
June 27, 2024
CoTec Holdings Corp. (TSXV:CTH)(OTCQB:CTHCF) ("CoTec" or the "Company") is pleased to announce the completion of an initial Mineral Resource Estimate (the "MRE") and positive Preliminary Economic Assessment ("PEA") for the Lac Jeannine Iron Tailings Project, Québec, Canada ("Lac Jeannine", or the "Project"). The PEA was prepared by independent experts Addison Mining Services Ltd., Soutex Inc, JPL GeoServices and other independent experts.
The highlights of the MRE and PEA are as follows:
- Initial Inferred Mineral Resource of 73 million tonnes (Mt) at 6.7% total Fe for 4.9 Mt of contained total Fe (Note: tonnes are metric tonnes)
- Identified tailings material surrounding the Inferred Mineral Resource (the "Adjacent Tailings"), if confirmed by drilling and analysis, could potentially add 50 to 70 Mt to the Project
- Total Fe grade in the Project schedule reduces from approximately 8.4% total Fe to 7.0% total Fe in the first 3.5 years of production to approximately 6.0% total Fe by year 8 and subsequently 5.6% total Fe in the final year
- Based on open-pit extraction methods and the production of a gravity concentrate via conventional processing techniques and at a discount rate of 7.0% (and based solely on the MRE), the pre-tax NPV is US$93.6M, and its IRR is 38%, and the after tax NPV is US$59.5M, and its IRR is 30%
- Product is a high purity iron concentrate at 66.8% total Fe, low contaminant SiO2, Al2O3 and phosphorus with an average production of circa 380k tonnes per annum for just over 10 years
- The up-front capital cost of the Project is US$64.6M (inclusive of a 15% contingency margin and estimated further study and engineering costs), with payback achieved in 2.5 years and a profitability index (PI) of 0.92[1]
- C1 cash costs of US$53/t (excl. transport to port and royalty payments)
- All-in Sustaining Cost (ASIC) of US$61/t (incl. transport to port and royalty payments)
- The Project significantly reduces the environmental liability of the Lac Jeannine site. The current tailings pile is considered an orphan site and the provincial government carries the environmental liability
- The Company will now proceed with the completion of a Feasibility Study for the Project to:
- Complete the next phase of drilling to upgrade the resource to indicated (and ultimately to a reserve category) and to extend the Project it to a larger portion of the Adjacent Tailings, detailed processing design targeting 67.5% total Fe concentrate to qualify for Provincial and Federal critical mineral incentives
- Investigate future low carbon pelletizing options to produce pellets in Québec using innovative, low carbon green technology, including the Binding Solutions Limited's cold bonding technology, which will further enhance the economics of the Project
- Explore potential economic support from Federal and Provincial governments, funding opportunities and other economic incentives including carbon price premiums that could improve economics, including those aiming to encourage the development of critical minerals and to promote a circular economy
- Derisk the Project in the key study areas of permitting, social acceptability, power supply and secure rail access for the transportation of the concentrate
Julian Treger, CoTec CEO commented; "the PEA represents a first step in demonstrating CoTec's strategy of recovering the great economic potential of large historical tailing sites with further potential enhancement of these projects through the deployment of CoTec technologies where applicable. The Labrador Trough hosts some of the largest historical resources of high-purity iron globally, creating an exceptional opportunity for Québec to become a global sustainable leader in the green steel supply chain.
It is now the intention of CoTec to pursue the development of the Project, including a program of infill and extension drilling at Lac Jeannine with the objective of upgrading the current Inferred Resource to the Indicated category and expanding the current resource tonnage.
The inclusion of the Adjacent Tailings has the potential to almost double the life of mine with no additional CAPEX and we will focus on this strategy as well as several other optimization opportunities to further enhance the exciting results of the PEA.
CoTec is also committed to continuing discussions with strategic partners in order to move rapidly onto preparation of a Feasibility Study (FS) with the support of all stakeholders, including the Government of Québec, First Nations and other interested parties.
The Lac Jeannine Project offers great potential for the resource industry to recover the economic benefit of large Fe tailing sites at competitive cost structures which can deliver high purity iron concentrates for the green steel industry.
The PEA confirms management's belief that CoTec's value proposition is not properly reflected in the market and we therefore continue to strongly support the Company through our participation in private placements and the purchase of shares in the open market."
The PEA study was undertaken by a multidisciplinary team appointed by CoTec and supported by JPL GeoServices Inc. and Soutex Inc. of Canada; Axe Valley Mining Consultants Ltd, Amerston Consulting Ltd. and Addison Mining Services Ltd of the United Kingdom. A Technical Report for the Project, including the details of the MRE and its PEA, will be filed on https://www.sedarplus.ca/ within 45 days.
The key financial and production metrics of the Project are summarized in Table 1. The PEA did not incorporate prospects for potential economic support from governments, funding opportunities or other economic incentives that could improve economics and influence a future Feasibility Study and investment decision, including those aiming to encourage the development of critical minerals and a circular economy.
