal layers at true thickness. The three holes reported here return TREO grades between ~0.40% and 0.42% with approximately 26% HREO, along with ZrO₂ values of 1.57–1.58% and gallium oxide contents of 93–99 ppm. These results are consistent with historical assays and demonstrate the persistence of grade and mineralogy across the Fjord deposit.
From a deposit classification perspective, the kakortokite-hosted REE mineralisation is best described as stratiform magmatic, confined entirely to the kakortokite unit and not observed in adjacent lithologies such as lujavrite or naujaite. This strong lithological control underpins confidence in resource modelling, supports bulk mining strategies, and provides reliable input for geology domaining.
Given the continuity of mineralization over several kilometres, the Fjord deposit represents a significant portion of the overall Tanbreez mineral inventory. Ongoing drilling is expected to further delineate these resources, with pending assays from additional holes likely to extend the known mineralised envelope and refine the grade distribution.
Sampling over the 2024 diamond holes was taken over kakortokite intervals above the Black Madonna lower boundary.
- Collar data: All collar locations, RLs, azimuths, dips, and hole lengths have been clearly presented in Table 2 of the report.
- Assay data: Table 1 in the report provides the suite of weighted average downhole assay results for TREO, HREO, Ga₂O₃, and other oxides.
- True widths: All drill holes are vertical (-90°) through sub horizontal mineralised layers, so intersections are true widths.
- No cut-off grades or metal equivalents were applied. All assays are reported at face value.
Gallium Results
The gallium oxide Ga2O3 mineralization assay results ranges from low to high is 90ppm to 100ppm for the four 2024 drillholes published to date.
Drill holes that were not assayed for gallium, tantalum and niobium in 2013 will be assayed from existing pulps submitted to ALS Metallurgical in Perth for analysis in the coming months.
ALS laboratories will also assay all sample for gallium for the 2024 and 2025 drill holes with results that will be published in September and October 2025. The gallium oxide results for all diamond holes published to date may add a credit to the TREO-HREO mixed concentrate.

Sign up to get your FREE
Metro Mining Investor Kit
and hear about exciting investment opportunities.
- Corporate info
- Insights
- Growth strategies
- Upcoming projects
GET YOUR FREE INVESTOR KIT
The Conversation (0)
02 March
Metro Mining
Pure-play low-cost producer of high-grade Australian bauxite
Pure-play low-cost producer of high-grade Australian bauxite Keep Reading...
26 February
Top Australian Mining Stocks This Week: European Resources Soars on Rare Earth Results
Welcome to the Investing News Network's weekly round-up of the top-performing mining stocks listed on the ASX, starting with news in Australia's resource sector.Gold, lithium and copper companies continue to dominate our top ASX stocks of the week. This week, the Northern Territory's Minister... Keep Reading...
25 February
China's Rare Earths Export Ban Hits Japanese Defense Sector
China has moved to freeze exports of rare earth magnets and other critical materials to dozens of major Japanese companies, with the measures to take effect immediately.China’s commerce ministry said Tuesday (February 24) that it will suspend shipments of so-called “dual-use” goods — referring... Keep Reading...
24 February
Application to Trade on OTCQB Market
Altona Rare Earths plc (LSE: REE), the critical raw materials exploration and development company focused on Africa, is pleased to announce that it has applied for its ordinary shares to be admitted to trading on the OTCQB Venture Market in the United States ( "OTCQB").The Company has submitted... Keep Reading...
24 February
Brazil, India Ink Rare Earths Pact to Expand Supply Chain Cooperation
Brazil and India have signed a new agreement to deepen cooperation on rare earths and critical minerals as both countries seek to strengthen supply chains and reduce reliance on trading partners.The non-binding memorandum of understanding, sealed on February 21 during Brazilian President Luiz... Keep Reading...
22 February
LKY Commences Diamond Drilling at Desert Antimony Mine
Locksley Resources (LKY:AU) has announced LKY Commences Diamond Drilling at Desert Antimony MineDownload the PDF here. Keep Reading...
20 February
Cellulose Breakthrough Could Simplify Rare Earths Separation
A team of researchers at Penn State have developed a plant-based nanomaterial capable of selectively extracting dysprosium from rare earth mixtures, according to a recent report.The findings published in the study detail how the team engineered a modified form of cellulose capable of isolating... Keep Reading...
Latest News

Sign up to get your FREE
Metro Mining Investor Kit
and hear about exciting investment opportunities.
- Corporate info
- Insights
- Growth strategies
- Upcoming projects
GET YOUR FREE INVESTOR KIT
Interactive Chart
Latest Press Releases
Related News
TOP STOCKS
American Battery4.030.24
Aion Therapeutic0.10-0.01
Cybin Corp2.140.00