Table 1: PEA Key Financial Metrics in US$
| Assumptions | Unit | |
| Mineral resources | M dmt | 73 |
| Project Duration | Years | 11 |
| Average annual production (dry) | K tonnes per annum | 380 |
| Average total Fe In-situ grade to plant | % | 6.7 |
| Average total Fe metallurgical recovery | % | 51.6 |
| Average concentrate grade sold | % Fe | 66.8 |
| Economic Assumptions | ||
| P65 Index CFR China Iron ore price | US$/dmt | 121 |
| Average realised price (Inc. high grade premium) | US$/dmt | 145 |
| Average shipping cost | US$/dmt | 21 |
| Capital Cost | ||
| Construction period | Years | 2 |
| Initial capex (excl. closure and sustaining) | US$ million | 64.6 |
| Operating cost per tonne | ||
| Total cash cost (C1 Cost) | US$/dmt | 53 |
| Total AISC | US$/dmt | 61 |
The PEA is preliminary in nature, and is based on Inferred Mineral Resources that are considered too speculative geologically to have the economic considerations applied to them that would enable them to be categorized as Mineral Reserves. As such, there may be no certainty that the PEA will be realized.
Basis of Mineral Resource Estimate
The MRE is based upon 13 vertical sonic drillholes totalling 522.0 m (ranging between 36.0 m and 40.5 m in depth). All drillholes were drilled vertically and spaced 200 m apart on a regular grid. The internal tube diameter was 4.05 inches. All material was logged for colour and grainsize characteristics, the average drillhole recovery was estimated at 93%. Routine quality control samples were inserted into the sample stream representing 39 out of 337 samples typically of length 1.5 m. Drilling and Sampling was directly supervised by Mr. John Lanton, Independent Qualified Person for Exploration, Drilling and Data Collection, in the September of 2023.
All drillhole material, minus a small 1.0 to 1.5 litre reference sample were dispatched in clearly labelled bags with sample tickets to Corem, a Québec-based laboratory for analysis. Corem is internationally accredited by the Canadian Standards Council through the Bureau de Normalization du Québec (BNQ) to ISO/IEC 17025:2017 Analytical Services Laboratory.
All material was recorded upon receipt, and weighed wet and after oven drying. Sub sampling was done by rotary sample splitter before pulverization and preparation of a tungsten fusion bead for XRF analysis of major oxides (SiO₂, Al₂O₃, Fe₂O₃, MgO, CaO, Na₂O, K₂O, TiO₂, MnO, P₂O₅, Cr₂O₃, V₂O₅, ZrO₂, and ZnO) plus Loss on Ignition.
Mineral Resource Statement
Mineral Resources, reported in accordance with National Instrument 43-101, Standards of Disclosure for Mineral Projects, ("NI 43-101") and prepared under Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum ("CIM") Definition Standards, have been estimated for the Project. Reasonable prospects of eventual economic extraction is supported by the PEA.
The estimated initial MRE, reported in accordance with NI 43-101 and the CIM Definition Standards is set out in Table 2 and the accompanying notes for further information and Figure 1 for an overview of the MRE:
- 73 Mt at 6.7% total Fe for 4.9 Mt of contained total Fe.
Table 2: Inferred Mineral Resource Estimate
Category | Million Tonnes | Total Fe grade % | Total Fe (Mt) | Fe2O3% |
Inferred | 73 | 6.7 | 4.9 | 9.6 |
Notes To Mineral Resource Estimate:
- Numbers are rounded to reflect that an estimate of tonnage and grade has been made, as such products may have discrepancies. Tonnages are expressed in the metric system and metal content as percentages.
- The Independent Qualified Person for Mineral Resources, Mr. Christian Beaulieu, P.Geo., is a member of l'Ordre des géologues du Québec (#1072). Mr. Beaulieu has reviewed the available geological, assay and quality control data and has completed a site visit on the 12th of June 2024. Mr Beaulieu has reviewed the MRE, associated models and methodology completed by Addison Mining Services Ltd. of the United Kingdom on behalf of CoTec and has completed an independent check estimate. Mr. Beaulieu has been an employee of Mineralis Consulting Services Inc. since the 1st of June 2023.
- The effective date of the MRE is the 19th of March 2024.
- These Mineral Resources are not Mineral Reserves as they do not have demonstrated economic viability. The quantity and grade of reported Inferred Resources in this MRE are uncertain in nature and there has been insufficient exploration to define these Inferred Resources as Indicated or Measured, it is reasonably expected that the majority of Inferred Mineral Resources could be upgraded to Indicated Mineral Resources with continued exploration. Additional drilling and bulk density determination are, however, required to increase the confidence in the MRE; increased levels of information brought about by further drilling may serve to either increase or decrease the MRE. No Measured or Indicated Mineral Resources are reported.
- The estimate was completed using Micromine 2024 software, a 50 m (east and west) by 3 m (vertical) regular block model was estimated using ordinary kriging of all elements analyzed. The block model was restricted using a wireframe volume generated from airborne drone topographic survey of the current tailings surface and a legacy 1:50k contour map of the pre-tailings situation.
- Drilling did not reach the bottom of the tailings in all but one drillhole and the resource was extrapolated ~10 m below the drillholes.
- The cut-off grade used to report the initial MRE is 3.3% total Fe, based on the following parameters:
- Iron price of US$ 124/t FOB for a 66.8% Fe concentrate
- Transport costs all in of US$ 6.32/t conc.
- Total ROM-based costs of US$ 2.76 /t
- Metallurgical recoveries of 51.6%
- Royalties of 0.5%.
- Bulk Density is reasonably assumed as 1.6 g/cm3 across all material which is typical for dry compact sand. The density assumption is supported by historical production mass balance records and dry sample weights received at the lab after allowance for removal of a reference sample at the drill site.
- The Mineral Resource extends from surface to approximately 50 m below surface, it is laterally extensive over an area of approximately 1.1 km from east to west and north to south and is extrapolated approximately 250 m beyond the limit of the drilling.
- CIM Definition Standards for Mineral Resources (2014) and Best Practices Guidelines outline by CIM (2019) have been followed.
- The independent Qualified Person for Resources is not aware of any additional known environmental, permitting, legal, title, taxation, socio-political, marketing, or other relevant issues that could materially affect the Mineral Resource Estimate.
- All Mineral Resources are of the Inferred category. The effective date of the MRE is 19th March 2024. No estimates of Mineral Reserves have been completed. Mineral Resources that are not Mineral Reserves do not have demonstrated economic viability. The estimate of Mineral Resources may be materially affected by environmental, permitting, legal, title, taxation, socio-political, marketing, or other relevant issues.
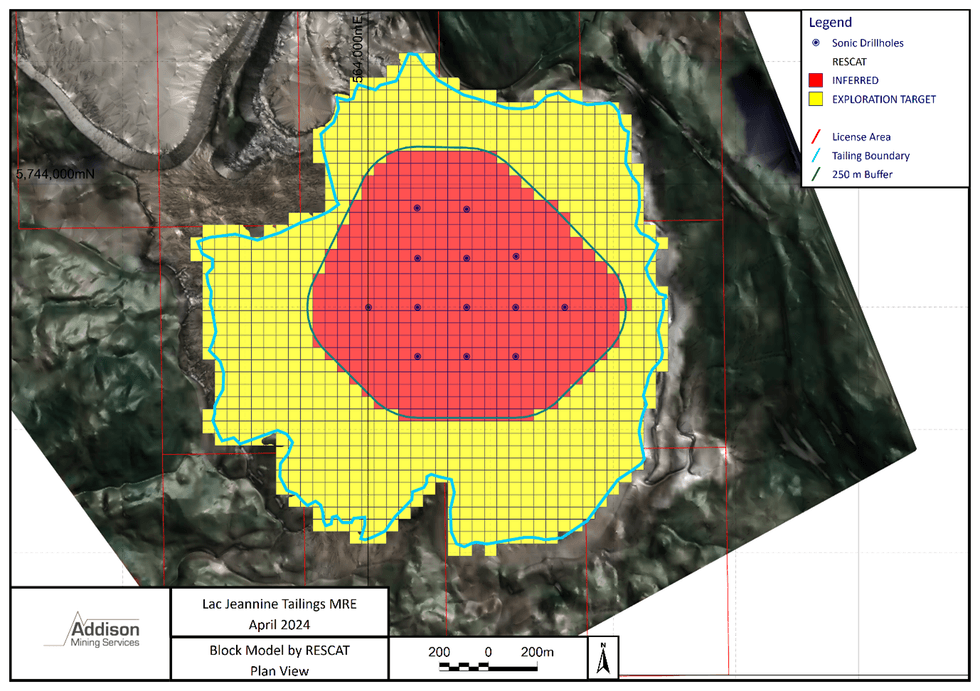
Figure 1: Extents of Mineral Resource relative to drilling and Exploration Target
Exploration Potential
Further tailings are present outside of the drilled area and it is reasonable to expect that with further appropriate exploration drilling the Mineral Resource tonnage could be increased. The surveyed area of the tailings has a total estimated tonnage of 145 million tonnes. This tonnage is likely estimated to relatively close limits (±5 million tonnes); however, iron grades are unknown with only limited sampling of the surface having been completed outside of the drill tested area; not all material may have a reasonable prospect of eventual economic extraction should grades be below economic cut-off, mixed with other waste material or contain significant quantities of deleterious elements.
A study completed by Soutex in 2007[2] postulated that 154 million tonnes of tailings grading 7.5% total Fe were deposited at the Lac Jeannine tailings pile. Soutex's estimate was based on historical production and mass balance records rather than systematic sampling. The results are similar to the findings of this study albeit at a slightly higher grade and loosely support the bulk density assumption of 1.6 g/cm3.
Assuming 70% to 100% of the tailing's material surrounding the Inferred Resource has a similar total Fe grade to the MRE, an exploration target tonnage of 50 to 75 Mt is postulated, with global average total Fe grade of 6.0% to 7.5% (±1 SD of the Resource block model) considered a reasonable possibility.
This potential range of tonnes and grade is conceptual in nature. Insufficient exploration to define a Mineral Resource has been completed and it is uncertain if a calculated mineral resource estimate of the surrounding material will be made in the future.
Basis of Preliminary Economic Assessment
Scoping-level design and preliminary economic analysis thereof was undertaken for the Project. The MRE has been used as a basis for this PEA.
Mining via open pit methods using a conventional truck and shovel fleet is contemplated, delivering approximately 7Mtpa of Run of Mine ("ROM") to stockpile for processing. On site mineral processing is via screening and size classification followed by gravity separation to produce a bulk iron bearing concentrate for sale. Rejected waste material from mineral processing is expected to be disposed off in the legacy Lac Jeannine open pit allowing rehabilitation of the mined parts of the current tailing's pile. Preliminary economic analysis has been performed in accordance with the conceptual mine design and schedule, metallurgical testing, and concentrate payability analysis developed in the study, and the estimates and analyses therein have been prepared to scoping level (+-30%). Key Project parameters are presented in Table 3.
Table 3: Summary of Project Parameters
| Parameter | Value | Units |
| Project Production Rate | Mtpa | 7.0 |
| Average Strip Ratio | t/t | 0.016 |
| Average total Fe Grade in Extracted Tailings | % | 6.7 |
| Total Mined Iron | Mt | 4.9 |
| LOM | Years | 11 |
| Extraction Cost - OPEX | US$/t | 0.9 |
| Process Cost - OPEX | US$/t | 1.56 |
| Anticipated Average Concentrate Grade | % | 66.8 |
Mining
The Project involves the extraction and reprocessing of the Lac Jeannine tailings based on an extraction rate of 7 Mtpa to produce on average 380 Ktpa of concentrate for just over 10 years. Based on the study to date, the concentrate is expected to be a premium grade product containing 66.8 % total Fe with very low concentrations of deleterious elements such as SiO2, P and Al2O3.
It is anticipated that the rejects from the reprocessing of the tailings will be pumped back into the former Lac Jeannine mine open pit so that the natural topography can, as much as possible, be returned to its natural state.
Whilst the Inferred Resource is currently restricted to approximately 73 Mt of material it is recognized that there is additional material present outside of the drill tested area. This material is classified as an exploration target and is presented as a range of grade and tonnes in this PEA study. Any material which is classified as part of the exploration target is treated as waste and stockpiled for the purpose of the PEA and is not considered as payable material in the financial analysis.
The Project design is relatively simple as the tailings pile forms a dome shape with an aerial extent of approximately 1.8 x 1.6 km and an estimated depth of up to 70 m at the central highest point. The Inferred Mineral Resource is currently restricted to an aerial extent of approximately 1.1 km x 1.2 km with thickness of approximately 50 m to 60 m.
There is a natural gradation in grade from high to low in the tailings pile, which means that the Inferred Resource can be extracted level by level (top to bottom) to eventually form a saucer shaped depression with a depth of up to 60 m from the existing tailings high point and a resultant maximum pit depth of 45 m (Figure 2). Grade variation is observed in the Project schedule as a linear reduction from approximately 8.4% total Fe to 7.0 % total Fe in the first 3.5 years of production, grade further reducing to approximately 6.0% total Fe by year 8 and subsequently 5.6% total Fe in the final year reflecting the vertical variation seen in the Resource block model

Figure 2: Optimized Pit limits based on Inferred Resources
The maximum extents of the pit were determined through pit optimization of the block model. Each block was allocated an economic value based on the revenue and costs and all blocks with a positive value were sent for processing. The economic cut-off grade was found to be 3.3 % total Fe.
Given there is no surface waste covering (organic material or low grade) it is expected that 100% of the MRE within the optimized pit limit can be re-processed as the grade of the blocks are all above the economic cut-off grade. The average grade for the Inferred material was 6.7 % total Fe.
The proposed extraction method is based on the recovery of 3 m high benches with a hydraulic excavator that loads 40t haul trucks. The haul trucks will shuttle between a temporary stockpile (ROM pad) and material from the ROM pad is then fed into the plant feed bin by one or more FELs.
The average production rate of 7 Mtpa equates to approximately 1,000 to 1,250 tph based on an equipment utilization of 62%. This can be achieved with one excavator and 3 or 4 trucks, provided the haul distance to the ROM pad is kept short and there are a minimum number of delays. Having two FELs at the ROM pad provides flexibility to deal with operational delays and unplanned breakdowns with the second FEL acting as a backup loader at the face.
It is expected that the extraction operation can continue throughout the year and material handling issues can be minimized by the rapid turnover of the faces (i.e. prevents permafrost forming). Although the material can become compacted, it is generally relatively dry and self-draining by virtue of the dome shape of the deposit. The digging conditions are not expected to be challenging, but the high silica content will mean that it is highly abrasive.
The Company is expected to be run with a contract miner who may also take on the contract for hauling the concentrate to the rail head.
The mining contractor will be responsible for operation and servicing of all excavation equipment and will bring in their own office and workshop facilities.
For the purpose of the PEA, 1.2 Mt of material that is within the pit limit and is classified as exploration target is treated as waste and will be stockpiled near to the plant. If this material can be shown to be economic through sampling, then it will be processed along with the Inferred material. It was not, however, considered in the PEA as payable material.
It is also pragmatic to consider the impact on the Project schedule and waste disposal requirements should the exploration target material be converted to a Mineral Resource. Were this to happen the addition of the exploration target material is unlikely to significantly change the sequence of extraction from a top-down approach, while it will mean the pit can be taken to the extents of the deposit, and this eliminates the formation of the saucer shaped pit. This will have advantages in terms of slope stability and ease of rehabilitation of the whole of the tailings area. It may also offer potential for an extended period of higher-grade feed in the early years, on the assumption that the higher-grade material seen at the top of the Inferred Mineral Resource extends towards the edge of the tailings. It is envisaged that waste material from the processing facility will be disposed of in the old Lac Jeannine open pit. It is estimated there is adequate space present to accommodate processing waste material from both the Mineral Resource and exploration target material.
Processing
The proposed concentrator plant is based on both historical, and 2023/2024 test work and knowledge acquired in the processing of iron ore deposits in Eastern Canada.
The Project is designed to process Lac Jeannine tailings material grading at approximately 7.0% total Fe at a nominal feed rate of 875 tph. The process flowsheet enables the production of a 66.8% total Fe concentrate for an iron recovery of 51.6%, allowing a production of circa 380ktpa of concentrate.
The flowsheet includes proven technologies for processing iron ore such as spirals, hydraulic classifier, jigs, ball mill and high-rate thickener. Figure 3: Simplified process flow diagram outlines the proposed process.
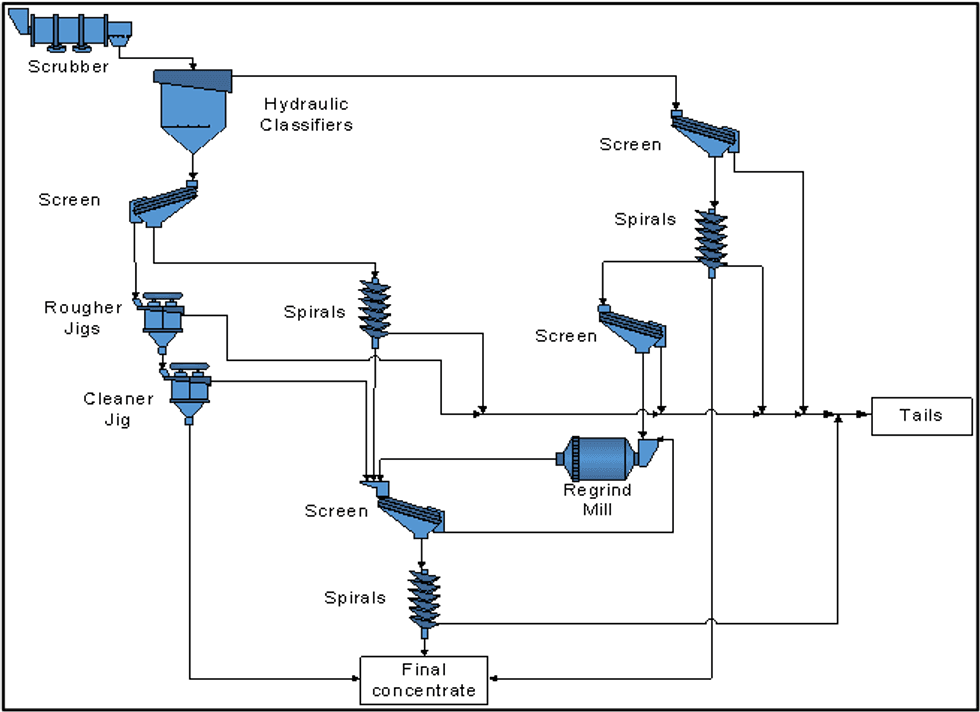
Figure 3: Simplified process flow diagram
Infrastructure and Services
The Project is expected to benefit from access to renewable hydroelectric power, water, roads, airfield, existing rail and port facilities in a proven regional labour market in a mining friendly jurisdiction with a long history of supporting iron ore operations. The Project is located directly to the west of ArcelorMittal's existing and operational Mont-Wright rail loop infrastructure, with access to end markets via port and rail. Rail access for the Lac Jeannine Project is expected to consist of two segments. The first stage, uses an existing road following the previous Lac Jeannie rail spur, which will transport the concentrate from the Project site to the Cartier Railway/Lac Jeannine rail junction. The second stage would utilise the existing Cartier railway operated by ArcelorMittal, connecting Mont-Wright Mine to the seaport at Port-Cartier (Québec). Once unloaded, the high purity Fe concentrate will be stockpiled, then loaded onto vessels to supply global customers. The Project requires a negotiated agreement in due course with ArcelorMittal for the use the Cartier railway for transportation.
Capital Costs
Initial capital expenditure (CAPEX) costs for the Lac Jeannine Project are based on a ROM of 7Mtpa with a nominal production capacity of circa. 400ktpa of 66.8% total Fe concentrate. Capex costs are estimated at US$65M, including EPCM costs, future study costs and a 15% contingency.
Sustaining capital over the Project life is estimated at 1.5% of operating costs (excluding G&A) and closure cost is estimated at 5% of total capex, resulting in total life of mine CAPEX cost of US$71M.
Table 4: Capital Costs
| Description | US$ (M) |
| Processing Plant | 44.2 |
| Infrastructure | 4.5 |
| Extraction | N/A as will be using contract mining |
| Indirect Costs (DE Study and EPCM) | 8.3 |
| Estimated Sub-Total Cost | 57 |
| Contingency 15% | 8 |
| Sustaining | 3 |
| Closure cost | 3 |
| Estimated Total Cost | 71 |
Operating Costs
The operating costs include manpower to run the overall operations, contractor rates for extraction and sub-contracted maintenance teams, power and utilities, materials handling, transport of the concentrate from the Project site to the port and G&A.
Table 5: Operating costs
| Area | US$/t ROM | US$/t concentrate |
| Tailings extraction (incl. tailings disposal) | 0.90 | 17.56 |
| Processing | 1.56 | 29.93 |
| Transport all in to port | 0.32 | 6.32 |
| G&A | 0.30 | 5.76 |
| Royalty (0.5% of revenue) | 0.035 | 0.69 |
| Total Opex | 3.12 | 60.26 |
Economic Analysis and Sensitivity
Table 6: Economic Results
| Economic Assumptions | Unit | |
| P65 Index CFR China Iron ore price | US$/dmt | 121 |
| Average realised price (Inc. high grade premium) | US$/dmt | 145 |
| Freight | US$/wmt | 21 |
| Pre-Tax NPV at 7% discount rate | US$M | 93.6 |
| Pre-Tax IRR | % | 38 |
| Post-Tax NPV 7% discount rate | US$M | 59.5 |
| Post-Tax IRR | % | 30 |
| Payback | years | 2.5 |
| PI | 0.92 |
A sensitivity analysis was performed whereby initial infrastructure capital cost, annual operating costs and product selling price were individually varied between +/-15% to determine the impact on Project IRR and NPV at a 7.0 % discount rate.
Results are presented in Table 7, as well as graphically in Figure 4 andFigure 5. The project financials are most sensitive to the commodity selling price followed by operating costs and finally initial capital expenditures.
Table 7: Sensitivity Analysis (US$,000)
Base Case | CAPEX | Selling price (FOB) | LOM OPEX | |||||
15% | -15% | 15% | -15% | 15% | -15% | |||
IRR | 30.3% | 25.8% | 35.9% | 38.8% | 20.3% | 25.9% | 34.3% | |
NPV | ||||||||
0% | $112,100 | $105,974 | $117,891 | $155,051 | $67,795 | $90,600 | $133,270 | |
5% | $71,415 | $65,511 | $77,063 | $102,257 | $39,487 | $ 56,146 | $86,434 | |
7% | $59,485 | $53,652 | $65,083 | $86,773 | $31,192 | $46,030 | $72,712 | |
10% | $44,910 | $39,176 | $50,433 | $67,844 | $21,076 | $33,666 | $55,953 |
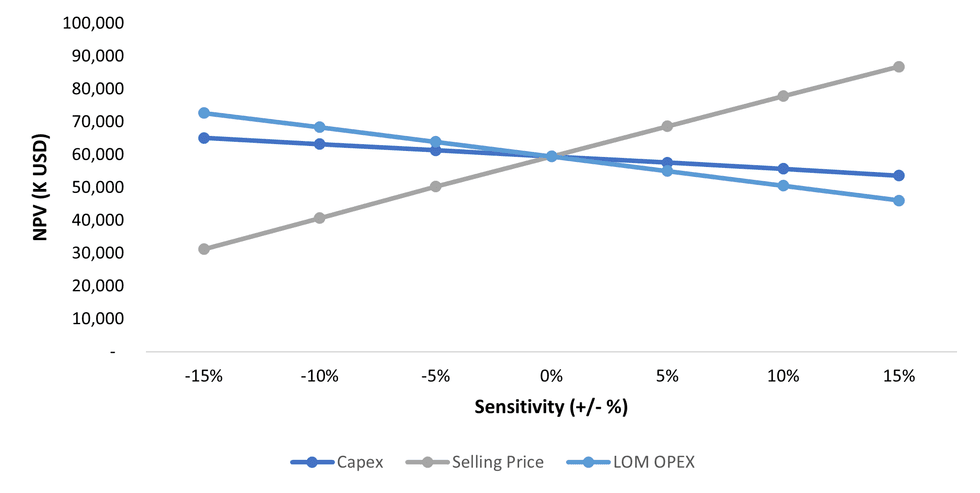
Figure 4: NPV Sensitivity Analysis Graph
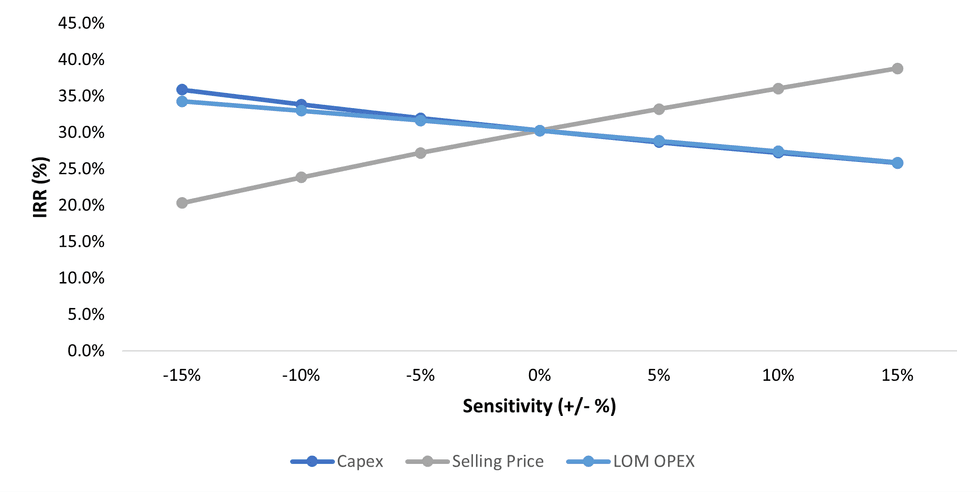
Figure 5: IRR Sensitivity Analysis Graph
Future Work
Recommendations for the Feasibility Study for the Project include:
- Inferred to Indicated Resources: Infill drilling to support the conversion of Inferred to Indicated Resources, step out exploration drilling and field programs in support of a Feasibility Study (to convert the estimated resources up to a reserve category).
- Metallurgy testing: Jig test work to upgrade the concentrate grade, test work to validate the equipment sizing (Comminution, thickening, filtration, hydraulic classifier, spiral), Tests to optimize the operating parameters of the current flowsheet to achieve higher concentrate grade with low impact on the recovery.
- Value Engineering: The data used to develop the processed flowsheet is based on initial test work using bulk samples obtained in 2023/24. Further test work will be undertaken to improve the grade/recovery data for the flowsheet, particularly in the area of the classifier and jig operations. In conjunction with this additional metallurgical testing, alternative flowsheets will be evaluated together with the current data to further optimise the flowsheet with the goal being to achieve a 67.5% total Fe concentrate with minimal impact to recovery. The capital and operating costs will be revisited as a result of the expected improvements to the overall process flowsheet.
A formal request for proposal (RFP) process will also be undertaken to solicit vendor quotes to improve the accuracy of the capital cost estimate. There will also be a study to consider a ‘packaged plant' approach whereby one supplier is appointed to develop and build the complete process plant.
- Transport: Negotiated agreement in due course with ArcelorMittal for the use the Cartier railway for transportation of the concentrate from the Lac Jeannine rail spur to the port.
- Low carbon Pelletization: Concentrate from the Corem testing programme was provided to Binding Solutions Limited for testing using their low carbon cold pelletising technology. Initial results have proved positive with some metrics such as cold compressive strength being above required industry standards. During the Feasibility Study, additional test work will be carried out to further enhance the pellet metrics and reduce binder costs.
- Product development: Continue metallurgy testing to support increasing the grade of concentrate which could then potentially classify as a Critical Mineral under the provincial and federal government critical mineral strategies.
- Infrastructure and Services: Confirm possibility of clean power supply from Hydro-Québec for the Project.
- Permitting and the environment: Commence hydrogeological investigations, and commencement of environmental baseline data collections including air, water, soil, fauna and flora studies, in order to initiate the permitting process applicable to the Project.
- Social and community: The Project is a frontier development and expected to create about circa 100 direct employment opportunities. The Company intends to begin discussions in due course with local and First Nation communities in the Project area.
- Financing: Continue discussion with potential strategic partners to support the Project financing.
- Pelletizing options: Investigate future low carbon to produce pellets in Québec using innovative, low carbon green technology which will further enhance the economics and environmental benefits of the Project.
- Economic support from Federal and Provincial governments: Explore potential for economic support from governments, funding opportunities and other economic incentives for the Project, including those aiming to encourage the development of critical minerals and a circular economy.
The Lac Jeannine Project
The Lac Jeannine property comprises a contiguous block of thirty-one (31) mineral claims covering an aggregate of 1,649.34 hectares (ha) in the Caniapiscau regional county municipality (RCM) of the Côte-Nord Region of eastern Québec (QC), approximately eight kilometres (km) southeast of the abandoned town-site of Gagnon and 290 km north of the City of Baie-Comeau.
The Project encompasses the former Lac Jeannine open pit mine, from which approximately 260 million long tons of ore at 33% iron, in mainly specular hematite form, was extracted between 1961 to 1976. The Property also covers the "Tailings Storage Facility (TSF)", the area where the tailings from the on-site ore concentrator were deposited. In 1984 the Lac Jeannine Lake mining and processing facilities were shut down and the mine site reclaimed.
CoTec's focus is on the tailing's material, planned to be re-processed for residual iron, and rehabilitate the TSF to as close to its natural state as possible.
The claims comprising the Project are registered 100% to Patricia Lafontaine. On August 9, 2023, CoTec announced that it had entered into an option agreement (the "Option Agreement") to acquire 100% of the right, title, and interest of the mining claims comprising the Project.
Pursuant to the Option Agreement, CoTec agreed to pay the vendor, US$250,000 on exercise of the option and US$1,000,000 at the start of commercial extraction of the tailings. CoTec may exercise its option to acquire the mining claims at any time until the earlier of (i) 15 business days after the issuance of all material permits required to construct and operate the Project and (ii) August 7, 2033. If the option is exercised, the vendor will also receive a 1% net smelter royalty (NSR) from the sale of minerals from the historical tailings and a 1.5% NSR from the sale of other minerals from the Project. The 1% NSR and 1.5% NSR could each be reduced, at CoTec's option, by half through the payment of US$1,000,000 and US$2,000,000 respectively.
Qualified Persons and Data Verification
The independent Qualified Persons as defined by NI 43-101, are Mr. Christian Beaulieu, P.Geo. of Mineralis Consulting Services Inc and Associate Consultant of Addison Mining Services Ltd. for Mineral Resources and Exploration Target; Mr. John Langton P.Geo. of JPL GeoServices Inc. for Mineral Exploration; Mr. Matthew Randall of Axe Valley Mining Consultants Ltd. for Mining; Mr. Daniel Roy P.Eng. of Soutex for Processing; Mr. Martin Errington P.Eng. of Amerston Consulting Limited for Infrastructure and Services, Capital Costs, Operating Costs and Economic Analysis and Sensitivity.
The Qualified Persons have reviewed and approved the scientific and technical content of this news release.
About CoTec
CoTec is a publicly traded investment issuer listed on the TSX Venture Exchange ("TSX- V") and the OTCQB and trades under the symbols CTH and CTHCF, respectively. The Company is an environment, social, and governance ("ESG")-focused company investing in innovative technologies that have the potential to fundamentally change the way metals and minerals can be extracted and processed for the purpose of applying those technologies to undervalued operating assets and recycling opportunities, as the Company transitions into a mid-tier mineral resource producer.
CoTec is committed to supporting the transition to a lower carbon future for the extraction industry, a sector on the cusp of a green revolution as it embraces technology and innovation. The Company has made four investments to date and is actively pursuing operating opportunities where current technology investments could be deployed.
For further information, please contact:
Braam Jonker - (604) 992-5600
Forward-Looking Information Cautionary Statement
Statements in this press release regarding the Company and its investments which are not historical facts are "forward-looking statements" which involve risks and uncertainties, including statements relating to the timing and completion of the maiden resource estimate, the bulk sample extraction, the Feasibility Study, the option exercise and the Project, as well as management's expectations with respect to the Lac Jeannine investment and other current and potential future investments and the benefits to the Company which may be implied from such statements. Since forward-looking statements address future events and conditions, by their very nature, they involve inherent risks and uncertainties. Actual results in each case could differ materially from those currently anticipated in such statements, due to known and unknown risks and uncertainties affecting the Company, including but not limited to resource and reserve risks; environmental risks and costs; labor costs and shortages; uncertain supply and price fluctuations in materials; increases in energy costs; labor disputes and work stoppages; leasing costs and the availability of equipment; heavy equipment demand and availability; contractor and subcontractor performance issues; worksite safety issues; project delays and cost overruns; extreme weather conditions; and social and transport disruptions. For further details regarding risks and uncertainties facing the Company please refer to "Risk Factors" in the Company's filing statement dated April 6, 2022, a copy of which may be found under the Company's SEDAR profile at www.sedar.com. The Company assumes no responsibility to update forward-looking statements in this press release except as required by law. Readers should not place undue reliance on the forward-looking statements and information contained in this news release and are encouraged to read the Company's continuous disclosure documents which are available on SEDAR at www.sedarplus.ca.
Neither TSX Venture Exchange nor its Regulation Services Provider (as that term is defined in the policies of the TSX Venture Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy or accuracy of this news release.
[1] Quinto Mining Corporation- Opportunity Study Beneficiation of the Lac Jeannine Tailings - Release 1, July 2007
[2] The profitability index is a measure of the capital efficiency of a project and is defined as the project's NPV divided by the project capital including the capital incurred to reach first run of production.
CTH:CA

Sign up to get your FREE
CoTec Holdings Investor Kit
and hear about exciting investment opportunities.
- Corporate info
- Insights
- Growth strategies
- Upcoming projects
GET YOUR FREE INVESTOR KIT
The Conversation (0)
14 October 2025
CoTec Holdings
Unlocking value with disruptive resource technologies
Unlocking value with disruptive resource technologies Keep Reading...
Latest News

Sign up to get your FREE
CoTec Holdings Investor Kit
and hear about exciting investment opportunities.
- Corporate info
- Insights
- Growth strategies
- Upcoming projects
GET YOUR FREE INVESTOR KIT
Interactive Chart
Latest Press Releases
Related News
TOP STOCKS
American Battery4.030.24
Aion Therapeutic0.10-0.01
Cybin Corp2.140.00
